NVC Bio 120 lect 9 cell respiration
... Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O ...
... Most of the chain’s components are proteins, which exist in multiprotein complexes The carriers alternate reduced and oxidized states as they accept and donate electrons Electrons drop in free energy as they go down the chain and are finally passed to O2, forming H2O ...
Problem Set 3_Chem165_Sp2014
... a long thin tube packed with material. The different compounds in the mixture move at different rates down the tube, so they are separated by the time they reach the end of the tube (see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_chromatography). Coupling this to a mass spectrometer gives (in many cases) the ...
... a long thin tube packed with material. The different compounds in the mixture move at different rates down the tube, so they are separated by the time they reach the end of the tube (see: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_chromatography). Coupling this to a mass spectrometer gives (in many cases) the ...
IDENTIFICATION OF NOVEL SELECTIVE ANTAGONISTS FOR BESTROPHIN-1 PROTEIN BY
... cause progressive vision loss. This disorder affects the retina, specifically cells in a small area near the center of the retina by causing a fatty yellow pigment (lipofuscin) which build up in cells under the macula1,2,3. The macula is the yellow oval spot at the center of the retina (back of the ...
... cause progressive vision loss. This disorder affects the retina, specifically cells in a small area near the center of the retina by causing a fatty yellow pigment (lipofuscin) which build up in cells under the macula1,2,3. The macula is the yellow oval spot at the center of the retina (back of the ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
... efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associations are often mediated through a transactivation domain, which in most cases ranges from 30-100 amino acids in length and contain variable functional amino acid arrangements such as glutamine- or proline-rich regions. Tr ...
... efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associations are often mediated through a transactivation domain, which in most cases ranges from 30-100 amino acids in length and contain variable functional amino acid arrangements such as glutamine- or proline-rich regions. Tr ...
Scheme of work – Cambridge IGCSE Biology (US) (0438)
... Unit 2: Animal nutrition Recommended prior knowledge Students can come into this unit with very little biological knowledge. However, they do need to understand some basic chemistry such as atoms, elements and compounds. An understanding of bonding and the role of ions in simple chemical reactions i ...
... Unit 2: Animal nutrition Recommended prior knowledge Students can come into this unit with very little biological knowledge. However, they do need to understand some basic chemistry such as atoms, elements and compounds. An understanding of bonding and the role of ions in simple chemical reactions i ...
Regulation of blood glucose (Homeostasis)
... Blood glucose levels is maintained within physiological limits to (65-110 mg/dl) "true glucose" in fasting state, and (100-140 mg/dl) following ingestion of carbohydrate containing meal ,or even under circumstances when a person does not eat for extended periods of time, blood glucose levels decreas ...
... Blood glucose levels is maintained within physiological limits to (65-110 mg/dl) "true glucose" in fasting state, and (100-140 mg/dl) following ingestion of carbohydrate containing meal ,or even under circumstances when a person does not eat for extended periods of time, blood glucose levels decreas ...
Enzymes1
... to the substrate, so that the conformation of substrate and enzyme active site is complementary only after binding. When the substrate binds to the enzyme it induces a change in the enzyme conformation the enzymes active site is then moulded into a precise conformation that is complementary to that ...
... to the substrate, so that the conformation of substrate and enzyme active site is complementary only after binding. When the substrate binds to the enzyme it induces a change in the enzyme conformation the enzymes active site is then moulded into a precise conformation that is complementary to that ...
The respiratory system
... 2. How many chambers does the heart have and what are they called? 3. Give a definition for the pulse. 4. Identify 3 places where you can take the pulse. 5. Name the 4 components of blood and give a brief description of each. ...
... 2. How many chambers does the heart have and what are they called? 3. Give a definition for the pulse. 4. Identify 3 places where you can take the pulse. 5. Name the 4 components of blood and give a brief description of each. ...
2 Organic Acidemias
... acidemias is urine organic acid analysis by GC/MS, utilizing a capillary column. Organic acids can be measured in any physiologic fluid. However, it is most effective to use urine to identify the organic acids that signal these disorders, as semiquantitative methods may not identify the important co ...
... acidemias is urine organic acid analysis by GC/MS, utilizing a capillary column. Organic acids can be measured in any physiologic fluid. However, it is most effective to use urine to identify the organic acids that signal these disorders, as semiquantitative methods may not identify the important co ...
The Scientific Method - Academic Computer Center
... Hypothesis. Beginning in the third/fourth grade students are encouraged to discuss what their data means, how they would change the experiment and how this information relates to their everyday life. At the collegiate level, students are expected to complete the same discussion. ...
... Hypothesis. Beginning in the third/fourth grade students are encouraged to discuss what their data means, how they would change the experiment and how this information relates to their everyday life. At the collegiate level, students are expected to complete the same discussion. ...
Cellular Respiration
... Fermentation in the Absence of Oxygen •Fermentation When oxygen is not present, fermentation follows glycolysis, regenerating NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue. •Lactic Acid Fermentation In lactic acid fermentation, bacteria and other animals covert pyruvate to lactic acid. Makes things SOUR! • ...
... Fermentation in the Absence of Oxygen •Fermentation When oxygen is not present, fermentation follows glycolysis, regenerating NAD+ needed for glycolysis to continue. •Lactic Acid Fermentation In lactic acid fermentation, bacteria and other animals covert pyruvate to lactic acid. Makes things SOUR! • ...
The Action of Chloramphenicol on Protein and Nucleic Acid
... occurring as part of normal growth, and consequently may have been interdependent. This latter interpretation is clearly supported by the progress curves for the synthesis of nucleic acid. The continued formation of nucleic acid at a logarithmic rate may require the simultaneous continued production ...
... occurring as part of normal growth, and consequently may have been interdependent. This latter interpretation is clearly supported by the progress curves for the synthesis of nucleic acid. The continued formation of nucleic acid at a logarithmic rate may require the simultaneous continued production ...
Click Here to download this tutorial as a PDF
... acids that the hydrogen bond connects and then use the hbonds off command. When Jmol calculates hydrogen bonds, it occasionally inserts a hydrogen bond between two amino acids on the same strand, with a single amino acid between the two. These types of hydrogen bonds create what almost looks like a ...
... acids that the hydrogen bond connects and then use the hbonds off command. When Jmol calculates hydrogen bonds, it occasionally inserts a hydrogen bond between two amino acids on the same strand, with a single amino acid between the two. These types of hydrogen bonds create what almost looks like a ...
The Action of Chloramphenicol on Protein and Nucleic Acid
... occurring as part of normal growth, and consequently may have been interdependent. This latter interpretation is clearly supported by the progress curves for the synthesis of nucleic acid. The continued formation of nucleic acid at a logarithmic rate may require the simultaneous continued production ...
... occurring as part of normal growth, and consequently may have been interdependent. This latter interpretation is clearly supported by the progress curves for the synthesis of nucleic acid. The continued formation of nucleic acid at a logarithmic rate may require the simultaneous continued production ...
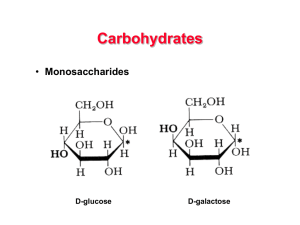
30 Synthesis of Glycosides, Lactose, Glycoproteins and Glycolipids
... UDP-galactose are used for glycosyltransferase reactions in many systems. Lactose, for example, is synthesized from UDP-galactose and glucose in the mammary gland. UDP-glucose also can be oxidized to form UDP-glucuronate, which is used to form glucuronide derivatives of bilirubin and xenobiotic comp ...
... UDP-galactose are used for glycosyltransferase reactions in many systems. Lactose, for example, is synthesized from UDP-galactose and glucose in the mammary gland. UDP-glucose also can be oxidized to form UDP-glucuronate, which is used to form glucuronide derivatives of bilirubin and xenobiotic comp ...
Chemistry Standards and Frameworks
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1. a.: Students know how to relate the position of an element in the perio ...
... 1. The periodic table displays the elements in increasing atomic number and shows how periodicity of the physical and chemical properties of the elements relates to atomic structure. As a basis for understanding this concept: 1. a.: Students know how to relate the position of an element in the perio ...
Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare
... d) Assume that you have a reaction X Y where ΔG = 0 and the energy of activation = 0.6 kcal/mole. In a cell, you find that the reaction proceeds almost exclusively in the forward direction. Explain why this might be the case. In a cell, the product can be used as soon as it is produced. This consump ...
... d) Assume that you have a reaction X Y where ΔG = 0 and the energy of activation = 0.6 kcal/mole. In a cell, you find that the reaction proceeds almost exclusively in the forward direction. Explain why this might be the case. In a cell, the product can be used as soon as it is produced. This consump ...
Environment: The Science Behind the Stories, 4e (Withgott)
... Full file at http://collegetestbank.eu/Test-Bank-Environment-4th-Edition-Withgott 2) In what ways are macromolecules essential to life? Describe the structures of three and describe their major role(s) in organisms. Answer: Macromolecules provide critical components of organismal structure, energy ...
... Full file at http://collegetestbank.eu/Test-Bank-Environment-4th-Edition-Withgott 2) In what ways are macromolecules essential to life? Describe the structures of three and describe their major role(s) in organisms. Answer: Macromolecules provide critical components of organismal structure, energy ...
FREE Sample Here
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-environment-4th-edition-withgott 2) In what ways are macromolecules essential to life? Describe the structures of three and describe their major role(s) in organisms. Answer: Macromolecules provide critical components of organismal structure, energy stor ...
... Full file at http://testbank360.eu/test-bank-environment-4th-edition-withgott 2) In what ways are macromolecules essential to life? Describe the structures of three and describe their major role(s) in organisms. Answer: Macromolecules provide critical components of organismal structure, energy stor ...
MEDICINAL CHEMISTRY-III
... Anti-inflammatory drugs may act by interfering with one or more of these processes:-antibody production or antigen-antibody complex. -interference with the formation and release of chemical mediator of inflammation. -stabilization of liposomal membranes. ...
... Anti-inflammatory drugs may act by interfering with one or more of these processes:-antibody production or antigen-antibody complex. -interference with the formation and release of chemical mediator of inflammation. -stabilization of liposomal membranes. ...
RNA
... • Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. • RNA contains coded information for making proteins. ...
... • Genetic messages can be decoded by copying part of the nucleotide sequence from DNA into RNA. • RNA contains coded information for making proteins. ...
2013 kcse trans mara..
... ii) Solution T – Hypotomic / less concentrated than cell sap, therefore water was drawn into the cells by osmosis hence strips become firm / turgid / rigid solutions Q – hypertomic / more concentrated than the cell sap, therefore cells lost water by osmosis / exosmosis hence strip / cell become flac ...
... ii) Solution T – Hypotomic / less concentrated than cell sap, therefore water was drawn into the cells by osmosis hence strips become firm / turgid / rigid solutions Q – hypertomic / more concentrated than the cell sap, therefore cells lost water by osmosis / exosmosis hence strip / cell become flac ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.