Respiratory System/Excretory System
... oxygen and removes carbon dioxide & water Two parts to respiration: 1. Breathing: a. Inhale - Diaphragm muscle moves down/lungs expand b. Exhale - Air moves out automatically 2. Cellular respiration: chemical reaction that uses oxygen to release energy from food. © 2014 Getting Nerdy, LLC ...
... oxygen and removes carbon dioxide & water Two parts to respiration: 1. Breathing: a. Inhale - Diaphragm muscle moves down/lungs expand b. Exhale - Air moves out automatically 2. Cellular respiration: chemical reaction that uses oxygen to release energy from food. © 2014 Getting Nerdy, LLC ...
Gas phase spectroscopy of the penta-peptide
... such as the C@O stretch have frequencies outside the 3100–3800 cm 1 range covered in this experiment. We observe from the experimental IR–UV spectrum that the hydroxyl of the serine residue is H-bonded. This conclusion follows from our previous study of the dipeptide phe-ser (F–S) [18]. In this pept ...
... such as the C@O stretch have frequencies outside the 3100–3800 cm 1 range covered in this experiment. We observe from the experimental IR–UV spectrum that the hydroxyl of the serine residue is H-bonded. This conclusion follows from our previous study of the dipeptide phe-ser (F–S) [18]. In this pept ...
High School Physical Science Glossary
... kinetic energy- energy of a system based on its motion (KE = ½mv2) law of conservation of matter and energy- matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be rearranged or transferred; thus the amount of energy and matter is constant in the universe liquid- state of matter having a d ...
... kinetic energy- energy of a system based on its motion (KE = ½mv2) law of conservation of matter and energy- matter and energy cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be rearranged or transferred; thus the amount of energy and matter is constant in the universe liquid- state of matter having a d ...
1. Cells and Organelles
... polar head (containing a hydroxyl group) and a rigid planar steroid ring structure. The membrane is asymmetric as glycolipids (lipids with carbohydrates attached) are on the extracellular side of the membrane with negative charges on the inside of the cell. The phospholipids rarely “flip-flop” ( ...
... polar head (containing a hydroxyl group) and a rigid planar steroid ring structure. The membrane is asymmetric as glycolipids (lipids with carbohydrates attached) are on the extracellular side of the membrane with negative charges on the inside of the cell. The phospholipids rarely “flip-flop” ( ...
Carbohydrate Metabolism of Staphylococcus aureus
... that this was partly due to assimilation, partly to diminution of endogenous metabolism by addition of substrate and, for a minor part, to the formation of other products. Thus the results described in this section suggest that a second system for the oxidation of glucose must exist. This system, pr ...
... that this was partly due to assimilation, partly to diminution of endogenous metabolism by addition of substrate and, for a minor part, to the formation of other products. Thus the results described in this section suggest that a second system for the oxidation of glucose must exist. This system, pr ...
Lecture 33 - Carbohydrate Metabolism 1
... tripeptide that has a free sulfhydryl group which functions as an electron donor in a variety of coupled redox reactions in the cell. ...
... tripeptide that has a free sulfhydryl group which functions as an electron donor in a variety of coupled redox reactions in the cell. ...
Biology TEKS
... (9) Science concepts. The student knows metabolic processes and energy transfers that occur in living organisms. The student is expected to: (A) compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids; (B) compare the energy ...
... (9) Science concepts. The student knows metabolic processes and energy transfers that occur in living organisms. The student is expected to: (A) compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules such as carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids; (B) compare the energy ...
From DNA to Protein
... A cell’s DNA sequence (genes) contains all the information needed to make the molecules of life Gene expression • A multistep process including transcription and translation, by which genetic information encoded by a gene is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
... A cell’s DNA sequence (genes) contains all the information needed to make the molecules of life Gene expression • A multistep process including transcription and translation, by which genetic information encoded by a gene is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
Nutrition Physiology Proteins Lesson Plan 6-8
... To figure out your protein needs, multiply your weight in pounds times 0.5 or you can just take your weight and divide by 2. For instance, a 70-pound (or 32-kilogram) kid should have about 35 grams of protein every day. If you only know your weight in kilograms, you need about 1 gram of protein each ...
... To figure out your protein needs, multiply your weight in pounds times 0.5 or you can just take your weight and divide by 2. For instance, a 70-pound (or 32-kilogram) kid should have about 35 grams of protein every day. If you only know your weight in kilograms, you need about 1 gram of protein each ...
Document
... A cell’s DNA sequence (genes) contains all the information needed to make the molecules of life Gene expression • A multistep process including transcription and translation, by which genetic information encoded by a gene is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
... A cell’s DNA sequence (genes) contains all the information needed to make the molecules of life Gene expression • A multistep process including transcription and translation, by which genetic information encoded by a gene is converted into a structural or functional part of a cell or body ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... Taste bitter and feel slippery (*NOTE: do not taste or touch in the lab) Have a pH less than 7 React with active metals to produce H2(g) ...
... Taste bitter and feel slippery (*NOTE: do not taste or touch in the lab) Have a pH less than 7 React with active metals to produce H2(g) ...
Unit 3 (ch 6)
... • Nearly all the cells in our body break down sugars for ATP production • Most cells of most organisms harvest energy aerobically, like slow muscle fibers – The aerobic harvesting of energy from sugar is called cellular respiration ...
... • Nearly all the cells in our body break down sugars for ATP production • Most cells of most organisms harvest energy aerobically, like slow muscle fibers – The aerobic harvesting of energy from sugar is called cellular respiration ...
Chapter 1
... Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions such as How does a single cell develop into an organism? How does the human mind work? How do living things interact in communities? Life defies a simple, one-sentence definition Life is recognized by what living things ...
... Biology is the scientific study of life Biologists ask questions such as How does a single cell develop into an organism? How does the human mind work? How do living things interact in communities? Life defies a simple, one-sentence definition Life is recognized by what living things ...
Cell, Mitosis and Cell Membrane Transport
... Chromatids. A chromosome has 1 or 2 Chromatids in it. A chromosome with 1 chromatid divides to form a chromosome with 2 Chromatids (sister). One chromatid is passed on to each daughter cell. Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: Most cells in body divide though at different rates. There are 2 distinct phases that ...
... Chromatids. A chromosome has 1 or 2 Chromatids in it. A chromosome with 1 chromatid divides to form a chromosome with 2 Chromatids (sister). One chromatid is passed on to each daughter cell. Cell Cycle Cell Cycle: Most cells in body divide though at different rates. There are 2 distinct phases that ...
2013 - SAASTA
... high levels of phenylalanine accumulate in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. Abnormal products of phenylalanine breakdown, such as ...
... high levels of phenylalanine accumulate in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and urine. Abnormal products of phenylalanine breakdown, such as ...
An overview on chemical modification of enzymes. The use of group
... is to learn how enzymes perform their task, which is fundamental for the very existence of life. There are several ways of approaching the study of enzyme mechanisms. One of them is to analyze the kinetics of the reaction catalyzed by a certain enzyme. By this means one can learn about the order in ...
... is to learn how enzymes perform their task, which is fundamental for the very existence of life. There are several ways of approaching the study of enzyme mechanisms. One of them is to analyze the kinetics of the reaction catalyzed by a certain enzyme. By this means one can learn about the order in ...
Bio 20 A - Holy Trinity Academy
... RNA differ in function and differ slightly in structure, and these structural differences account for the differing functions. 2. In proteins, the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide (primary structure) interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein, which al ...
... RNA differ in function and differ slightly in structure, and these structural differences account for the differing functions. 2. In proteins, the specific order of amino acids in a polypeptide (primary structure) interacts with the environment to determine the overall shape of the protein, which al ...
hemoglobin - MBBS Students Club
... Formed by the linkage of four tetrapyrrole rings, through methenyl bridges. Structural Features: 1. Side chains- All the porphyrins vary in the nature of their side chains that are attached to their pyrrole rings.e.g. ...
... Formed by the linkage of four tetrapyrrole rings, through methenyl bridges. Structural Features: 1. Side chains- All the porphyrins vary in the nature of their side chains that are attached to their pyrrole rings.e.g. ...
High - eduBuzz.org
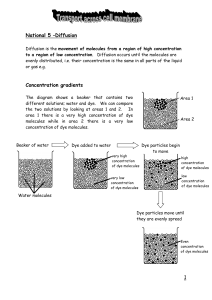
... energy. Sometimes some substances enter or leave cells against a concentration gradient and this does need energy. This is known as Active Transport. National 5- Active transport The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. ...
... energy. Sometimes some substances enter or leave cells against a concentration gradient and this does need energy. This is known as Active Transport. National 5- Active transport The cell membrane is made up of phospholipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. ...
Consensus temporal order of amino acids and evolution
... Forty different single-factor criteria and multi-factor hypotheses about chronological order of appearance of amino acids in the early evolution are summarized in consensus ranking. All available knowledge and thoughts about origin and evolution of the genetic code are thus combined in a single list ...
... Forty different single-factor criteria and multi-factor hypotheses about chronological order of appearance of amino acids in the early evolution are summarized in consensus ranking. All available knowledge and thoughts about origin and evolution of the genetic code are thus combined in a single list ...
Microbial Metabolism
... which participates in the synthesis of DNA, has a turnover number of 15, whereas the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, which removes hydrogen atoms from lactic acid, has a turnover number of 1000. Many enzymes exist in the cell in both active and inactive forms. The rate at which enzymes switch between ...
... which participates in the synthesis of DNA, has a turnover number of 15, whereas the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase, which removes hydrogen atoms from lactic acid, has a turnover number of 1000. Many enzymes exist in the cell in both active and inactive forms. The rate at which enzymes switch between ...
Document
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
... • The cells in your body cannot store large amounts of oxygen for cellular respiration • Breathing normal will provide you with enough oxygen for your regular activities • When you are doing high levels of activity your body cannot bring in enough oxygen for your cells even though you breathe faster ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.