Lecture 9: Citric Acid Cycle/Fatty Acid Catabolism
... cycle at all the labels would have been scrambled, and half of the CO2 would have been 14C. Prochiral Citrate. In a two-minute thought experiment, Alexander Ogston in 1948 (Nature, 162: 963) argued that citrate has the potential to be treated as chiral. In chemistry, prochiral molecules can be conve ...
... cycle at all the labels would have been scrambled, and half of the CO2 would have been 14C. Prochiral Citrate. In a two-minute thought experiment, Alexander Ogston in 1948 (Nature, 162: 963) argued that citrate has the potential to be treated as chiral. In chemistry, prochiral molecules can be conve ...
SYNTHESIS OF ASPIRIN Acetyl Salicylic acid Scheme
... (antipyretic). When ingested, acetylsalicylic acid in the basic medium of the upper intestinal and acetate ions. ...
... (antipyretic). When ingested, acetylsalicylic acid in the basic medium of the upper intestinal and acetate ions. ...
... the left helical wheel as an example, residues 3, 7, 11 would be non-polar, i.e. every 3rd or 4th residue. iii) The energetic cost to insert the polar mainchain atoms into the bilayer is unfavorable, (by +1 kcal/mol). Therefore the sidechain must be large enough such that the transfer energy exceeds ...
6b. Thermodynamics
... defined in different ways. • Reactants that convert in to products with the release of energy (Exothermic reactions) can be termed as thermodynamically stable. • Some reactions do not take place on their own. • They require activation energy to initiate the reaction. • The reaction that occurs with ...
... defined in different ways. • Reactants that convert in to products with the release of energy (Exothermic reactions) can be termed as thermodynamically stable. • Some reactions do not take place on their own. • They require activation energy to initiate the reaction. • The reaction that occurs with ...
The effects of calcium ions on the activites of hexokinase
... of hexokinase by glucose 6-phosphate, phosphofructokinase by ATP and fructose 1,6-diphosphatase by AMP. However, high concentrations of Ca2+ (1000,tM) inhibited these enzymes, although the inhibitions by glucose 6-phosphate, ATP and AMP were not changed. Margreth, Cantani & Schiaffino; (1967) have s ...
... of hexokinase by glucose 6-phosphate, phosphofructokinase by ATP and fructose 1,6-diphosphatase by AMP. However, high concentrations of Ca2+ (1000,tM) inhibited these enzymes, although the inhibitions by glucose 6-phosphate, ATP and AMP were not changed. Margreth, Cantani & Schiaffino; (1967) have s ...
BCH 4024, Spring 2017 - Department of Biochemistry and Molecular
... the course, and you will also have less time to study for the final. The makeup exams are specific to the missed exam, not cumulative. No make-up exam is available for Exam 4, so to complete BCH4024 students must take Exam 4 as scheduled. Students failing to take an exam will receive zero points for ...
... the course, and you will also have less time to study for the final. The makeup exams are specific to the missed exam, not cumulative. No make-up exam is available for Exam 4, so to complete BCH4024 students must take Exam 4 as scheduled. Students failing to take an exam will receive zero points for ...
Slideshow - Roswell Park Cancer Institute
... convert nutrients and endogenous molecules to energy and matter (proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids) that sustain life ...
... convert nutrients and endogenous molecules to energy and matter (proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids) that sustain life ...
Current Uses of Synthetic Biology for Chemicals
... conversions from carbohydrate to finished fuel are catalyzed in the cell, with the finished product secreted. The fuel forms an immiscible light organic phase that is non-toxic to the organism and is easily recovered from the broth through centrifugation. There is no need for further chemical conver ...
... conversions from carbohydrate to finished fuel are catalyzed in the cell, with the finished product secreted. The fuel forms an immiscible light organic phase that is non-toxic to the organism and is easily recovered from the broth through centrifugation. There is no need for further chemical conver ...
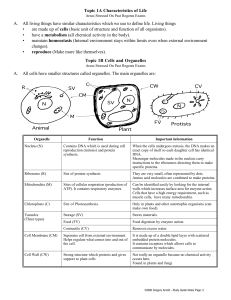
Topic 1A Characteristics of Life A. All living things have similar
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
... Organisms will react in ways that will maintain an internal environment allowing the chemical activities of life to occur regardless if the external environment changes. This process is known as homeostasis (steady state). For example, the heart and breathing rate will change due to various levels o ...
Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... *ideal is summer vacation 74. He and H most ideal because small and weak forces of attraction 75. Mixtures can be separated by physical means *distillation, different boiling points (evaporation too) *filtration different solubilities *chromatography different attraction for separating medium 76. Pe ...
... *ideal is summer vacation 74. He and H most ideal because small and weak forces of attraction 75. Mixtures can be separated by physical means *distillation, different boiling points (evaporation too) *filtration different solubilities *chromatography different attraction for separating medium 76. Pe ...
Lesson 6
... 11. Chemical reactions involving an acid added to a base to produce a new compound and water are called _____________ reactions. 12. What area of homemaking often involves acid-base reactions? ...
... 11. Chemical reactions involving an acid added to a base to produce a new compound and water are called _____________ reactions. 12. What area of homemaking often involves acid-base reactions? ...
Free Amino Acid and Reducing Sugar Composition of Pandan
... cooking. This study investigated the composition of free amino acids and reducing sugars that could be precursors of ACPY in pandan leaves. Fresh pandan leaves contained 2.38 mg/g fructose and 1.77 mg/ g glucose. Major free amino acid in pandan was glutamic acid (0.41 mg/g). Proline, a precursor of ...
... cooking. This study investigated the composition of free amino acids and reducing sugars that could be precursors of ACPY in pandan leaves. Fresh pandan leaves contained 2.38 mg/g fructose and 1.77 mg/ g glucose. Major free amino acid in pandan was glutamic acid (0.41 mg/g). Proline, a precursor of ...
幻灯片 1 - TUST
... sequence (usually TTGACA), approximately 35 base pairs before the transcription starting point, is present in E. coli promoters. A TATAAT sequence or Pribnow box lies within the promoter about 10 base pairs before the starting point of transcription or around 16 to 18 base pairs from the first hexam ...
... sequence (usually TTGACA), approximately 35 base pairs before the transcription starting point, is present in E. coli promoters. A TATAAT sequence or Pribnow box lies within the promoter about 10 base pairs before the starting point of transcription or around 16 to 18 base pairs from the first hexam ...
Beta sheets are twisted
... •First protein to be crystallized - 1849. •First protein to have its mass accurately measured. •First protein to be studied by ultracentrifugation. •First protein to associated with a physiological condition. •First protein to show that a point mutation can cause problems. •First proteins to have X- ...
... •First protein to be crystallized - 1849. •First protein to have its mass accurately measured. •First protein to be studied by ultracentrifugation. •First protein to associated with a physiological condition. •First protein to show that a point mutation can cause problems. •First proteins to have X- ...
revised
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
... Using the TMHMM program, a total of 21473 TMs for the mesophilic set of proteins and 13340 for the thermophilic organims were predicted. The average length of the predicted TMs was 22 for both sets of proteins (thermophilic and mesophilic), which is in good agreement with the average length of TMs p ...
Solution
... A. If N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many protons and the nuclide will undergo positron emission or electron capture. B. If N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable. C. If N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay. D. The valley of ...
... A. If N/Z ratio is too high, there are too many protons and the nuclide will undergo positron emission or electron capture. B. If N/Z ratio lies somewhere below 1, the nuclide is stable. C. If N/Z ratio is too low, there are too many neutrons and the nuclide will undergo beta decay. D. The valley of ...
Karbohidrat Metabolizması
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
... Problems with the AMPK activation theory Some of the enzyme activities modulated through changed gene expression (e.g. fatty acid synthetase and liver pyruvate kinase) or direct phosphorylation (acetyl CoA carboxylase) are in the opposite direction to insulin. Many experiments have been performed a ...
By Allison Byrum / Intern
... family of chemokines that it introduced could hold the answer to many of basic questions abut how the body works at a molecular level. ...
... family of chemokines that it introduced could hold the answer to many of basic questions abut how the body works at a molecular level. ...
Respiratory System Notes
... Carbon dioxide is transported by three different methods. i. A small amount is dissolved in the blood plasma ii. Some is loosely combined with amino groups in the hemoglobin molecule. iii. Most of the carbon dioxide is converted in erythrocytes to ____________________ by the enzyme carbonic anhydr ...
... Carbon dioxide is transported by three different methods. i. A small amount is dissolved in the blood plasma ii. Some is loosely combined with amino groups in the hemoglobin molecule. iii. Most of the carbon dioxide is converted in erythrocytes to ____________________ by the enzyme carbonic anhydr ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY - Life Sciences 4 All
... • the use of micro-organisms by humans to make substances, humans want • E.g. In the manufacture of food, antibiotics, biogas These substances include: Medicines antibiotics and insulin Food Maas, bread, wine and cheese ...
... • the use of micro-organisms by humans to make substances, humans want • E.g. In the manufacture of food, antibiotics, biogas These substances include: Medicines antibiotics and insulin Food Maas, bread, wine and cheese ...
CIS 595 Bioinformatics
... transcription, RNA polymerase requires a number of general transcription factors (called TFIIA, TFIIB, and so on). (A) The promoter contains a DNA sequence called the TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site at which transcription is initiated. (B) The TATA box is recognized and ...
... transcription, RNA polymerase requires a number of general transcription factors (called TFIIA, TFIIB, and so on). (A) The promoter contains a DNA sequence called the TATA box, which is located 25 nucleotides away from the site at which transcription is initiated. (B) The TATA box is recognized and ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.