Retinoblastoma
... but cancer is not inherited The offspring CANNOT inherit two mutated genes Rb is just one example Inheritance of brca1(lf) mutation results in predisposition for breast cancer ...
... but cancer is not inherited The offspring CANNOT inherit two mutated genes Rb is just one example Inheritance of brca1(lf) mutation results in predisposition for breast cancer ...
DNA and Genetic Engineering Midterm Review Chapter 12 Review
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
... 13. The condition in which cells have many sets of chromosomes; it may instantly produce new plant species that are larger and stronger. 16. Gel electrophoresis enables scientists to separate and analyze DNA fragments, to compare genomes of different individuals and organisms, and to identify a spec ...
Lung Cancer and the MAP2K1 K57N Mutation This material will help
... In healthy cells, MAP2K1 is a key protein in a growth pathway (Figure 1). As the growth signal reaches each protein in the pathway, it turns on the protein. When the RAS protein receives the signal, it passes it on to a RAF protein. RAF passes it on to MAP2K1, and MAP2K1 passes it on to ERK. Figure ...
... In healthy cells, MAP2K1 is a key protein in a growth pathway (Figure 1). As the growth signal reaches each protein in the pathway, it turns on the protein. When the RAS protein receives the signal, it passes it on to a RAF protein. RAF passes it on to MAP2K1, and MAP2K1 passes it on to ERK. Figure ...
Notes: Mutations
... • Sometimes cells can make mistakes when copying their DNA. These mistakes are called mutations. • Mutations- are changes in the DNA sequence that affects the genetic information • Mutations that occur in sex cells can be inherited. ...
... • Sometimes cells can make mistakes when copying their DNA. These mistakes are called mutations. • Mutations- are changes in the DNA sequence that affects the genetic information • Mutations that occur in sex cells can be inherited. ...
Mutations Notes - Oakman School News
... Read the following notes and complete the concept map – attached - on your own paper Gene Mutations ...
... Read the following notes and complete the concept map – attached - on your own paper Gene Mutations ...
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
... How is diffuse gastric cancer different from other gastric cancers? Diffuse gastric cancer (DGC) is also referred to as signet ring carcinoma. DGC is difficult to detect because no visible tumor is formed. Cancer cells spread under normal gastric tissue and are not visible on the surface of the stom ...
... How is diffuse gastric cancer different from other gastric cancers? Diffuse gastric cancer (DGC) is also referred to as signet ring carcinoma. DGC is difficult to detect because no visible tumor is formed. Cancer cells spread under normal gastric tissue and are not visible on the surface of the stom ...
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
... • The agent of such changes can be random spontaneous mutations or environmental influences such as chemical carcinogens or physical mutagens. • Cancer-causing genes, oncogenes, were initially discovered in retroviruses, but close counterparts, proto-oncogenes were found in other organisms. Copyrigh ...
... • The agent of such changes can be random spontaneous mutations or environmental influences such as chemical carcinogens or physical mutagens. • Cancer-causing genes, oncogenes, were initially discovered in retroviruses, but close counterparts, proto-oncogenes were found in other organisms. Copyrigh ...
Exam 3 review - Iowa State University
... B. Signal cells to progress through the cell cycle C. Mutations cause them to be under-expressed or nonfunctional D. Induce apoptosis 16. What is the difference between a malignant and benign tumor? A. Benign tumors must be removed through surgery B. Malignant tumors can have a blood supply spreadin ...
... B. Signal cells to progress through the cell cycle C. Mutations cause them to be under-expressed or nonfunctional D. Induce apoptosis 16. What is the difference between a malignant and benign tumor? A. Benign tumors must be removed through surgery B. Malignant tumors can have a blood supply spreadin ...
Imaging in CRISPR/Cas9 Applications
... technology by developing an inducible lentiviral system. This platform facilitates efficient gene targeting and utilizes an imagingbased tool for phenotypic assessment following deletion of essential genes and identification of tumor-promoting mutations. The CRISPR/Cas9 strategy is based on the DN ...
... technology by developing an inducible lentiviral system. This platform facilitates efficient gene targeting and utilizes an imagingbased tool for phenotypic assessment following deletion of essential genes and identification of tumor-promoting mutations. The CRISPR/Cas9 strategy is based on the DN ...
PCR-assay of intragenic DNA lesions induced by ionizing radiation
... γ-rays and neutrons at the regulatory and coding parts of yellow gene Drosophila melanogaster. 3.2. Background and Topicality of Project: A large body of experimental data shows that deletions of the greater part or a whole gene in mammalian somatic cells in vitro or in vivo are mainly induced by di ...
... γ-rays and neutrons at the regulatory and coding parts of yellow gene Drosophila melanogaster. 3.2. Background and Topicality of Project: A large body of experimental data shows that deletions of the greater part or a whole gene in mammalian somatic cells in vitro or in vivo are mainly induced by di ...
NOVA – Cracking the Code of Life
... 2. To what degree are all humans identical at the genetic level? 3. About what percentage of the genes in a banana are also in a human? ____ Why is this figure so high? ...
... 2. To what degree are all humans identical at the genetic level? 3. About what percentage of the genes in a banana are also in a human? ____ Why is this figure so high? ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... To sequence & determine the exact order of the nucleotides (A,C,T,G) for ALL of the DNA in a human cell To determine which sections of DNA represent the individual genes To store this information in databases for analysis ...
... To sequence & determine the exact order of the nucleotides (A,C,T,G) for ALL of the DNA in a human cell To determine which sections of DNA represent the individual genes To store this information in databases for analysis ...
PERSONAL GENOMICS
... “Lukas Wartman, a leukemia doctor and researcher, developed the disease himself. As he faced death, his colleagues sequenced his cancer genome. The result was a totally unexpected treatment.” ...
... “Lukas Wartman, a leukemia doctor and researcher, developed the disease himself. As he faced death, his colleagues sequenced his cancer genome. The result was a totally unexpected treatment.” ...
my talk - David Rasnick, PhD
... …analyzed… colon cancer data from Zhang et al. (1997) Science 276:1268-1272 ...
... …analyzed… colon cancer data from Zhang et al. (1997) Science 276:1268-1272 ...
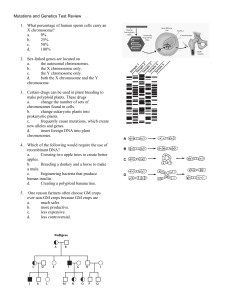
Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
... Mutations and Genetics Test Review 1. What percentage of human sperm cells carry an X chromosome? a. ...
What is skin cancer?
... Skin cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It occurs when unrepaired DNA damage to skin cells (most often caused by ultraviolet radiation from sunshine or tanning beds) triggers mutations, or genetic defects, that lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. ...
... Skin cancer is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It occurs when unrepaired DNA damage to skin cells (most often caused by ultraviolet radiation from sunshine or tanning beds) triggers mutations, or genetic defects, that lead the skin cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. ...
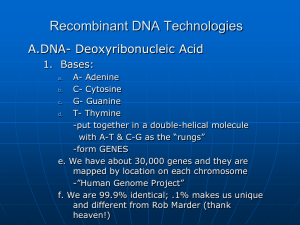
Recombinant DNA Technologies
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
... d. T- Thymine -put together in a double-helical molecule with A-T & C-G as the “rungs” -form GENES e. We have about 30,000 genes and they are mapped by location on each chromosome -”Human Genome Project” f. We are 99.9% identical; .1% makes us unique and different from Rob Marder (thank heaven!) a. ...
Section 8.7 Mutations
... When Mutations Occur 1. Errors can occur during: DNA Replication Protein Synthesis Meiosis ...
... When Mutations Occur 1. Errors can occur during: DNA Replication Protein Synthesis Meiosis ...
CANCER COURSE MODULE SIGN
... Submit a separate form for each course you plan to take- you may not take the same module for more than one course. Appropriate modules offered by the Immunology Research Group may be used for electives upon approval by the course and module coordinators- see for a description of these modules. ...
... Submit a separate form for each course you plan to take- you may not take the same module for more than one course. Appropriate modules offered by the Immunology Research Group may be used for electives upon approval by the course and module coordinators- see for a description of these modules. ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.