Enzyme LG 09
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
... e. Competitive inhibitors are inorganic c. Enzymes catalyze specific reactions. substances such as metal ions; d. Enzymes are the reactants in a chemical reaction. noncompetitive inhibitors are vitamins or e. All enzymes depend on protein cofactors to vitamin derivatives. function. 21. Bacterial pro ...
2006, Biology
... During the fall reproductive season, the belly of a male brook trout becomes bright orange. The orange belly provides some camouflage and helps attract females. This trait evolved in brook trout because, compared to males with pale bellies, males with bright orange bellies are more likely to A. live ...
... During the fall reproductive season, the belly of a male brook trout becomes bright orange. The orange belly provides some camouflage and helps attract females. This trait evolved in brook trout because, compared to males with pale bellies, males with bright orange bellies are more likely to A. live ...
electron transport chain
... -are oxidations – loss of electrons -are also dehydrogenations lost electrons are accompanied by hydrogen what is actually lost is a hydrogen atom (1 electron, 1 proton). • A hydrogen atom is equivalent to a hydrogen ion plus an electron H = H+ + e-electrons carry energy from one molecule to another ...
... -are oxidations – loss of electrons -are also dehydrogenations lost electrons are accompanied by hydrogen what is actually lost is a hydrogen atom (1 electron, 1 proton). • A hydrogen atom is equivalent to a hydrogen ion plus an electron H = H+ + e-electrons carry energy from one molecule to another ...
General and Physiological Chemistry
... Define and illustrate by means of names and formulas what is meant by a salt. Write equations illustrating how salts may be prepared by the action of an acid on a metal, on a metal hydroxide, on a metal carbonate, and on a metal bicarbonate. State the difference between a strong electrolyte, a weak ...
... Define and illustrate by means of names and formulas what is meant by a salt. Write equations illustrating how salts may be prepared by the action of an acid on a metal, on a metal hydroxide, on a metal carbonate, and on a metal bicarbonate. State the difference between a strong electrolyte, a weak ...
ATP
... 2.Oxidative phosphorylation - occurs during cellular respiration in all aerobic cells The addition of each phosphate molecule requires 30.6 kJ of energy. If less than this, energy cannot be stored as ATP but lost as heat. ATP is a means of transferring free energy from energy-rich compounds to cellu ...
... 2.Oxidative phosphorylation - occurs during cellular respiration in all aerobic cells The addition of each phosphate molecule requires 30.6 kJ of energy. If less than this, energy cannot be stored as ATP but lost as heat. ATP is a means of transferring free energy from energy-rich compounds to cellu ...
Predicting Secondary Structures of Proteins
... information is processed first by performing a multiple alignment between a set of similar sequences and extracting a matrix of profiles (PSSM). The first method to incorporate profile-based inputs and achieve more than 70% in accuracy was PHD [5]. The method is composed of cascading networks. Predi ...
... information is processed first by performing a multiple alignment between a set of similar sequences and extracting a matrix of profiles (PSSM). The first method to incorporate profile-based inputs and achieve more than 70% in accuracy was PHD [5]. The method is composed of cascading networks. Predi ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Notes
... • Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control • If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down • Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway ...
... • Feedback inhibition is the most common mechanism for control • If ATP concentration begins to drop, respiration speeds up; when there is plenty of ATP, respiration slows down • Control of catabolism is based mainly on regulating the activity of enzymes at strategic points in the catabolic pathway ...
Honors-Final-Review-2014
... 3. Covalent compounds are formed when a ______________ bonds to a _____________. Describe what the valence electrons are doing. 4. Ionic compounds form when a _______________ bonds to a ______________. The resulting compound is called a _______________. Describe what the electrons are doing. 5. Revi ...
... 3. Covalent compounds are formed when a ______________ bonds to a _____________. Describe what the valence electrons are doing. 4. Ionic compounds form when a _______________ bonds to a ______________. The resulting compound is called a _______________. Describe what the electrons are doing. 5. Revi ...
BFP401
... introducing foreign DNA fragments into host cells so that certain functions specific to the 5 foreign DNA can be carried out within them. Enzyme immobilisation is a technique which is used to chemically bind enzymes to certain substances so that they are not lost in a single chemical reaction but ca ...
... introducing foreign DNA fragments into host cells so that certain functions specific to the 5 foreign DNA can be carried out within them. Enzyme immobilisation is a technique which is used to chemically bind enzymes to certain substances so that they are not lost in a single chemical reaction but ca ...
Sample Chapter 5: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... four subsections. Amino acids are classified according to their capacity to interact with water. By using this criterion, four classes may be distinguished: (1) nonpolar and neutral, (2) polar and neutral, (3) acidic, and (4) basic. The neutral nonpolar amino acids contain mostly hydrocarbon R group ...
... four subsections. Amino acids are classified according to their capacity to interact with water. By using this criterion, four classes may be distinguished: (1) nonpolar and neutral, (2) polar and neutral, (3) acidic, and (4) basic. The neutral nonpolar amino acids contain mostly hydrocarbon R group ...
C7 Revision Notes 2015
... •The best-known are hydrocarbons, which are made of only carbon and hydrogen. •There are several subclasses of hydrocarbons, the simplest being the "alkanes", which are straight or branch-chained molecules, all joined with single C-C bonds. •The simplest alkane is methane (CH4), followed by ethane ( ...
... •The best-known are hydrocarbons, which are made of only carbon and hydrogen. •There are several subclasses of hydrocarbons, the simplest being the "alkanes", which are straight or branch-chained molecules, all joined with single C-C bonds. •The simplest alkane is methane (CH4), followed by ethane ( ...
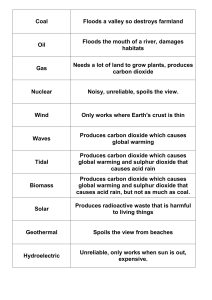
agricultural fertilizers: nitrogen, potassium
... Anyone who has grown a garden, maintained a lawn, or kept house plants knows that it is necessary to apply a fertilizer to the soil to keep cultivated plants healthy. As they grow, plants extract nutrients they need from the soil. Unless these nutrients are replenished, plants will eventually cease ...
... Anyone who has grown a garden, maintained a lawn, or kept house plants knows that it is necessary to apply a fertilizer to the soil to keep cultivated plants healthy. As they grow, plants extract nutrients they need from the soil. Unless these nutrients are replenished, plants will eventually cease ...
Reasons for the occurrence of the twenty coded protein amino acids
... amino acid with an a-hydrogen or by the carboxylation of an amine such as isopropylamine. Replacement of the a-hydrogen by larger substituent, such as a methyl group, would also increase significantly steric hinderance around the amino and carboxyl groups. Steric difficulties have been encountered i ...
... amino acid with an a-hydrogen or by the carboxylation of an amine such as isopropylamine. Replacement of the a-hydrogen by larger substituent, such as a methyl group, would also increase significantly steric hinderance around the amino and carboxyl groups. Steric difficulties have been encountered i ...
The Bohr Effect: The delivery of oxygen from the blood to the
... “an exercising muscle is hot and generates carbon dioxide, and it benefits from increased unloading of O2 [oxygen] from its capillaries.”3 In simple terms: haemoglobin is a protein found in the blood, and one of its functions is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and cells. The crucial po ...
... “an exercising muscle is hot and generates carbon dioxide, and it benefits from increased unloading of O2 [oxygen] from its capillaries.”3 In simple terms: haemoglobin is a protein found in the blood, and one of its functions is to carry oxygen from the lungs to the tissues and cells. The crucial po ...
Practice Test Stoichiometry
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
Final Exam Practice Problems Set 2
... matter and energy are really the same thing. it is impossible to know anything with certainty. it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of an electron. there can only be one uncertain digit in a reported number. it is impossible to know how many electrons there are in an atom. ...
... matter and energy are really the same thing. it is impossible to know anything with certainty. it is impossible to know both the exact position and momentum of an electron. there can only be one uncertain digit in a reported number. it is impossible to know how many electrons there are in an atom. ...
Sugar Amino Acids - The Krasavin research group
... species resulted in the formylated derivative 3, which was subjected to oxidation with Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of star ...
... species resulted in the formylated derivative 3, which was subjected to oxidation with Ag2 O, followed by esterification with diazomethane, and final catalytic hydrogenation over Pd/C catalysis to give the final furanoid α-amino acid 5, as the α- or β-anomer, depending on the stereochemistry of star ...
Protein Secondary Structure
... What terminates an -helix? Statistically, a very high percentage (~60%) of helices are terminated by a single amino acid, Proline: ...
... What terminates an -helix? Statistically, a very high percentage (~60%) of helices are terminated by a single amino acid, Proline: ...
Slide 1
... Protein structure classification •Classification systems allows identification of relationships between structures •Provide evolutionary view of all structures •Newly solved structures can be fitted into hierarchy, defining possible functions SCOP (Structural Classification of Proteins) Manual; exa ...
... Protein structure classification •Classification systems allows identification of relationships between structures •Provide evolutionary view of all structures •Newly solved structures can be fitted into hierarchy, defining possible functions SCOP (Structural Classification of Proteins) Manual; exa ...
enzymes - MrsGorukhomework
... Demo – scissors used to cut paper, stapler used to put together, both not changed Metabolism – (Greek for change) all chemical processes Enzymes are globular protein catalysts. Catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed or used up themselves. Reactions require bonds th ...
... Demo – scissors used to cut paper, stapler used to put together, both not changed Metabolism – (Greek for change) all chemical processes Enzymes are globular protein catalysts. Catalysts increase the rate of a chemical reaction without being consumed or used up themselves. Reactions require bonds th ...
Recognition of an Essential Adenine at a Protein
... variation in the aromatic ring. In contrast, the RNA affinity of the Tyr mutant is substantially lower than the wild type peptide. Similar RNA affinities for the Tyr and Trp mutants have been reported recently by Kranz and Hall.10 They proposed that the RNA complex of the Tyr mutant may be destabili ...
... variation in the aromatic ring. In contrast, the RNA affinity of the Tyr mutant is substantially lower than the wild type peptide. Similar RNA affinities for the Tyr and Trp mutants have been reported recently by Kranz and Hall.10 They proposed that the RNA complex of the Tyr mutant may be destabili ...
Advancing active learning in biochemistry RACI 2010 Bond Energy
... Correct answer means correctly answering all three items related to that concept ...
... Correct answer means correctly answering all three items related to that concept ...
Nonstandard Hydrogen Bonding in Duplex Oligonucleotides. The
... min; 0.1 M Et3NH+-OAc, pH 7.1, containing 10%MeCN). The same equilibrium ratio of products was obtained starting from oligonucleotides containing either anomer. While epimerization does not preclude laboratory experiments such as those described here, it is clearly undesirable in a DNA molecule inte ...
... min; 0.1 M Et3NH+-OAc, pH 7.1, containing 10%MeCN). The same equilibrium ratio of products was obtained starting from oligonucleotides containing either anomer. While epimerization does not preclude laboratory experiments such as those described here, it is clearly undesirable in a DNA molecule inte ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.