Multiple Barriers to Nonhomologous DNA End Joining
... construction of a new double mutant stock and observed a similar suppression in g-H2AV persistence (P , 0.0001, Figure 2). In contrast, mei-218; spn-A double mutants exhibited similar levels of persistent g-H2AV foci to that of spn-A single mutants (P = 0.2841), indicating mei-218 mutants retain the ...
... construction of a new double mutant stock and observed a similar suppression in g-H2AV persistence (P , 0.0001, Figure 2). In contrast, mei-218; spn-A double mutants exhibited similar levels of persistent g-H2AV foci to that of spn-A single mutants (P = 0.2841), indicating mei-218 mutants retain the ...
Neurofibromatosis, Type 1 - St. Jude Children`s Research Hospital
... a family. However, the severity of the condition and which body areas are affected can vary from person to person. How is neurofibromatosis, type 1, diagnosed? A diagnosis of neurofibromatosis, type 1, can be decided with or without genetic testing. Genetic testing can be offered to people who have ...
... a family. However, the severity of the condition and which body areas are affected can vary from person to person. How is neurofibromatosis, type 1, diagnosed? A diagnosis of neurofibromatosis, type 1, can be decided with or without genetic testing. Genetic testing can be offered to people who have ...
Belote, J. m., F. M. Hoffmann, M. McKeown, R. Chorsky, and B. S. Baker. (1990). Cytogenetic analysis of chromosome region 73AD of Drosophila melanlgaster. Genetics 125: 783-793.
... the 21 st mutants, 13 were associated with chromosome rearrangements (2 inversions, 9 deficiencies and 2 complex rearrangements) involving the 7 3 A 3 . 4 region(Table I). A detaileddescription of the st mutants isolated in this screen is presented in TEARLE et al. (1989). Of the remaining 24 mutant ...
... the 21 st mutants, 13 were associated with chromosome rearrangements (2 inversions, 9 deficiencies and 2 complex rearrangements) involving the 7 3 A 3 . 4 region(Table I). A detaileddescription of the st mutants isolated in this screen is presented in TEARLE et al. (1989). Of the remaining 24 mutant ...
A Genetic Mosaic Analysis With a Repressible Cell
... receptor (FGFR) signaling pathway. The Drosophila FGF ligand Branchless (Bnl) and the FGFR Breathless (Btl/FGFR) are required for cell migration during the establishment of the interconnected network of tracheal tubes. However, due to an important maternal contribution of members of the FGFR pathway ...
... receptor (FGFR) signaling pathway. The Drosophila FGF ligand Branchless (Bnl) and the FGFR Breathless (Btl/FGFR) are required for cell migration during the establishment of the interconnected network of tracheal tubes. However, due to an important maternal contribution of members of the FGFR pathway ...
Exam 2
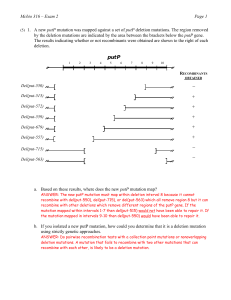
... 5. The F-plasmid can be stabily maintained in both Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. However, Hfr’s are formed much less frequently in S. typhimurium than in E. coli. In addition, there are many fewer insertion sites in S. typhimurium compared to E. coli. Given what you know about how Hfr ...
... 5. The F-plasmid can be stabily maintained in both Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. However, Hfr’s are formed much less frequently in S. typhimurium than in E. coli. In addition, there are many fewer insertion sites in S. typhimurium compared to E. coli. Given what you know about how Hfr ...
Cytogenetic genotype-phenotype studies: Improving genotyping
... et al., 1999). The location of both candidate genes is depicted in Fig. 2. In 2000 an Italian group reported the cytogenetic, molecular, and clinical findings in 16 WHS patients (Zollino et al., 2000). Submicroscopic deletions ranging from 2.8 to 4.4 Mb were detected in four patients. In one patient ...
... et al., 1999). The location of both candidate genes is depicted in Fig. 2. In 2000 an Italian group reported the cytogenetic, molecular, and clinical findings in 16 WHS patients (Zollino et al., 2000). Submicroscopic deletions ranging from 2.8 to 4.4 Mb were detected in four patients. In one patient ...
Genetic Polymorphism of Human CYP2E1
... To evaluate the functional importance of the mutations in the CYP2E1*2 and CYP2E1*3 alleles, site-directed mutagenesis was used to introduce these mutations into the wild-type CYP2E1 cDNA. The cDNAs were inserted into the pCMV4 expression vector and subsequently expressed in COS-1 cells. For compari ...
... To evaluate the functional importance of the mutations in the CYP2E1*2 and CYP2E1*3 alleles, site-directed mutagenesis was used to introduce these mutations into the wild-type CYP2E1 cDNA. The cDNAs were inserted into the pCMV4 expression vector and subsequently expressed in COS-1 cells. For compari ...
POCUS: mining genomic sequence annotation to predict disease
... The diseases were grouped by number of disease genes to investigate the effects of locus number. Enrichment levels were calculated for two categories of disease gene sets, 3-5 loci and 6-11 loci, and enrichment was found to vary with the number of loci. At each locus size the 6-11-loci category was ...
... The diseases were grouped by number of disease genes to investigate the effects of locus number. Enrichment levels were calculated for two categories of disease gene sets, 3-5 loci and 6-11 loci, and enrichment was found to vary with the number of loci. At each locus size the 6-11-loci category was ...
DNA cytosine methylation in plant development
... Cytosine bases of the nuclear genome in higher plants are often extensively methylated. Cytosine methylation has been implicated in the silencing of both transposable elements (TEs) and endogenous genes, and loss of methylation may have severe functional consequences. The recent methylation profilin ...
... Cytosine bases of the nuclear genome in higher plants are often extensively methylated. Cytosine methylation has been implicated in the silencing of both transposable elements (TEs) and endogenous genes, and loss of methylation may have severe functional consequences. The recent methylation profilin ...
Adenomatous Polyp
... Three interrelated features determine the risk of cancerous transformation: polyp size, histologic architecture, and severity of dysplasia. (1) Cancer is rare in tubular adenomas less than 1 cm in diameter. (2) The likelihood of cancer is high (about 50%) in sessile villous adenomas that are greater ...
... Three interrelated features determine the risk of cancerous transformation: polyp size, histologic architecture, and severity of dysplasia. (1) Cancer is rare in tubular adenomas less than 1 cm in diameter. (2) The likelihood of cancer is high (about 50%) in sessile villous adenomas that are greater ...
Cancer Prone Disease Section Multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma in Oncology and Haematology
... Broesby-Olsen S, Gomez-Lira M, Girolomoni G, Maize JC, Feldman RJ, Kato N, Koga Y, Ferguson-Smith MA, Goudie DR, Lane EB. Multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma in different ethnic groups: more than a founder mutation disorder? J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Oct;127(10):2336-44 ...
... Broesby-Olsen S, Gomez-Lira M, Girolomoni G, Maize JC, Feldman RJ, Kato N, Koga Y, Ferguson-Smith MA, Goudie DR, Lane EB. Multiple self-healing squamous epithelioma in different ethnic groups: more than a founder mutation disorder? J Invest Dermatol. 2007 Oct;127(10):2336-44 ...
Williams syndrome deficits in visual spatial Chromosome 7q11.23
... using a panel of 24 BACs and cosmids spanning the region commonly deleted and single gene analysis using Southern blotting. From the cohort of subjects, three had atypical deletions. Physical examinations and cognitive tests were administered to the three subjects and the results were compared to th ...
... using a panel of 24 BACs and cosmids spanning the region commonly deleted and single gene analysis using Southern blotting. From the cohort of subjects, three had atypical deletions. Physical examinations and cognitive tests were administered to the three subjects and the results were compared to th ...
Clinical and genetic patterns ofneurofibromatosis 1 and 2
... intron (a 'non-coding region') of the NFl gene. These small genes 'within a gene' are interesting: the OMgp (oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein) gene because of its role in cellcell communication in the central nervous system,'1 and the EV12A and EV12B genes because of their mouse homologues playin ...
... intron (a 'non-coding region') of the NFl gene. These small genes 'within a gene' are interesting: the OMgp (oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein) gene because of its role in cellcell communication in the central nervous system,'1 and the EV12A and EV12B genes because of their mouse homologues playin ...
VUMC team pinpoints genes that dictate five fingers
... Nature that two genes called Sonic hedgehog and Gli3 work together to regulate the number of digits and their identity. Mice that are missing both of these genes end up with between six and 11 digits per limb, and all of them are the same type of digit. The results were a surprise, Chiang said, beca ...
... Nature that two genes called Sonic hedgehog and Gli3 work together to regulate the number of digits and their identity. Mice that are missing both of these genes end up with between six and 11 digits per limb, and all of them are the same type of digit. The results were a surprise, Chiang said, beca ...
Balancer Chromosomes – An Optional Minitutorial What follows is a
... unless m is a dominant lethal; these flies have the curly wings) and m/m (might survive; but won’t have the curly wings). The fact that there are inversions built into the balancer chromosome means that crossover cannot occur between the balancer and the other chromosome. Hence, if the researcher se ...
... unless m is a dominant lethal; these flies have the curly wings) and m/m (might survive; but won’t have the curly wings). The fact that there are inversions built into the balancer chromosome means that crossover cannot occur between the balancer and the other chromosome. Hence, if the researcher se ...
Genomic Organization of Evolutionarily Correlated Genes in
... Chromosome conformation, genome organization and gene expression may be expected to be interdependent. Evidence for nonrandom genome layout, defined as relative gene positioning, stems from two main approaches. Firstly, the analysis of contiguous genome segments across species has highlighted the con ...
... Chromosome conformation, genome organization and gene expression may be expected to be interdependent. Evidence for nonrandom genome layout, defined as relative gene positioning, stems from two main approaches. Firstly, the analysis of contiguous genome segments across species has highlighted the con ...
Gene Section ETV6 (ets variant 6) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... constitutive activation of the kinase activity of the partner protein, modification of the original functions of a transcription factor, loss of function of the fusion gene, affecting ETV6 and the partner gene, activation of a proto-oncogene in the vicinity of a chromosomal translocation and dominan ...
... constitutive activation of the kinase activity of the partner protein, modification of the original functions of a transcription factor, loss of function of the fusion gene, affecting ETV6 and the partner gene, activation of a proto-oncogene in the vicinity of a chromosomal translocation and dominan ...
Genetic Testing For FMR1 Mutations (Including
... performed as part of a comprehensive genetic evaluation that includes routine cytogenetic evaluation. Cytogenetic evaluation is important in these circumstances because constitutional chromosome abnormalities have been identified as frequently as or more frequently than fragile X mutations in mental ...
... performed as part of a comprehensive genetic evaluation that includes routine cytogenetic evaluation. Cytogenetic evaluation is important in these circumstances because constitutional chromosome abnormalities have been identified as frequently as or more frequently than fragile X mutations in mental ...
Drug-specific Sites of Topoisomerase II DNA
... unrelated inhibitors, mAMSA and VM-26, suggesting that the in vivo site selectivity is determined, at least in part, by the inhibitor. Thus, to establish whether the drug sequence specificity is a deter minant of drug-enhanced DNA cleavage in the chromatin of living cells, we have examined at a sequ ...
... unrelated inhibitors, mAMSA and VM-26, suggesting that the in vivo site selectivity is determined, at least in part, by the inhibitor. Thus, to establish whether the drug sequence specificity is a deter minant of drug-enhanced DNA cleavage in the chromatin of living cells, we have examined at a sequ ...
Oncogenomics
Oncogenomics is a relatively new sub-field of genomics that applies high throughput technologies to characterize genes associated with cancer. Oncogenomics is synonymous with ""cancer genomics"". Cancer is a genetic disease caused by accumulation of mutations to DNA leading to unrestrained cell proliferation and neoplasm formation. The goal of oncogenomics is to identify new oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes that may provide new insights into cancer diagnosis, predicting clinical outcome of cancers, and new targets for cancer therapies. The success of targeted cancer therapies such as Gleevec, Herceptin, and Avastin raised the hope for oncogenomics to elucidate new targets for cancer treatment.Besides understanding the underlying genetic mechanisms that initiates or drives cancer progression, one of the main goals of oncogenomics is to allow for the development of personalized cancer treatment. Cancer develops due to an accumulation of mutations in DNA. These mutations accumulate randomly, and thus, different DNA mutations and mutation combinations exist between different individuals with the same type of cancer. Thus, identifying and targeting specific mutations which have occurred in an individual patient may lead to increased efficacy of cancer therapy.The completion of the Human Genome Project has greatly facilitated the field of oncogenomics and has increased the abilities of researchers to find cancer causing genes. In addition, the sequencing technologies now available for sequence generation and data analysis have been applied to the study of oncogenomics. With the amount of research conducted on cancer genomes and the accumulation of databases documenting the mutational changes, it has been predicted that the most important cancer-causing mutations, rearrangements, and altered expression levels will be cataloged and well characterized within the next decade.Cancer research may look either on the genomic level at DNA mutations, the epigenetic level at methylation or histone modification changes, the transcription level at altered levels of gene expression, or the protein level at altered levels of protein abundance and function in cancer cells. Oncogenomics focuses on the genomic, epigenomic, and transcript level alterations in cancer.