Genetic Engineering
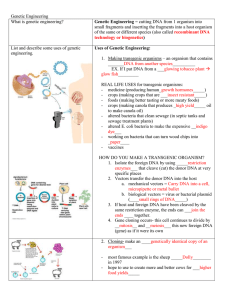
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using _____restriction enzymes___ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = Carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid (____ ...
Supplementary materials and methods: Colony forming assay
... subjected to the primer extension with biotinylated primer for 12 cycles followed by LM-PCR amplification. DNA methylation assay Genomic DNA purified from individual cell types was digested with 10U of the methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes MaeII or HpaII, respectively. After inactivation of ...
... subjected to the primer extension with biotinylated primer for 12 cycles followed by LM-PCR amplification. DNA methylation assay Genomic DNA purified from individual cell types was digested with 10U of the methylation-sensitive restriction enzymes MaeII or HpaII, respectively. After inactivation of ...
8 How Cellular Information is Altered
... Selectable mutation: mutants can survive under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necess ...
... Selectable mutation: mutants can survive under a set of specific set of environmental conditions Direct selection: an example of direct selection to find a mutant resistant to an antibiotic or toxic compound Indirect selection: isolate mutants that are deficient in their capacity to produce a necess ...
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and TRENDS Unit Cover Page Topic
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
... particular segment of the DNA. The instructions for forming species characteristics are carried in DNA. All cells in an organism have the same genetic content, but the genes expressed by the cell may be regulated in different ways. Not all DNA codes for a protein; some segments of DNA are involved i ...
DNA intro review - Ms Kim`s Biology Class
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a ...
... 1. A nucleotide is made of three parts: a ___________________ group, a five carbon __________________, and a ...
Chapter 13 – Genetic Engineering
... • Induce mutations – the ultimate source of genetic variations among a group of organisms – Mutagens used – radiation and chemicals – Some organisms are formed that have more ...
... • Induce mutations – the ultimate source of genetic variations among a group of organisms – Mutagens used – radiation and chemicals – Some organisms are formed that have more ...
BIO SOL Review 16
... stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the following would most likely change the current classification of two closely related flower species to a single species? (1 point) a. The discovery of a new, r ...
... stomach of a grasshopper would be expected to have the same — a. metabolic rates b. cell shape c. DNA d. cell size 12. (2003-9) Which of the following would most likely change the current classification of two closely related flower species to a single species? (1 point) a. The discovery of a new, r ...
Slide 1
... • A bulge forms on the cell and it eventually breaks off in the form of a new yeast cell. • This is by mitosis. ...
... • A bulge forms on the cell and it eventually breaks off in the form of a new yeast cell. • This is by mitosis. ...
Study guideCh8
... wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of methylguanine? Is this another form of base substitution? What kind of mutation do inter ...
... wrong base pair, instead of the base substation happening randomly). Base analogs can be introduced into the cells, which bind to the wrong base pair. How is this similar in resulting mutation to the presence of methylguanine? Is this another form of base substitution? What kind of mutation do inter ...
Genetic engineering - Mad River Local Schools
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
... lives. As a gene therapist, you'll treat human patients with genetic illnesses. Otherwise, you might work in a non-medical environment as a biochemist or biophysicist, exploring living organisms such as plants used as food crops. You'll typically work full-time with a ...
Slide 1
... fungi, protozoa, and even some plants and animals. They are separate from chromosomes. ...
... fungi, protozoa, and even some plants and animals. They are separate from chromosomes. ...
molecular genetics unit review
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current knowledge of DNA structure and DNA replication: a) Chargaff b) Rosalind Franklin c) Watson and Crick d) Meselson and Stahl Describe the structure of DNA. Include terms like anti-parallel, nucleotide (phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous ...
... Describe the contributions of the following scientists to our current knowledge of DNA structure and DNA replication: a) Chargaff b) Rosalind Franklin c) Watson and Crick d) Meselson and Stahl Describe the structure of DNA. Include terms like anti-parallel, nucleotide (phosphate, sugar, nitrogenous ...
Genetics
... Genetics is the branch of biology that deals with heredity and the expression of inherited traits. Charles Darwin did not know anything about how traits (like flower color) where passed-on from parent to offspring. But that did not stop Darwin from studying change through time of species. (evolu ...
... Genetics is the branch of biology that deals with heredity and the expression of inherited traits. Charles Darwin did not know anything about how traits (like flower color) where passed-on from parent to offspring. But that did not stop Darwin from studying change through time of species. (evolu ...
Mutations and DNA Technology Notes
... - Making changes to the DNA code of an organism. How can I take a gene from one organism and insert it into another completely different organism? A. Recombinant DNA - DNA made by connecting fragments of DNA from different sources. A + B =C ...
... - Making changes to the DNA code of an organism. How can I take a gene from one organism and insert it into another completely different organism? A. Recombinant DNA - DNA made by connecting fragments of DNA from different sources. A + B =C ...
2013 DNA, Repl, Trans and Transl Review
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
... 1. What are the subunits called that make up DNA? 2. What three things make up a nucleotide? 3. Describe the structure of DNA. 4. An organism's characteristics and directions for proteins synthesis are coded for by molecules of __________. 5. What are the monomers of proteins? How many of these mono ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... eg. A virus carrying a normal gene is inhaled by the patient. The virus is able to provide the patient with the normal gene product that the patient was missing due to a ...
... eg. A virus carrying a normal gene is inhaled by the patient. The virus is able to provide the patient with the normal gene product that the patient was missing due to a ...