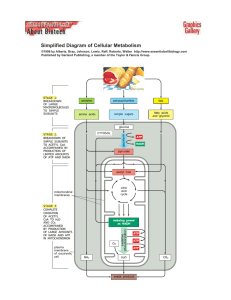
Simplified Diagram of Cellular Metabolism
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
... . http://www.essentialcellbiology.com Published by Garland Publishing, a member of the Taylor & Francis Group. ...
Uncommon amino acids, amino acids forming proteins
... When proteins are at their isoelectric point they are least soluble in water and can be precipitated from the solution ...
... When proteins are at their isoelectric point they are least soluble in water and can be precipitated from the solution ...
Name
... c. May have evolved from gibbons but not rats d. Is more closely related to humans than to rats e. May have evolved from rats but not from humans and gibbons 8. Proteins like hemoglobin and insulin have different structures because they have different ______________________, which is also known as t ...
... c. May have evolved from gibbons but not rats d. Is more closely related to humans than to rats e. May have evolved from rats but not from humans and gibbons 8. Proteins like hemoglobin and insulin have different structures because they have different ______________________, which is also known as t ...
Metabolic Processes Unit
... ATP (How does substrate level phosphorylation differ from oxidative phosphorylation?) Reduce Co-enzymes (What is the role of NADH?) 4 Steps of Cellular Respiration o Glycolysis (How does glycolysis differ from the other 3 steps?) o Pyruvate oxidation (What 3 changes occur during this stage?) o Kreb’ ...
... ATP (How does substrate level phosphorylation differ from oxidative phosphorylation?) Reduce Co-enzymes (What is the role of NADH?) 4 Steps of Cellular Respiration o Glycolysis (How does glycolysis differ from the other 3 steps?) o Pyruvate oxidation (What 3 changes occur during this stage?) o Kreb’ ...
Quiz8ch8.doc
... 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the CO2 molecules in this equation come from __________ during reactions of __________. a. O2, glycolysis b. O2, the electron transport system c. O2, the Krebs cycle d. C6H112O6, glyco ...
... 2. The overall equation for glucose metabolism is C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP and heat. The carbon atoms in the CO2 molecules in this equation come from __________ during reactions of __________. a. O2, glycolysis b. O2, the electron transport system c. O2, the Krebs cycle d. C6H112O6, glyco ...
Biomolecule 20 Questions
... 20) How are genes used by cells to build proteins? A) DNA is transcribed into an amino acid sequence. B) The genes in RNA direct the synthesis of proteins directly. C) The genes in RNA direct the synthesis of a DNA molecule, which is used to build a protein. D) The genes in DNA direct the synthesis ...
... 20) How are genes used by cells to build proteins? A) DNA is transcribed into an amino acid sequence. B) The genes in RNA direct the synthesis of proteins directly. C) The genes in RNA direct the synthesis of a DNA molecule, which is used to build a protein. D) The genes in DNA direct the synthesis ...
Representations of 3D Structures
... Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from 5-20 models X-ray crystallography give one average structure NMR structures can be averaged to give one average structure as well ...
... Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from 5-20 models X-ray crystallography give one average structure NMR structures can be averaged to give one average structure as well ...
Free Form Amino Acids
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
Biomolecule Test Review 2015
... Biomolecules Test Review -KEY 1. What are the 4 large categories of organic compounds that we call biomolecules? Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids 2. What are examples of each biomolecule? Examples Starch, glucose, Cellulose, Glycogen ...
... Biomolecules Test Review -KEY 1. What are the 4 large categories of organic compounds that we call biomolecules? Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids 2. What are examples of each biomolecule? Examples Starch, glucose, Cellulose, Glycogen ...
Biomolecules Test Review -KEY
... Biomolecules Test Review -KEY 1. What are the 4 large categories of organic compounds that we call biomolecules? Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids 2. What are examples of each biomolecule? Examples Starch, glucose, Cellulose, Glycogen ...
... Biomolecules Test Review -KEY 1. What are the 4 large categories of organic compounds that we call biomolecules? Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids 2. What are examples of each biomolecule? Examples Starch, glucose, Cellulose, Glycogen ...
Fermentation and Cellular Respiration 1. Define: Glycolysis
... acceptor. For those examples used in class, pyruvic acid serves as the final electron acceptor, but some organisms use other compounds. Heterofermentative – The term heterofermentative applies to organisms that produce a variety of end products (more than one) as the result of their fermentation act ...
... acceptor. For those examples used in class, pyruvic acid serves as the final electron acceptor, but some organisms use other compounds. Heterofermentative – The term heterofermentative applies to organisms that produce a variety of end products (more than one) as the result of their fermentation act ...
Bio 1000 Human Biology for Non-Majors
... solution; it measures how acidic or basic a solution is ...
... solution; it measures how acidic or basic a solution is ...
Notes
... _______________________, Lipids, _________________, Nucleic Acids are all biological macromolecules The ________________________________ uses lipids, carbohydrates and proteins to help maintain _________________________ in organisms! Nucleic acids are part of your __________! Carbohydrates S ...
... _______________________, Lipids, _________________, Nucleic Acids are all biological macromolecules The ________________________________ uses lipids, carbohydrates and proteins to help maintain _________________________ in organisms! Nucleic acids are part of your __________! Carbohydrates S ...
Organic Compounds
... a huge number of large, complex molecules called organic molecules. These molecules make up organisms and carry out life processes. Carbohydrates are organic molecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are made up of repeating units called saccharides. They provide cells with energy ...
... a huge number of large, complex molecules called organic molecules. These molecules make up organisms and carry out life processes. Carbohydrates are organic molecules that consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. They are made up of repeating units called saccharides. They provide cells with energy ...
6) Metabolism
... • As bonds break they release energy • During metabolism, energy, water and carbon dioxide are released ...
... • As bonds break they release energy • During metabolism, energy, water and carbon dioxide are released ...
(CH2) 2 - CHM152-SP10
... component of the name indicates whether there is a ketone group or an aldehyde group attached to it. If there is a ketone group attached then the name will begin with the prefix “keto” and if there is an aldehyde group attached to it then the name will begin with the prefix “aldo.” The second compon ...
... component of the name indicates whether there is a ketone group or an aldehyde group attached to it. If there is a ketone group attached then the name will begin with the prefix “keto” and if there is an aldehyde group attached to it then the name will begin with the prefix “aldo.” The second compon ...
STUDY GUIDE - West Ashley High School
... Lipids: made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and will not dissolve in water. Examples of lipids are fats, waxes, and sterols. used by living things for energy storage, contain even more energy than the carbohydrates. form an important part of cellular membranes Fats are composed of fatty acid ...
... Lipids: made up of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen and will not dissolve in water. Examples of lipids are fats, waxes, and sterols. used by living things for energy storage, contain even more energy than the carbohydrates. form an important part of cellular membranes Fats are composed of fatty acid ...
Amino acid An organic compound containing both an
... A chemical reaction which involves at least one of the following: loss of electrons, the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen. (Rust is the result of the oxidation of iron; the oxidation of fats in foods results in rancidity.) ...
... A chemical reaction which involves at least one of the following: loss of electrons, the gain of oxygen or the loss of hydrogen. (Rust is the result of the oxidation of iron; the oxidation of fats in foods results in rancidity.) ...
Problem Set 9 Key
... 1. Describe the process of delivering amino acids to the liver from: a. Dietary proteins Gastrin Hormone is secreted by gastric mucosal cells which signals the release of HCl and Pepsinogen (pepsin zymogen) by gastric glands. The low pH triggesr Secretin release, which stimulates pancrease to releas ...
... 1. Describe the process of delivering amino acids to the liver from: a. Dietary proteins Gastrin Hormone is secreted by gastric mucosal cells which signals the release of HCl and Pepsinogen (pepsin zymogen) by gastric glands. The low pH triggesr Secretin release, which stimulates pancrease to releas ...
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life
... many as 4 other atoms (elements) Usually with H, O, N, or C Example: C6H12O6 (_________) ...
... many as 4 other atoms (elements) Usually with H, O, N, or C Example: C6H12O6 (_________) ...
Midterm IV Key
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.























