1 - gcisd
... 30. Water has several unique properties such as high boiling point, high surface tension and low vapor pressure. What are the main causes for these properties? 31. What happens at the triple point on a phase diagram? 32. Like dissolves like refers to the molecule’s _________________________. 33. Wha ...
... 30. Water has several unique properties such as high boiling point, high surface tension and low vapor pressure. What are the main causes for these properties? 31. What happens at the triple point on a phase diagram? 32. Like dissolves like refers to the molecule’s _________________________. 33. Wha ...
Hepatic encephalopathy
... Impairment of energy metabolism in brain ammonia reacts with α-ketoglutatrate to produce glutamate and glutamine consumption of α-ketoglutatrate, NADH and ATP, inhibition of pyruvate decarboxylase leading to the reduction of acetyl CoA and acetylcholine ...
... Impairment of energy metabolism in brain ammonia reacts with α-ketoglutatrate to produce glutamate and glutamine consumption of α-ketoglutatrate, NADH and ATP, inhibition of pyruvate decarboxylase leading to the reduction of acetyl CoA and acetylcholine ...
Biochemistry of cell organelles
... • Overall structure of mitochondria, their shape and size; • Origin of mitochondria; • Dynamic behaviour of mitochondria; • Composition of mitochondria, functional role of different subcompartments; • Isolation of mitochondria, how to analyse the composition of mitochondria; • Visualization (imaging ...
... • Overall structure of mitochondria, their shape and size; • Origin of mitochondria; • Dynamic behaviour of mitochondria; • Composition of mitochondria, functional role of different subcompartments; • Isolation of mitochondria, how to analyse the composition of mitochondria; • Visualization (imaging ...
AB Balance Lecture 1_2015
... AB in minutes) and kidneys play a major role (regulate AB balance in days) ...
... AB in minutes) and kidneys play a major role (regulate AB balance in days) ...
Biology 12 – Practice Final Exam 5) Describe the changes that occur
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
... 7) A student set up the experiment illustrated above and kept it at 37°C. After five minutes, the distilled water in the beaker was tested and found to contain a sugar but no starch. a) What had occurred inside the tube? (1 mark) Starch is too large of a molecule to cross the membrane, therefore no ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 23: Phospholipid Biosynthesis
... phospholipid derivatives are phosphatidyl-X. Phospholipids also tend to have a saturated fatty acid in position 1 and an unsaturated fatty acid in position 2. ...
... phospholipid derivatives are phosphatidyl-X. Phospholipids also tend to have a saturated fatty acid in position 1 and an unsaturated fatty acid in position 2. ...
AP Syllabus
... students. Most years we have two classes of AP Chemistry. Our school has a seven period day with each class being 55 minutes long. The first period of the day is optional, available for those that choose to take seven periods per day. We are on the year round schedule so we begin school in late July ...
... students. Most years we have two classes of AP Chemistry. Our school has a seven period day with each class being 55 minutes long. The first period of the day is optional, available for those that choose to take seven periods per day. We are on the year round schedule so we begin school in late July ...
Oxidation of Carbohydrate
... – High net ATP yield but slow ATP production – Must be broken down into free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol – Only FFAs are used to make ATP ...
... – High net ATP yield but slow ATP production – Must be broken down into free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol – Only FFAs are used to make ATP ...
Extending the limits of paleodietary studies of humans with
... transfer of simple single carbon molecules (i.e. C-1) in metabolic pathways of plants. Depending on the physiological state of the plant, the C isotopic composition of glycine (two carbons) and serine (three carbons) may shift substantially, in part because the transfer of one carbon atom will have ...
... transfer of simple single carbon molecules (i.e. C-1) in metabolic pathways of plants. Depending on the physiological state of the plant, the C isotopic composition of glycine (two carbons) and serine (three carbons) may shift substantially, in part because the transfer of one carbon atom will have ...
enzymes - La Salle High School
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
Ch16-1 Fatty-acid-and-triacylglycerol
... Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In adult humans, fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the liver and lactating mammary glands and, to a l ...
... Carbohydrates, protein, and other molecules obtained from the diet in excess of the body's needs for these compounds can be converted to fatty acids, which are stored as triacylglycerols. In adult humans, fatty acid synthesis occurs primarily in the liver and lactating mammary glands and, to a l ...
Changes in cardiac metabolism: a critical step from stable angina to
... low when insulin levels are high after a meal. On the other hand, noradrenaline increases fatty acid release from fat cells so that fatty acid levels are elevated under times of stress, such as physical exercise, fasting, or myocardial ischaemia. Diabetic patients (both types 1 and 2) have high fatt ...
... low when insulin levels are high after a meal. On the other hand, noradrenaline increases fatty acid release from fat cells so that fatty acid levels are elevated under times of stress, such as physical exercise, fasting, or myocardial ischaemia. Diabetic patients (both types 1 and 2) have high fatt ...
08_LectureOutline_LOBLANK
... Activation energy may be supplied in the form of __________ that the reactant molecules absorb from the surroundings. The bonds of the reactants break only when the molecules have __________ enough energy to become __________ and, therefore, more reactive. The absorption of thermal energy increases ...
... Activation energy may be supplied in the form of __________ that the reactant molecules absorb from the surroundings. The bonds of the reactants break only when the molecules have __________ enough energy to become __________ and, therefore, more reactive. The absorption of thermal energy increases ...
Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
... Catalysts for biological reactions Most are proteins Lower the activation energy Increase the rate of reaction Activity lost if denatured May be simple proteins May contain cofactors such as metal ions or organic (vitamins) ...
Phosphorylation - Biology Junction
... regulation by final products & raw materials levels of intermediates compounds in the pathways regulation of earlier steps in pathways levels of other biomolecules in body regulates rate of siphoning off to synthesis pathways ...
... regulation by final products & raw materials levels of intermediates compounds in the pathways regulation of earlier steps in pathways levels of other biomolecules in body regulates rate of siphoning off to synthesis pathways ...
CNS NEUROTRANSMITTERS
... neurotensin, enkephalines, etc. (3) Biogenic amines( e.g. Monoamines: norepinephrine, dopamine & serotonin, and acetylcholine). ...
... neurotensin, enkephalines, etc. (3) Biogenic amines( e.g. Monoamines: norepinephrine, dopamine & serotonin, and acetylcholine). ...
Guidelines for the Investigation of Hyperammonaemia
... The most common cause of raised plasma ammonia is artefactual due to poor sample collection or a delay in analysis. (see Appendix –Measurement of Ammonia in Blood/Plasma) Hyperammonaemia can be caused by inherited deficiencies of the enzymes of the urea cycle. They are individually rare disorders bu ...
... The most common cause of raised plasma ammonia is artefactual due to poor sample collection or a delay in analysis. (see Appendix –Measurement of Ammonia in Blood/Plasma) Hyperammonaemia can be caused by inherited deficiencies of the enzymes of the urea cycle. They are individually rare disorders bu ...
EOC_STUDY_GUIDE_adapted_from_Gaston_County
... made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen plants and animals use carbohydrates for maintaining structure within the cells - Proteins Nitrogen-containing compounds made up of chains of amino acids 20 amino acids can combine to form a great variety of protein molec ...
... made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen with a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen plants and animals use carbohydrates for maintaining structure within the cells - Proteins Nitrogen-containing compounds made up of chains of amino acids 20 amino acids can combine to form a great variety of protein molec ...
Fermentation
... several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid from the body. ...
... several minutes in order to pay back the built-up “oxygen debt” and clear the lactic acid from the body. ...
Lec. 4 - Ketogenesis (Biosynthesis of ketone bodies)
... their production becomes significant during starvation, when ketone bodies are needed to provide energy to the peripheral tissues. Liver actively produces ketone bodies, but it can't utilize it as a fuel because [can not reconvert acetoacetate to acetyl CoA] ,while in extrahepatic tissues, acetoacet ...
... their production becomes significant during starvation, when ketone bodies are needed to provide energy to the peripheral tissues. Liver actively produces ketone bodies, but it can't utilize it as a fuel because [can not reconvert acetoacetate to acetyl CoA] ,while in extrahepatic tissues, acetoacet ...
CT1
... 6. The cell membrane consists of two layers of _lipids__________ as well as ___proteins____ that help to transport materials. 7. Carbon dioxide is leaving the cell. Oxygen is entering the cell. Both molecules are moving down the concentration gradient. The molecules are being transported by the proc ...
... 6. The cell membrane consists of two layers of _lipids__________ as well as ___proteins____ that help to transport materials. 7. Carbon dioxide is leaving the cell. Oxygen is entering the cell. Both molecules are moving down the concentration gradient. The molecules are being transported by the proc ...
Respiratory System/Excretory System
... oxygen and removes carbon dioxide & water Two parts to respiration: 1. Breathing: a. Inhale - Diaphragm muscle moves down/lungs expand b. Exhale - Air moves out automatically 2. Cellular respiration: chemical reaction that uses oxygen to release energy from food. © 2014 Getting Nerdy, LLC ...
... oxygen and removes carbon dioxide & water Two parts to respiration: 1. Breathing: a. Inhale - Diaphragm muscle moves down/lungs expand b. Exhale - Air moves out automatically 2. Cellular respiration: chemical reaction that uses oxygen to release energy from food. © 2014 Getting Nerdy, LLC ...
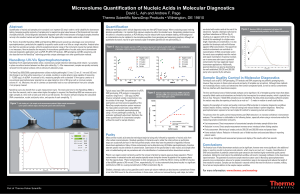
Microvolume Quantification of Nucleic Acids in Molecular Diagnostics
... than an hour. However, if failed DNA extractions are not identified, the delay while accumulating sufficient samples for analysis may delay the reporting of results by as much as 1 – 3 weeks in medium to small sized facilities. Applying this paradigm of nucleic acid quality control post-DNA extracti ...
... than an hour. However, if failed DNA extractions are not identified, the delay while accumulating sufficient samples for analysis may delay the reporting of results by as much as 1 – 3 weeks in medium to small sized facilities. Applying this paradigm of nucleic acid quality control post-DNA extracti ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.