Chem TB Flashcards Unit 5
... 89) What statements concerning mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is incorrect? 90) A noncoding RNA is one that: 91) Regarding transcription, the proteins that help to position eukaryotic RNA polymerase II at the core promoter region are referred to as: 92) The proteins that wrap DNA tightly to condense it i ...
... 89) What statements concerning mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) is incorrect? 90) A noncoding RNA is one that: 91) Regarding transcription, the proteins that help to position eukaryotic RNA polymerase II at the core promoter region are referred to as: 92) The proteins that wrap DNA tightly to condense it i ...
Exam II ReviewQuestions
... 4. Hemoglobin functions to transport oxygen to the tissues where it is used to oxidize food molecules. The oxidation reactions release chemical energy to meet the energy needs of these tissues. The byproducts of these reactions include small molecular weight acids and CO2. Describe how hemoglobin ha ...
... 4. Hemoglobin functions to transport oxygen to the tissues where it is used to oxidize food molecules. The oxidation reactions release chemical energy to meet the energy needs of these tissues. The byproducts of these reactions include small molecular weight acids and CO2. Describe how hemoglobin ha ...
Винницкий национальный медицинский университет им
... bonds and mutual influence of atoms in molecule. 4. Literature: 4.1. Lecture. 4.2. Zurabyan S.E., Fundumentals of bioorganic chemistry, Moscow, 2004, pp. 225238. 5. The main questions of the seminar: 5.1. The main aspects of the international (systematic) nomenclature (IUPAC). 5.2.. Space isomerizat ...
... bonds and mutual influence of atoms in molecule. 4. Literature: 4.1. Lecture. 4.2. Zurabyan S.E., Fundumentals of bioorganic chemistry, Moscow, 2004, pp. 225238. 5. The main questions of the seminar: 5.1. The main aspects of the international (systematic) nomenclature (IUPAC). 5.2.. Space isomerizat ...
Malonyl-CoA: the regulator of fatty acid synthesis and oxidation
... fatty acids for energy, so the production of ketones is protective (1, 2). It is quite remarkable how many distinguished scientists began to study ketogenesis decades ago, among them the Nobel laureates Professors H.A. Krebs and Feodor Lynen. Early on, a widespread belief was that a deficiency of ox ...
... fatty acids for energy, so the production of ketones is protective (1, 2). It is quite remarkable how many distinguished scientists began to study ketogenesis decades ago, among them the Nobel laureates Professors H.A. Krebs and Feodor Lynen. Early on, a widespread belief was that a deficiency of ox ...
RESPIRATION
... within the red blood cells, in a sequence of reversible reactions. The bicarbonate ions then enter the plasma. 2. In regions with high PCO2, carbon dioxide enters the red blood cell and combines with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. The same r ...
... within the red blood cells, in a sequence of reversible reactions. The bicarbonate ions then enter the plasma. 2. In regions with high PCO2, carbon dioxide enters the red blood cell and combines with water to form carbonic acid. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase. The same r ...
Exam Four material
... the _____________________________ that leaves the capillaries and _ – Mostly water • Also contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid and more ...
... the _____________________________ that leaves the capillaries and _ – Mostly water • Also contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid and more ...
6-HarvestingEner
... Topics you are not responsible for: The individual enzymatic steps of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and the ETC The details of fat metabolism through β-oxidation Be able to answer questions: Self-test #s 1,3,6-13 ...
... Topics you are not responsible for: The individual enzymatic steps of glycolysis, Krebs cycle and the ETC The details of fat metabolism through β-oxidation Be able to answer questions: Self-test #s 1,3,6-13 ...
Biological Molecules Ch 2: Chemistry Comes to Life
... Triglycerides are so named because they are formed by a reaction between three fatty acid molecules and one ___________. ...
... Triglycerides are so named because they are formed by a reaction between three fatty acid molecules and one ___________. ...
Chapter 1 - Cell Biology Review Extended Response Answers
... d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane; e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot; f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any pili; g. plasmid – circular ring of DNA; h. capsule – drawn outside ...
... d. nucleoid/(naked) DNA – shown as a tangle of thread or irregular shape without a nuclear membrane; e. (70S) ribosomes – drawn as a small circle or dark dot; f. pili – hair like structures / flagellum – shown to be longer than any pili; g. plasmid – circular ring of DNA; h. capsule – drawn outside ...
13 Protein Synthesis Making a Sentence Activity Key
... 5. The t-RNA searches the cell (classroom) for the correct amino acid (word on the back of the anti-codon card) and begins to create the protein (sentence). This completes the translation step of protein synthesis. The t-RNA should write the sentence on the lines below. (3 Points) ...
... 5. The t-RNA searches the cell (classroom) for the correct amino acid (word on the back of the anti-codon card) and begins to create the protein (sentence). This completes the translation step of protein synthesis. The t-RNA should write the sentence on the lines below. (3 Points) ...
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
... the heavy chain of immunoglobulin when immunoprecipitates containing pp6Osrc are incubated with Mg2+ and ATP (2, 4, 6, 7). The linkage of the phosphate incorporated into the heavy chain was completely stable to treatment with 1 M HCl for 2 hr at 55°C. This ruled out the possibility that the phosphat ...
... the heavy chain of immunoglobulin when immunoprecipitates containing pp6Osrc are incubated with Mg2+ and ATP (2, 4, 6, 7). The linkage of the phosphate incorporated into the heavy chain was completely stable to treatment with 1 M HCl for 2 hr at 55°C. This ruled out the possibility that the phosphat ...
Lipid Metabolizması - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
... Fatty Acid Synthesis • Fatty acids are built from 2-C units derived from acetyl-CoA • Acetate units are activated for transfer to growing FA chain by conversion to malonylCoA • Decarboxylation of malonyl-CoA and reducing power of NADPH drive chain growth • Chain grows to 16-carbons (eight acetylCoA ...
Mechanism of Carbanion Stabilization by PLP, Cont`d
... phosphate was created to provide satisfaction and enlightenment to those enzymologists and chemists who enjoy pushing electrons, for no other coenzyme is involved in such a wide variety of reactions, in both enzyme and model systems, which can be reasonably interpreted in terms of the chemical prope ...
... phosphate was created to provide satisfaction and enlightenment to those enzymologists and chemists who enjoy pushing electrons, for no other coenzyme is involved in such a wide variety of reactions, in both enzyme and model systems, which can be reasonably interpreted in terms of the chemical prope ...
OXIDATION OF FATTY ACIDS (LIPOLYSIS) Fatty acids stored in
... hydrolysis of triacylglycerol .This process is initiated by hormonesensitive lipase (HSL), which removes a fatty acid from carbon 1 and/or carbon 3 of the TAG. Epinephrine (as well as norepinephrine) and glucagon stimulate fatty acid release from triglycerides stored in adipocyte fat droplets, where ...
... hydrolysis of triacylglycerol .This process is initiated by hormonesensitive lipase (HSL), which removes a fatty acid from carbon 1 and/or carbon 3 of the TAG. Epinephrine (as well as norepinephrine) and glucagon stimulate fatty acid release from triglycerides stored in adipocyte fat droplets, where ...
effect of protein on gene expression
... • Single cell organisms are able to adjust their metabolic capacity in response to variation in the nutrient supply in the culture medium e.g. nutrient dependent regulation of the lactose, histidine and tryptophane operons by their respective substrates has been well characterized in bacteria. • In ...
... • Single cell organisms are able to adjust their metabolic capacity in response to variation in the nutrient supply in the culture medium e.g. nutrient dependent regulation of the lactose, histidine and tryptophane operons by their respective substrates has been well characterized in bacteria. • In ...
EFFECT OF NUTRIENTS ON THE GENE EXPRESSION: Nutri
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
... • In the liver, glucose, in the presence of insulin, induces expression of genes encoding glucose transporters and glycolytic and lipogenic enzymes, e.g. L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and fatty acid synthase, and represses genes of the gluconeogenic pathway, such as t ...
Document
... To better understand the molecular and physiological bases of the capacity of marine picocyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria to resist high fluxes of visible and ultraviolet light occurring in the top layer of oceans. To study degradation of DOM including polysaccharides, proteins, carbonyls an ...
... To better understand the molecular and physiological bases of the capacity of marine picocyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria to resist high fluxes of visible and ultraviolet light occurring in the top layer of oceans. To study degradation of DOM including polysaccharides, proteins, carbonyls an ...
of the fatty acid is oxidized. Fatty acid oxidation is divided into two
... complete degradation of saturated fatty acids having an even number of carbon atoms. Most fatty acids have such structures because of their mode of synthesis . The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon ato ...
... complete degradation of saturated fatty acids having an even number of carbon atoms. Most fatty acids have such structures because of their mode of synthesis . The oxidation of fatty acids containing double bonds requires additional steps. Likewise, fatty acids containing an odd number of carbon ato ...
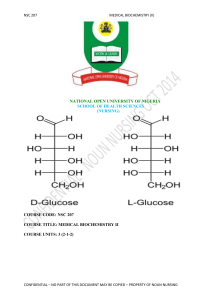
NSC 207 - National Open University of Nigeria
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
... The glycolytic pathway has a dual role (i) It degrades glucose to generate ATP and (ii) It provides building blocks for synthetic reactions. The rate of conversion of glucose into pyruvate is regulated to meet these 2 major cellular needs. Enzymes catalyzing essentially irreversible reactions are po ...
Unit 2 Chemistry of Life
... Question: Which of the following statements is correct regarding the electrical charge of subatomic particles: a. Protons +,electrons -, Neutrons Neutral ...
... Question: Which of the following statements is correct regarding the electrical charge of subatomic particles: a. Protons +,electrons -, Neutrons Neutral ...
Acetylation
... Most xenobiotics are hydrophobic (lipophilic) compounds and this property enables their nonspecific penetration across the phospholipid dilayer of plasmatic membranes. The elimination of xenobiotics from the body depends on their transformation to more hydrophilic compounds. The most hydrophobic xe ...
... Most xenobiotics are hydrophobic (lipophilic) compounds and this property enables their nonspecific penetration across the phospholipid dilayer of plasmatic membranes. The elimination of xenobiotics from the body depends on their transformation to more hydrophilic compounds. The most hydrophobic xe ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.