Monday Oct
... that deals with analysis of muscle biopsy material in subjects taking Andro or placebo. ...
... that deals with analysis of muscle biopsy material in subjects taking Andro or placebo. ...
Exam Review - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
... The reaction of solutions of ammonium phosphate and barium nitrate gives a precipitate of barium phosphate. The equation that best represents this statement is a) 2(NH4)3PO4(s) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(aq) + 6NH4NO3(s). b) 2(NH4)3PO4(aq) + 3Ba(NO3)2(aq) → Ba3(PO4)2(s) + 6NH4NO3(aq). c) 2(NH4)3PO4 ...
Transcription Translation
... Medium (agar) had 20 amino acids to supplement mutant’s growth even if 1 was missing. Plated these on specific medium to determine what supplements were missing from fungi ...
... Medium (agar) had 20 amino acids to supplement mutant’s growth even if 1 was missing. Plated these on specific medium to determine what supplements were missing from fungi ...
In 1948, Hendrik Casimir predicted that two uncharged, perfectly conducting plates
... polypeptide chain are usually prevented. If they are not, a quality-control mechanism ensures premature termination of erroneous sequences. For cells to flourish, the genetic code must be translated with great accuracy into the amino acids that proteins are made from. During translation, the cell’s ...
... polypeptide chain are usually prevented. If they are not, a quality-control mechanism ensures premature termination of erroneous sequences. For cells to flourish, the genetic code must be translated with great accuracy into the amino acids that proteins are made from. During translation, the cell’s ...
The Role of Fulvic Acid in Sport and Exercise
... To discuss the positive role that fulvic acid can play for people who exercise regularly, it is important to understand the processes of exercise and the physiological and biochemical changes that occur during sport. ...
... To discuss the positive role that fulvic acid can play for people who exercise regularly, it is important to understand the processes of exercise and the physiological and biochemical changes that occur during sport. ...
Structure and Function of Amino Acid Ammonia
... been reported to occur in the peptide lantiobiotics such as Nisin (Sahl et al., 1995). Comparison of the primary structures of HAL and PAL from various sources showed that four Ser residues are conserved (Taylor et al. , 1991). When the conserved Ser residues were changed to Ala by sitedirected muta ...
... been reported to occur in the peptide lantiobiotics such as Nisin (Sahl et al., 1995). Comparison of the primary structures of HAL and PAL from various sources showed that four Ser residues are conserved (Taylor et al. , 1991). When the conserved Ser residues were changed to Ala by sitedirected muta ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 3 (a triple) 99. Ionic ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl It loses its 1 valence electron leaving 2 below it 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 3 (a triple) 99. Ionic ...
Cellular Process: RNA and Protein Synthesis
... E. Identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes; (READINESS STANDARDS) H. Describe how techniques such as DNA fingerprinting, genetic modifications, and chromosomal analysis are used to study the genomes of organisms. B.9 Science concepts. The student knows t ...
... E. Identify and illustrate changes in DNA and evaluate the significance of these changes; (READINESS STANDARDS) H. Describe how techniques such as DNA fingerprinting, genetic modifications, and chromosomal analysis are used to study the genomes of organisms. B.9 Science concepts. The student knows t ...
New AHSGE Science Study Guide
... "twisted ladder" structure. The sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside of the double helix, and the bases are on the inside, so that a base on one strand points directly toward a base on the second strand. When using the twisted ladder analogy, think of the sugar-phosphate backbones as the two s ...
... "twisted ladder" structure. The sugar-phosphate backbone is on the outside of the double helix, and the bases are on the inside, so that a base on one strand points directly toward a base on the second strand. When using the twisted ladder analogy, think of the sugar-phosphate backbones as the two s ...
normal myocardial metabolism: fueling cardiac contraction
... metabolic pathways that generate ATP, but it is clear that the products of ATP utilization, ADP and Pi, regulate ATP utilization and control the free energy that is released when ATP is consumed.28 In general, the rates of substrate movement through common pathways are determined as metabolites pass ...
... metabolic pathways that generate ATP, but it is clear that the products of ATP utilization, ADP and Pi, regulate ATP utilization and control the free energy that is released when ATP is consumed.28 In general, the rates of substrate movement through common pathways are determined as metabolites pass ...
The Synthetic Machinery of the Cell
... The Golgi complex contains different enzymesin different compartments. Some of these enzymes can be stained cytochemically or used as identification markers. In this electron micrograph the trans face has been stained for thiamine pyrophosphatase. ...
... The Golgi complex contains different enzymesin different compartments. Some of these enzymes can be stained cytochemically or used as identification markers. In this electron micrograph the trans face has been stained for thiamine pyrophosphatase. ...
Pentose Phosphate Pathway (aka Hexose monophosphate shunt)
... • G6PD is the most regulated enzyme: inhibition by NADPH, expression is dependent on insulin thus it is only expressed at high glucose concentration • Since the non-oxidative pathway is reversible, the direction is dependent on the need of the cell for ATP / acetyl CoA (energy / fatty acid synthesis ...
... • G6PD is the most regulated enzyme: inhibition by NADPH, expression is dependent on insulin thus it is only expressed at high glucose concentration • Since the non-oxidative pathway is reversible, the direction is dependent on the need of the cell for ATP / acetyl CoA (energy / fatty acid synthesis ...
Chapter 25: Urinary System
... amino group (NH2) • converts it to ammonia (NH3) & then urea • urea excreted in the urine ...
... amino group (NH2) • converts it to ammonia (NH3) & then urea • urea excreted in the urine ...
O - Batavia CSD
... (ATP) How do we get energy? • Need an energy currency• Adenosine triphosphate ...
... (ATP) How do we get energy? • Need an energy currency• Adenosine triphosphate ...
NOB Ch 5 Answers - MCC Year 12 Biology
... An increase in glucagon production by alpha cells acts on the liver and stimulates the conversion of stored glycogen to glucose, which is discharged into the bloodstream and raises blood glucose levels. A reduction in insulin production results in reduced absorption of glucose by cells, which raises ...
... An increase in glucagon production by alpha cells acts on the liver and stimulates the conversion of stored glycogen to glucose, which is discharged into the bloodstream and raises blood glucose levels. A reduction in insulin production results in reduced absorption of glucose by cells, which raises ...
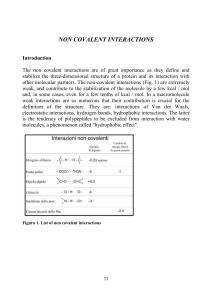
i principi di base - Structural Biology
... spectroscopy, observing the vibration band of the NH group, that is different depending on whether the molecule is in the monomeric or dimeric form (the proton, interacting with the carbonyl of another molecule, vibrates differently). ...
... spectroscopy, observing the vibration band of the NH group, that is different depending on whether the molecule is in the monomeric or dimeric form (the proton, interacting with the carbonyl of another molecule, vibrates differently). ...
Respiratory System
... • During the day you eat only a few times, but you breathe thousands of times. • Your body cannot store much Oxygen. ...
... • During the day you eat only a few times, but you breathe thousands of times. • Your body cannot store much Oxygen. ...
Lecture 1
... In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations in the genome, called "origins". Unwinding of DNA at the origin, and synthesis of new strands, forms a replication fork. In addition to DNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes the new DNA by adding nucleotides matched to the template strand ...
... In a cell, DNA replication begins at specific locations in the genome, called "origins". Unwinding of DNA at the origin, and synthesis of new strands, forms a replication fork. In addition to DNA polymerase, the enzyme that synthesizes the new DNA by adding nucleotides matched to the template strand ...
Lab12
... Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase pro ...
... Halo around the streak (clearing of lipids) = complete hydrolysis of triglycerides, positive for lipase production (agar could be pale blue due to complete clearing of all fatty acids or dark blue because a few fatty acids remain) Pale blue agar, no halo = tributyrin present, negative for lipase pro ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.