Download PDF
... in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and apply these chemical principles to the complex structural environment presented by natural proteins, ...
... in living organisms. In order to truly understand the detailed mechanisms of these diverse reactions, one must assimilate aspects of organic chemistry, inorganic chemistry, and physical chemistry and apply these chemical principles to the complex structural environment presented by natural proteins, ...
Ch. 6 outline - sciencewithskinner
... o particles will continue to move until they have reached equilibrium (are evenly spread out) Organic compounds ...
... o particles will continue to move until they have reached equilibrium (are evenly spread out) Organic compounds ...
The Chemistry of Life
... Diffusion: the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration o Example: Smell of cookies moves from the kitchen (high concentration) to the rest of the house (low concentration) o Example: materials diffuse into and out of cells o particles will continu ...
... Diffusion: the movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration o Example: Smell of cookies moves from the kitchen (high concentration) to the rest of the house (low concentration) o Example: materials diffuse into and out of cells o particles will continu ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Answer: b. Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular composition but differ in structural arrangement and/or bonding associations. 5. ____________ is a storage polysaccharide commonly found in the cells of animals. a. Glucose b. Sucrose c. Glycogen d. Starch ...
... Answer: b. Isomers are molecules that have the same molecular composition but differ in structural arrangement and/or bonding associations. 5. ____________ is a storage polysaccharide commonly found in the cells of animals. a. Glucose b. Sucrose c. Glycogen d. Starch ...
Biomolecules I. Introduction. - biochemistry: study of chemical
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
... C. Polysaccharides: long chains of simple sugars linked together by dehydration synthesis. - due to size, they are water insoluble. - great storage products; also have structural roles. - polysaccharides of importance to body: starch & glycogen, both glucose polymers. 1. starch: storage CH2 O formed ...
NTI Day 9 - Russell County Schools
... A organic molecule is one that typically consists of carbon atoms in rings or long chains, where other atoms (e.g. hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are attached. ...
... A organic molecule is one that typically consists of carbon atoms in rings or long chains, where other atoms (e.g. hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen) are attached. ...
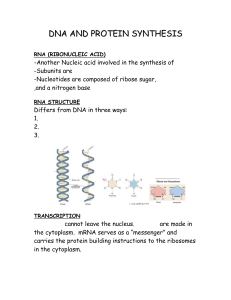
DNA AND PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
... bases in mRNA into the amino acids of a protein. 1 Codon = 3 nucleotides on mRNA 1 Codon = Some codons are redundant (can be used again to give the same amino acid) RESULT OF TRANSLATION ...
File
... form of acetyl coenzyme A or if oxygen is lacking be converted to lactate. The presence of oxygen determines these paths. ...
... form of acetyl coenzyme A or if oxygen is lacking be converted to lactate. The presence of oxygen determines these paths. ...
BIOCHEMISTRY REVIEW SHEET
... d. Give an example of this ratio (make one up)_________________________________ e. Name the 3 types of lipids_______________________________________________ f. At room temperature fats are______________________________________ g. At room temperature lipids are _______________________________________ ...
... d. Give an example of this ratio (make one up)_________________________________ e. Name the 3 types of lipids_______________________________________________ f. At room temperature fats are______________________________________ g. At room temperature lipids are _______________________________________ ...
Proteins, Lipids, and Carbs!!!
... Denaturation a. Disruption of protein structure by 1. Heat: Break apart H bonds and disrupt hydrophobic attractions 2. Acids/ bases: Break H bonds between polar R groups and ionic bonds 3. Heavy metal ions: React with S-S bonds to ...
... Denaturation a. Disruption of protein structure by 1. Heat: Break apart H bonds and disrupt hydrophobic attractions 2. Acids/ bases: Break H bonds between polar R groups and ionic bonds 3. Heavy metal ions: React with S-S bonds to ...
MACROMOLECULE WEBQUEST Name: Site 1 The Lipids Site
... What elements are found in carbohydrates? ______________ What is the ratio of Carbon to Hydrogen to Oxygen? ________ Carbohydrates comprise what percentage of our body cells? ________ List 4 monosaccharide ...
... What elements are found in carbohydrates? ______________ What is the ratio of Carbon to Hydrogen to Oxygen? ________ Carbohydrates comprise what percentage of our body cells? ________ List 4 monosaccharide ...
Amino Acid/Protein Structure
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
... Honors Anatomy and Physiology Amino Acids and Proteins THE AMINO ACID http://www.vivo.colostate.edu/hbooks/genetics/biotech/basics/prostruct.html ...
Nutrition - Athens Academy
... A. you eat as many sweets as you want. B. your diet should contain a variety of foods. C. meats are the most important part of your diet. D. milk and cheese should be the main part of your diet. E. you should only eat one or two servings of bread, cereal, rice, or pasta per day. ...
... A. you eat as many sweets as you want. B. your diet should contain a variety of foods. C. meats are the most important part of your diet. D. milk and cheese should be the main part of your diet. E. you should only eat one or two servings of bread, cereal, rice, or pasta per day. ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Vocabulary File
... Occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Starting molecules: NADH and FADH2 and oxygen o Uses the NADH and FADH2 from the Kreb’s Cycle and another NADH from Glycolysis. Produces: Water and 32 ATP’s o FADH2 and NADH, release H’s so they can attach to oxygen and produce water 15) NADH & ...
... Occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria Starting molecules: NADH and FADH2 and oxygen o Uses the NADH and FADH2 from the Kreb’s Cycle and another NADH from Glycolysis. Produces: Water and 32 ATP’s o FADH2 and NADH, release H’s so they can attach to oxygen and produce water 15) NADH & ...
Biomolecule Reading
... activation energy of the chemical reaction. Activation energy is the amount of energy needed before a chemical reaction can start. By lowering the activation energy of chemical reactions, enzymes help cells build and break down complex molecules like starches and proteins. Much like the other biomol ...
... activation energy of the chemical reaction. Activation energy is the amount of energy needed before a chemical reaction can start. By lowering the activation energy of chemical reactions, enzymes help cells build and break down complex molecules like starches and proteins. Much like the other biomol ...
The Making of Macromolecules - Cornell Center for Materials
... For ex: carbon – riding on bus (carbon emission) hydrogen – atoms in water oxygen – breathing nitrogen – breathing; fertilizers phosphorus – matches, fertilizers, food additives Do Now Assignment (Two options depending on the level of the students): Option A: 1) What is a monomial? 2) What is a poly ...
... For ex: carbon – riding on bus (carbon emission) hydrogen – atoms in water oxygen – breathing nitrogen – breathing; fertilizers phosphorus – matches, fertilizers, food additives Do Now Assignment (Two options depending on the level of the students): Option A: 1) What is a monomial? 2) What is a poly ...
Ch_4 Notes - West Broward High School
... 5. Water is less dense as a solid (ice has more air between molecules) 6. Universal solvent = Water dissolves many things Chemistry of Cells ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: contain carbon Carbon can form many kinds of compounds, which are called organic molecules or macromolecules (large molecules). Polymer: a l ...
... 5. Water is less dense as a solid (ice has more air between molecules) 6. Universal solvent = Water dissolves many things Chemistry of Cells ORGANIC COMPOUNDS: contain carbon Carbon can form many kinds of compounds, which are called organic molecules or macromolecules (large molecules). Polymer: a l ...
Chemical Basis of Life – Biochemistry - Har
... Cellulose—glucose polymer used to form fibers for plant structures. Humans can’t digest (fiber). Most abundant organic molecule. ...
... Cellulose—glucose polymer used to form fibers for plant structures. Humans can’t digest (fiber). Most abundant organic molecule. ...
Bio 20 enzymes and nutrition notes
... 1) Glucose: The main monosaccharide. Needed for Cellular Respiration! 2) Fructose: a simple sugar often found in fruits – Fructose and Glucose are isomers of each other, which means that they have the same molecular formula, but different structural arrangement ...
... 1) Glucose: The main monosaccharide. Needed for Cellular Respiration! 2) Fructose: a simple sugar often found in fruits – Fructose and Glucose are isomers of each other, which means that they have the same molecular formula, but different structural arrangement ...
Answers to exam 1 review #2
... 27. An enzyme releases free energy so a reaction can occur T F 28. An enzyme creates free energy so a reaction occurs more quickly T F 29. Mitochondria doesn't have which of the following: a. inner matrix b. adenosine triphosphate c. acetyl coA d. inner membrane e. guanine 30. Mitochondria doesn't d ...
... 27. An enzyme releases free energy so a reaction can occur T F 28. An enzyme creates free energy so a reaction occurs more quickly T F 29. Mitochondria doesn't have which of the following: a. inner matrix b. adenosine triphosphate c. acetyl coA d. inner membrane e. guanine 30. Mitochondria doesn't d ...
Biochemistry Objective Sheet Test Objectives Bio.1.2.1 • Explain
... • Develop a cause and effect model for specificity of enzymes - the folding produces a 3-D shape that is linked to the protein function, enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions (catalysts) by lowering the activation energy, are re-usable and specific, and are affected by such factors a ...
... • Develop a cause and effect model for specificity of enzymes - the folding produces a 3-D shape that is linked to the protein function, enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions (catalysts) by lowering the activation energy, are re-usable and specific, and are affected by such factors a ...
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE DEPARTMENT OF BIOCHEMISTRY ADVANCED PLACEMENT TEST (SAMPLE)
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
... 1. Which of the following statements about the biophysical property of water is INCORRECT? A. Water molecule forms H-bonds B. Water retains heat well C. Water is dielectrict D. Water at freezing point has the highest density E. Water is polar 2. Which of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte and ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.