Lesson 12 Mutations
... In an insertion, one or more nitrogenous bases are inserted during the copying ...
... In an insertion, one or more nitrogenous bases are inserted during the copying ...
Gene mutations
... Inversion: ◦ Chromosome segment breaks off and then reattaches in reverse orientation to the same chromosome ...
... Inversion: ◦ Chromosome segment breaks off and then reattaches in reverse orientation to the same chromosome ...
Grant IGA MZČR 8563-5/2005 Genetický profilů genů metabolismu
... course: Development of cells and tissues ...
... course: Development of cells and tissues ...
Document
... This is called genetic drift. Rarely, mutations enhance their carrier’s survival chances within their environment, and become the norm in that group. The latter two types of mutations have produced the existing races and sub-races from groups isolated in different environs. Geneticists have been abl ...
... This is called genetic drift. Rarely, mutations enhance their carrier’s survival chances within their environment, and become the norm in that group. The latter two types of mutations have produced the existing races and sub-races from groups isolated in different environs. Geneticists have been abl ...
DNA Connection (pgs.101-106)
... Human Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is Abnormal condition that a ...
... Human Genetic Disorders A genetic disorder is Abnormal condition that a ...
Exploring Mutant Organisms Teacher Extended Background
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
... originated from the same population and had spread out over numerous islands. Some birds developed physical traits, specifically distinct beak shapes, which gave them an advantage in their new habitats and made it easier for them to access food. Darwin suggested that these advantageous traits were p ...
Cancer is Caused by Cumulative Gene Mutations
... DNA repair genes - become damaged/mutated no repair damage DNA replicated, mutations may not be repaired and will build up. Proto-oncogenes - Code for growth factors, or signalling proteins (promote growth) o o o o ...
... DNA repair genes - become damaged/mutated no repair damage DNA replicated, mutations may not be repaired and will build up. Proto-oncogenes - Code for growth factors, or signalling proteins (promote growth) o o o o ...
BRCA1 and BRCA2 in Men
... BRCA1 and BRCA2 in Men Everyone has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These genes help repair damage to the DNA within cells. However, some individuals inherit a mutation in one of their BRCA genes, which increases their risk for certain cancers, including breast (female and male), ovarian, pancreatic and pros ...
... BRCA1 and BRCA2 in Men Everyone has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. These genes help repair damage to the DNA within cells. However, some individuals inherit a mutation in one of their BRCA genes, which increases their risk for certain cancers, including breast (female and male), ovarian, pancreatic and pros ...
CELL DIVISION
... series of portraits at the SOFT (Support for Families with Trisomy 18, 13 and Related Disorders) conference in Roanoke, Virginia during July 2009. I am trying to raise awareness that while only 10% of these kids survive their first year the ones that do live a rich life. Expectant parents are often ...
... series of portraits at the SOFT (Support for Families with Trisomy 18, 13 and Related Disorders) conference in Roanoke, Virginia during July 2009. I am trying to raise awareness that while only 10% of these kids survive their first year the ones that do live a rich life. Expectant parents are often ...
Biology 3 Study Guide – Exam #3
... the inheritance of single genes incomplete dominance and codominance inheritance of ABO blood type inheritance of two genes at a time inheritance of X-linked genes solving of genetics problems using Punnett squares use of pedigrees ...
... the inheritance of single genes incomplete dominance and codominance inheritance of ABO blood type inheritance of two genes at a time inheritance of X-linked genes solving of genetics problems using Punnett squares use of pedigrees ...
CRACKING THE CODE OF LIFE QUESTIONS
... 12. What was every week like at Solaris? 13. How many of the 17 children have arthritis? 14. What are the “guys in the funny suits” making? 15. BRCA mutations cause what percentage of breast cancers? 16. What would most changes we make to DNA today do to the machine? 17. What do you come away from r ...
... 12. What was every week like at Solaris? 13. How many of the 17 children have arthritis? 14. What are the “guys in the funny suits” making? 15. BRCA mutations cause what percentage of breast cancers? 16. What would most changes we make to DNA today do to the machine? 17. What do you come away from r ...
extranuclear inheritance
... • Analysis of mutant alleles in organelles can be complex because many genes for organelle components are nuclear-encoded – And even subunits of a multicomponent enzyme may be partially encoded in both locations – Heteroplasmy makes things even worse… ...
... • Analysis of mutant alleles in organelles can be complex because many genes for organelle components are nuclear-encoded – And even subunits of a multicomponent enzyme may be partially encoded in both locations – Heteroplasmy makes things even worse… ...
Dr. Shivani_extranuclear inheritance
... • Analysis of mutant alleles in organelles can be complex because many genes for organelle components are nuclear-encoded – And even subunits of a multicomponent enzyme may be partially encoded in both locations – Heteroplasmy makes things even worse… ...
... • Analysis of mutant alleles in organelles can be complex because many genes for organelle components are nuclear-encoded – And even subunits of a multicomponent enzyme may be partially encoded in both locations – Heteroplasmy makes things even worse… ...
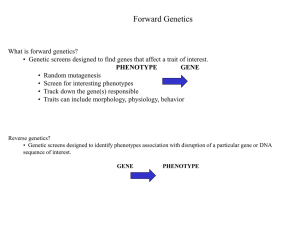
Complementation
... • Track down the gene(s) responsible • Traits can include morphology, physiology, behavior ...
... • Track down the gene(s) responsible • Traits can include morphology, physiology, behavior ...
Cell Theory Quiz Study Guide Name
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
... 17. The order of the nitrogen bases on the DNA molecule is known as the genetic _______. 18. In 1952, Rosalind ____________ discovered DNA is 2 chains of molecules. 19. In 1953, using the above scientist’s research, _____________ and ____________ made a model of DNA. 20. A _____________________ is a ...
Lecture #8 Date
... proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division, have essential functions in normal cells. An oncogene arises from a genetic change that leads to an increase in the proto-oncogene’s protein or the activity of each protein molecule. These genetic changes include movements of DNA within th ...
... proteins that stimulate normal cell growth and division, have essential functions in normal cells. An oncogene arises from a genetic change that leads to an increase in the proto-oncogene’s protein or the activity of each protein molecule. These genetic changes include movements of DNA within th ...
Molecular Biology & Medicine
... affected gene(s) – human genomic libraries can be screened with sequence-specific probes • deduced from protein sequence • from mRNA • from other species • identified by a “positional” clue ...
... affected gene(s) – human genomic libraries can be screened with sequence-specific probes • deduced from protein sequence • from mRNA • from other species • identified by a “positional” clue ...
Down syndrome
... male breast cancer pancreatic cancer Although the risk of male breast cancer and pancreatic cancer may be under 10 ...
... male breast cancer pancreatic cancer Although the risk of male breast cancer and pancreatic cancer may be under 10 ...
The Genetics of C elegans (Brenner)
... define the unitary steps of development in terms of genetic analysis … “ 1963 Research Proposal: “The New Major problem in molecular biology is the genetics … of control mechanisms” ...
... define the unitary steps of development in terms of genetic analysis … “ 1963 Research Proposal: “The New Major problem in molecular biology is the genetics … of control mechanisms” ...
39 million to advance NSW cancer research
... Among the Career Development Fellows, the University of Sydney’s Dr Anne Cust who first proved links between tanning beds and melanomas - is embarking on a new project to improve the disease’s treatment and prevention. Early Career Fellows include Dr Elizabeth Hinde from UNSW, who is working on new ...
... Among the Career Development Fellows, the University of Sydney’s Dr Anne Cust who first proved links between tanning beds and melanomas - is embarking on a new project to improve the disease’s treatment and prevention. Early Career Fellows include Dr Elizabeth Hinde from UNSW, who is working on new ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.