Supplementary Text 2: Extensions to the prototype model
... complex sphingolipids, and free sphingoid bases and their phosphates. Modeling this observation requires the inclusion of C26-CoA as a dynamically changing (rather than constant input) variable. The elongation of fatty acids beyond C16/C18 proceeds two carbons at a time, and to model this repetitive ...
... complex sphingolipids, and free sphingoid bases and their phosphates. Modeling this observation requires the inclusion of C26-CoA as a dynamically changing (rather than constant input) variable. The elongation of fatty acids beyond C16/C18 proceeds two carbons at a time, and to model this repetitive ...
12 Complement system BA
... produced in the liver in an inactive form (zymogen). Activation is induced by proteolitic cleavage. ...
... produced in the liver in an inactive form (zymogen). Activation is induced by proteolitic cleavage. ...
CHEM1611 2014-J-9 June 2014 • Alanine ( ala) and lysine (lys) are
... The peptide links in a protein chain are said to be resonance stabilised. Use a diagram to explain what is meant by this term, and indicate one important consequence relating to protein structure and one important consequence relating to the chemistry of proteins. Resonance occurs when two or more L ...
... The peptide links in a protein chain are said to be resonance stabilised. Use a diagram to explain what is meant by this term, and indicate one important consequence relating to protein structure and one important consequence relating to the chemistry of proteins. Resonance occurs when two or more L ...
Document
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
Human body
... The Human Body 1. Complex multicellular organisms have systems that interact to carry out life processes through physical and chemical means a. b. c. d. e. f. ...
... The Human Body 1. Complex multicellular organisms have systems that interact to carry out life processes through physical and chemical means a. b. c. d. e. f. ...
Chapter 23 (Section 3) Pregnancy, Birth, and Childhood
... *d. ____________ individually or combined form everything in the universe including __________ *1. Human body’s most abundant ___________: carbon [__], oxygen [__], hydrogen [__], and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & _________ = calcium [___] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [___]; for nervous s ...
... *d. ____________ individually or combined form everything in the universe including __________ *1. Human body’s most abundant ___________: carbon [__], oxygen [__], hydrogen [__], and nitrogen [__]; for teeth & _________ = calcium [___] and phosphorus [__]; for taste buds = zinc [___]; for nervous s ...
Biochemistry Ch 33 597-624 [4-20
... -ACP contains phosphopantetheine derived from CoA -initial step of fatty acid synthesis, an acetyl moiety is transferred from acetyl coA to ACP phosphopantetheinyl group of one subunit and then to cysteinyl sulfhydryl group of other subunit -malonyl CoA attaches to ACP phosphopantetheinyl sulfhydryl ...
... -ACP contains phosphopantetheine derived from CoA -initial step of fatty acid synthesis, an acetyl moiety is transferred from acetyl coA to ACP phosphopantetheinyl group of one subunit and then to cysteinyl sulfhydryl group of other subunit -malonyl CoA attaches to ACP phosphopantetheinyl sulfhydryl ...
Dalton Model Reading
... unless some cause appear to the contrary". This was merely an assumption, derived from faith in the simplicity of nature. No evidence was then available to scientists to deduce how many atoms of each element combine to form compound molecules. But this or some other such rule was absolutely necessar ...
... unless some cause appear to the contrary". This was merely an assumption, derived from faith in the simplicity of nature. No evidence was then available to scientists to deduce how many atoms of each element combine to form compound molecules. But this or some other such rule was absolutely necessar ...
For H 2 O
... charge. These two numbers do not add up to zero. Thus, we find a least common denominator and find out what we must multiply each number by to get this result. Out LCD is 6, thus we multiply +2 by 3 and -3 by 2. This results in +6 and -6 cancelling out to zero. ...
... charge. These two numbers do not add up to zero. Thus, we find a least common denominator and find out what we must multiply each number by to get this result. Out LCD is 6, thus we multiply +2 by 3 and -3 by 2. This results in +6 and -6 cancelling out to zero. ...
Symbiotic bacteria enable insect to use a nutritionally inadequate diet
... animals is complicated by the fact that nitrogen sources vary in their nutritional value (Karasov & Martı́nez del Rio 2007). In particular, animals cannot synthesize de novo the carbon skeletons of some amino acids that contribute to protein; these are called essential amino acids. As a consequence ...
... animals is complicated by the fact that nitrogen sources vary in their nutritional value (Karasov & Martı́nez del Rio 2007). In particular, animals cannot synthesize de novo the carbon skeletons of some amino acids that contribute to protein; these are called essential amino acids. As a consequence ...
Nutraceuticals- Emerging Field of Metabolic Engineering of Lactic
... • The efficiency lactose utilization by L.lactis can be increased by metabolic engineering • Secondly lactose metabolism in L. lactis can be modified in such a way that the glucose moiety will end up in the product, while galactose will be fully used for growth, in this way providing a natural sweet ...
... • The efficiency lactose utilization by L.lactis can be increased by metabolic engineering • Secondly lactose metabolism in L. lactis can be modified in such a way that the glucose moiety will end up in the product, while galactose will be fully used for growth, in this way providing a natural sweet ...
ACIDITY (free fatty acid) | fat matrix
... the diluent. Mix the oil with diluent, after adding, by inverting test cuvette. Use 2,5 uL of diluted sample for testing. **Application method for curve Acid. dil ‐ 50: Take 50 µL of oil, using the specific pipette (see Note 1) and add it to the diluent. Mix the oil with diluent, after adding, by ...
... the diluent. Mix the oil with diluent, after adding, by inverting test cuvette. Use 2,5 uL of diluted sample for testing. **Application method for curve Acid. dil ‐ 50: Take 50 µL of oil, using the specific pipette (see Note 1) and add it to the diluent. Mix the oil with diluent, after adding, by ...
6115/01 Edexcel GCE
... The diagrams below show population pyramids for Uganda and the USA for the year 2000 and the estimates for the year 2025. Population pyramids for Uganda and the USA in year 2000 Uganda: 2000 ...
... The diagrams below show population pyramids for Uganda and the USA for the year 2000 and the estimates for the year 2025. Population pyramids for Uganda and the USA in year 2000 Uganda: 2000 ...
Biology - Bideford College Sixth Form
... The fact that water is an extremely effective solvent is of great biological importance. All of the substances which are essential for the functioning of cells and whole organisms (glucose, amino acids, fats, vitamins, respiratory gases etc.) are transported around in solution. Similarily, all metab ...
... The fact that water is an extremely effective solvent is of great biological importance. All of the substances which are essential for the functioning of cells and whole organisms (glucose, amino acids, fats, vitamins, respiratory gases etc.) are transported around in solution. Similarily, all metab ...
Divergent Evolution of Function in the ROK Sugar
... progenitor catalyst are targeted for alteration during the specialization of enzyme function. A detailed investigation of laboratory-based experimental enzyme evolution promises to reveal common mechanisms for the generation of new catalytic activities during sequential rounds of mutational drift an ...
... progenitor catalyst are targeted for alteration during the specialization of enzyme function. A detailed investigation of laboratory-based experimental enzyme evolution promises to reveal common mechanisms for the generation of new catalytic activities during sequential rounds of mutational drift an ...
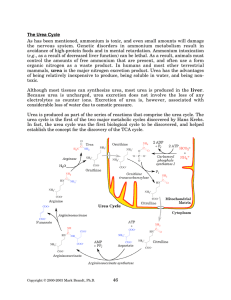
The Urea Cycle - Rose
... g-aminobutyric acid (GABA), another neurotransmitter. In addition, synthesis of glutamate requires a-ketoglutarate, and therefore release of glutamine depletes the tissue of TCA cycle intermediates, unless the tissue is well supplied with replacement intermediates. Because of its use as an ammonium ...
... g-aminobutyric acid (GABA), another neurotransmitter. In addition, synthesis of glutamate requires a-ketoglutarate, and therefore release of glutamine depletes the tissue of TCA cycle intermediates, unless the tissue is well supplied with replacement intermediates. Because of its use as an ammonium ...
Macroevolution (power point)
... Von Baer’s Law features common to all members of major phylogenetic group of animals develop earlier in ontogeny than do features that distinguish subdivisions of the group ...
... Von Baer’s Law features common to all members of major phylogenetic group of animals develop earlier in ontogeny than do features that distinguish subdivisions of the group ...
Respiration - segaran1996
... enzymes that transfer energy in food molecules, eg. sugars and lipids, to ATP. • ATP is compound that is able to supply on-the-spot, instant and usable energy for cell activities. • Mitochondria are the organelles that house the enzymes and substrates associated with aerobic respiration. • Respirati ...
... enzymes that transfer energy in food molecules, eg. sugars and lipids, to ATP. • ATP is compound that is able to supply on-the-spot, instant and usable energy for cell activities. • Mitochondria are the organelles that house the enzymes and substrates associated with aerobic respiration. • Respirati ...
Interpreting the Genetic Code
... randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic code evolution Thus variation in the genetic code suggests a polyphyletic origin for life Taken together, this evidence indicates the hand of a Designer in the genetic code and does not support the theory that life ori ...
... randomness in assignment of amino acids to codons No mechanism exists for genetic code evolution Thus variation in the genetic code suggests a polyphyletic origin for life Taken together, this evidence indicates the hand of a Designer in the genetic code and does not support the theory that life ori ...
The molecular orientation of DNA bases on H
... Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of the spatial orientation of the antibonding p* and r* orbitals for three classes of diatomic molecules. The combination of three single and three double bond units leads to the configuration of the aromatic ring [17]. ...
... Fig. 3. Schematic illustration of the spatial orientation of the antibonding p* and r* orbitals for three classes of diatomic molecules. The combination of three single and three double bond units leads to the configuration of the aromatic ring [17]. ...
Vitamin B1 - Thiamin
... • IF WE DON’T HAVE ENOUGH THIAMIN IN OUR DIET, THE BODY CAN DEVELOP A DISEASE CALLED BERI – BERI WHICH CAN CAUSE MUSCLE WASTAGE. • THIAMIN CAN BE DESTROYED BY HEAT WHEN COOKING AND IS EASILY DISSOLVED IN WATER. ...
... • IF WE DON’T HAVE ENOUGH THIAMIN IN OUR DIET, THE BODY CAN DEVELOP A DISEASE CALLED BERI – BERI WHICH CAN CAUSE MUSCLE WASTAGE. • THIAMIN CAN BE DESTROYED BY HEAT WHEN COOKING AND IS EASILY DISSOLVED IN WATER. ...
Micronutrient Cofactors
... converts serine to glycine makes thymidylic acid for DNA rep de novo purines histidine metabolism Methyl, adenosyl groups MeB12 AdoB13 Corrin ring which central metal ion is cobalt (resembles heme) 4/6 metal coordination sites are provided by corrin ring nitrogen’s 5th coordination size is with dime ...
... converts serine to glycine makes thymidylic acid for DNA rep de novo purines histidine metabolism Methyl, adenosyl groups MeB12 AdoB13 Corrin ring which central metal ion is cobalt (resembles heme) 4/6 metal coordination sites are provided by corrin ring nitrogen’s 5th coordination size is with dime ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.