Larger Cycloalkanes
... Synthetic steroids are used in the treatment of cancer, arthritis, allergies, and in birth control. Steroids consist of 3 fused cyclohexane rings fused to a cyclopentane ring. The ring junctions are usually trans. The rings are labeled A,B,C,D. Methyl groups at C10 and C13 and oxygen at C3 and C17 a ...
... Synthetic steroids are used in the treatment of cancer, arthritis, allergies, and in birth control. Steroids consist of 3 fused cyclohexane rings fused to a cyclopentane ring. The ring junctions are usually trans. The rings are labeled A,B,C,D. Methyl groups at C10 and C13 and oxygen at C3 and C17 a ...
Chapter 6 Microbial Growth
... ii. Facultative halophiles do not require high salt concentrations, but can grow in salt concentrations up to 2%, which inhibits the growth of many microbes. 2. When a microbe is suspended in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell via osmosis. If the microbe has a relatively weak cell wall, it ...
... ii. Facultative halophiles do not require high salt concentrations, but can grow in salt concentrations up to 2%, which inhibits the growth of many microbes. 2. When a microbe is suspended in a hypotonic solution, water enters the cell via osmosis. If the microbe has a relatively weak cell wall, it ...
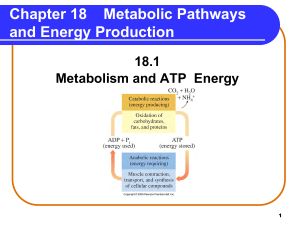
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are hydrolyzed to monosaccharides, mostly glucose, which ent ...
... breaks down polysaccharides to smaller polysaccharides (dextrins), maltose, and some glucose. • continue digestion in the small intestine, where pancreatic amylase hydrolyzes dextrins to maltose and glucose. • maltose, lactose, and sucrose are hydrolyzed to monosaccharides, mostly glucose, which ent ...
Overview: The Energy of Life
... • The living cell is a miniature chemical factory where thousands of reactions occur • The cell extracts energy and applies energy to perform work • Some organisms even convert energy to light, as in bioluminescence Concept 8.1: An organism’s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the l ...
... • The living cell is a miniature chemical factory where thousands of reactions occur • The cell extracts energy and applies energy to perform work • Some organisms even convert energy to light, as in bioluminescence Concept 8.1: An organism’s metabolism transforms matter and energy, subject to the l ...
CHEMISTRY I Final..#1..rev 4KEY
... Objective 2.07: Assess covalent bonding in molecular compounds as related to chemical and physical properties and molecular geometry. 38. The boiling point of HBr is lower than that of HF because: a. HBr is heavier than HF and therefore it requires less energy to vaporize. b. HBr has dipole-dipole ...
... Objective 2.07: Assess covalent bonding in molecular compounds as related to chemical and physical properties and molecular geometry. 38. The boiling point of HBr is lower than that of HF because: a. HBr is heavier than HF and therefore it requires less energy to vaporize. b. HBr has dipole-dipole ...
Cell Nucleus and Chromatin Structure
... amphibians contain ten times as much DNA than humans. If all the DNA contained within the human chromosomes were to be unwound, it would be two meters in length, of which only about 1% of the genetic information is actually used in the normal life cycle of the cell. Some of the additional DNA is inv ...
... amphibians contain ten times as much DNA than humans. If all the DNA contained within the human chromosomes were to be unwound, it would be two meters in length, of which only about 1% of the genetic information is actually used in the normal life cycle of the cell. Some of the additional DNA is inv ...
Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (Lessons 1, 2, 5, 6, 8
... Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (Lessons 1, 2, 5, 6, 8) Bio.1.1 Understand the relationship between the structures and functions of cells and their organelles. Bio.1.1.1 Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell ...
... Structures and Functions of Living Organisms (Lessons 1, 2, 5, 6, 8) Bio.1.1 Understand the relationship between the structures and functions of cells and their organelles. Bio.1.1.1 Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell ...
journalclub
... In the late 1960s Carl R. Woese present this independent RNA idea. The phrase "RNA World" was first used by Nobel laureate Walter Gilbert in 1986, in a commentary on recent observations of the catalytic properties of various forms of RNA. This is a world in which RNA catalyzed all the reactions nece ...
... In the late 1960s Carl R. Woese present this independent RNA idea. The phrase "RNA World" was first used by Nobel laureate Walter Gilbert in 1986, in a commentary on recent observations of the catalytic properties of various forms of RNA. This is a world in which RNA catalyzed all the reactions nece ...
Kitchen Chemistry Review
... Chemical Reactions, Role of Baking Ingredients, Biochemicals, Acids and Bases ...
... Chemical Reactions, Role of Baking Ingredients, Biochemicals, Acids and Bases ...
Characterization of the production regions ofChardonnay - Vitis-vea
... 21 amino acids are presented as mg amino acid per 100 mg amino nitrogen in order to minimize the variation in the nitrogen fraction arising from climatic conditions or viticultural practices . The regions ofproduction will therefore be characterized as a function ofthe diversity offree amino acids i ...
... 21 amino acids are presented as mg amino acid per 100 mg amino nitrogen in order to minimize the variation in the nitrogen fraction arising from climatic conditions or viticultural practices . The regions ofproduction will therefore be characterized as a function ofthe diversity offree amino acids i ...
Functions of the Rumen
... • Principal constituent of organs and soft tissues • Highest concentration of any nutrient, except water, in the body of all living organisms and animals • Required for life ...
... • Principal constituent of organs and soft tissues • Highest concentration of any nutrient, except water, in the body of all living organisms and animals • Required for life ...
Amino acid transport in Penicillium chrysogenum in relation to
... Microbodies (also termed peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, glycosomes depending on the organism and function) are indispensable organelles that can be found in practically all eukaryotic cells. Although their morphology is relatively simple (a proteinaceous matrix surrounded by a single membrane) their phys ...
... Microbodies (also termed peroxisomes, glyoxysomes, glycosomes depending on the organism and function) are indispensable organelles that can be found in practically all eukaryotic cells. Although their morphology is relatively simple (a proteinaceous matrix surrounded by a single membrane) their phys ...
File
... 35 Pollutant oxide Y, which contains non-metallic element X, is formed in a car engine. Further oxidation of Y to Z occurs in the atmosphere. In this further oxidation, 1 mol of Y reacts with 0.5 mol of gaseous oxygen molecules. X could be either nitrogen or sulfur. Which statements about X, Y and Z ...
... 35 Pollutant oxide Y, which contains non-metallic element X, is formed in a car engine. Further oxidation of Y to Z occurs in the atmosphere. In this further oxidation, 1 mol of Y reacts with 0.5 mol of gaseous oxygen molecules. X could be either nitrogen or sulfur. Which statements about X, Y and Z ...
essential cell biology
... Unity and Diversity of Cells Cells Vary Enormously in Appearance and Function Living Cells All Have a Similar Basic Chemistry All Present-Day Cells Have Apparently Evolved from the Same Ancestor Genes Provide the Instructions for Cellular Form, Function, and Complex Behavior Cells Under the Microsco ...
... Unity and Diversity of Cells Cells Vary Enormously in Appearance and Function Living Cells All Have a Similar Basic Chemistry All Present-Day Cells Have Apparently Evolved from the Same Ancestor Genes Provide the Instructions for Cellular Form, Function, and Complex Behavior Cells Under the Microsco ...
Fe-S
... The glyoxylate cycle results in the net conversion of two acetyl-CoA to succinate instead of 4 CO2 in citric acid cycle. ...
... The glyoxylate cycle results in the net conversion of two acetyl-CoA to succinate instead of 4 CO2 in citric acid cycle. ...
BS3050 Physiology of Sport and Exercise
... Mobilization of triacylglycerol involves hydrolysis with the release of fatty acids (and glycerol). Fatty acids are long chain hydrocarbon acids which are transported in the blood stream as a complex with albumin to the sites where they can be metabolised, including muscle, by a process of -oxidati ...
... Mobilization of triacylglycerol involves hydrolysis with the release of fatty acids (and glycerol). Fatty acids are long chain hydrocarbon acids which are transported in the blood stream as a complex with albumin to the sites where they can be metabolised, including muscle, by a process of -oxidati ...
Biology 11 C
... Know statements of the cell theory Cell organelles (Figure 3 on page 10); know labels and basic functions of major organelles; know differences between plant and animal cells 4 major macromolecules: o Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Know basic structure and functions (i.e. sub ...
... Know statements of the cell theory Cell organelles (Figure 3 on page 10); know labels and basic functions of major organelles; know differences between plant and animal cells 4 major macromolecules: o Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Know basic structure and functions (i.e. sub ...
Reactive Oxygen Species
... produces HOCl, degrades H2O2 to oxygen and water, converts tyrosine and other phenols and anilines to free radicals, and hydroxylates aromatic substrates via a cytochrome P450-like activity ...
... produces HOCl, degrades H2O2 to oxygen and water, converts tyrosine and other phenols and anilines to free radicals, and hydroxylates aromatic substrates via a cytochrome P450-like activity ...
Reduced amino acid alphabets exhibit an improved sensitivity and
... naturally occurring amino acids into two- and five-letter groups (CB). Prlić et al. (2000) derived new substitution matrices based on structural alignments of proteins with low-sequence identity and then clustered the amino acids based on those matrices (SDM and HSDM). On the basis of a comparison ...
... naturally occurring amino acids into two- and five-letter groups (CB). Prlić et al. (2000) derived new substitution matrices based on structural alignments of proteins with low-sequence identity and then clustered the amino acids based on those matrices (SDM and HSDM). On the basis of a comparison ...
Enzyme LG 09
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
AP Chemistry Summer Assignment
... Answer each of the following questions and give an example that helps with your explanation. 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the ...
... Answer each of the following questions and give an example that helps with your explanation. 1. If a compound ends in –ide, what does it tell you about the compound? 2. If a compound ends in –ate what does it tell you about the compound? 3. If a compound ends in –ite what does it tell you about the ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.