W09micr430Lec17 - Cal State LA
... cleave the phosphodiester bond next to the AP site, usually on the 5’ side This generates 3’-hydroxyl end, which is extended by DNA pol I as the 5’-exonuclease activity of this enzyme removes a portion of damaged DNA ahead. DNA ligase seals the nick. ...
... cleave the phosphodiester bond next to the AP site, usually on the 5’ side This generates 3’-hydroxyl end, which is extended by DNA pol I as the 5’-exonuclease activity of this enzyme removes a portion of damaged DNA ahead. DNA ligase seals the nick. ...
Study Guide
... b. Where do sperms get energy to propel itself? ii. Egg – Form and Function 1. Why are eggs so large? What is the role of the vitelline membrane? b. Early Cleavage to Blastula– What is the purpose of this first phase of development? i. What do you start with and what do you end up with before cells ...
... b. Where do sperms get energy to propel itself? ii. Egg – Form and Function 1. Why are eggs so large? What is the role of the vitelline membrane? b. Early Cleavage to Blastula– What is the purpose of this first phase of development? i. What do you start with and what do you end up with before cells ...
Restriction Enzymes, Vectors, and Genetic Libraries
... contains all the genetic information of an individual = genomic library - gene bank Chromosomes, set of genes of single cell type etc. ...
... contains all the genetic information of an individual = genomic library - gene bank Chromosomes, set of genes of single cell type etc. ...
Understanding DNA
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
... 2. Draw the cell and label the ff structures: a. cell membrane Note: Follow guidelines on b. chromosomes Making Diagrams ...
DNA - eduBuzz.org
... This characteristic number is known as the chromosome complement and varies from species to species. Each individuals DNA is unique. Genes are passed on from parent to offspring. Structure of chromosomes Chromosomes are made from tightly coiled molecules of a chemical substance called DNA. DNA All t ...
... This characteristic number is known as the chromosome complement and varies from species to species. Each individuals DNA is unique. Genes are passed on from parent to offspring. Structure of chromosomes Chromosomes are made from tightly coiled molecules of a chemical substance called DNA. DNA All t ...
Causes
... • A human has 1014 nucleated cells each with 3x 109 base pairs of DNA. If about 1016 cell divisions occur in a lifetime and • 10−10 mutations per base pair per cell generation escape repair, • there may eventually be as many as one mutation per 106 bp in the genome. • Fortunately,most of these will ...
... • A human has 1014 nucleated cells each with 3x 109 base pairs of DNA. If about 1016 cell divisions occur in a lifetime and • 10−10 mutations per base pair per cell generation escape repair, • there may eventually be as many as one mutation per 106 bp in the genome. • Fortunately,most of these will ...
Genetics - California Science Teacher
... 15. Process in which a protein is assembled at a ribosome. 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced ...
... 15. Process in which a protein is assembled at a ribosome. 16. Process in which naked DNA is taken up by bacterial or yeast cell 17. Process in which RNA is produced by using a DNA template. 18. Process that results in the production of cDNA from an RNA molecule. 19. Process in which DNA is produced ...
fix my dna text
... four different types of bases, shown as A, T, C and G. In DNA, two strands coil together to form a double helix. There are chemical cross-links between the two strands, formed by pairs of bases. ...
... four different types of bases, shown as A, T, C and G. In DNA, two strands coil together to form a double helix. There are chemical cross-links between the two strands, formed by pairs of bases. ...
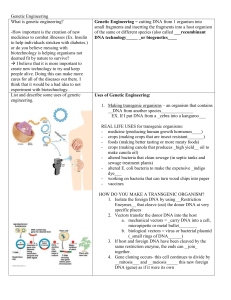
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
Why do cells need to divide?
... Cell Divison grade 10.ecw 2D Mitosis fill in the blanks worksheet.doc Mitosis fill in the blanks worksheet.doc ...
... Cell Divison grade 10.ecw 2D Mitosis fill in the blanks worksheet.doc Mitosis fill in the blanks worksheet.doc ...
DNA- Experiments and People
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
DNA People - Biology Junction
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
... Grow E. coli bacteria with radioactive 15N (its heavier than 14N) so bacteria incorporate heavy N into their DNA Then grow in media with only 14N Centrifuge DNA at different times to separate by size. (The more 15N it has the heavier it is) Pattern shows which model is correct ...
Visualizing DNA
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
... Thus, larger fragments will move slower than smaller fragments. This allows separation of all different sizes of DNA fragments. ...
MUTATIONS
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
... DNA just happen. Our DNA can change without warning, which changes the genes and how they behave. Factors that cause changes in our DNA: Errors when DNA is copied for new cells Environmental factors change DNA (nicotine, sunlight, x-rays, chemicals Mutations are inherited from the parents ...
No Slide Title
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
My Dinosaur
... • Don’t forget the surrogate mother! • With birds being the closet relative to a dinosaur our team of researches were able to use a Hawk as the surrogate mother for the cloning. ...
... • Don’t forget the surrogate mother! • With birds being the closet relative to a dinosaur our team of researches were able to use a Hawk as the surrogate mother for the cloning. ...
Organism Genome (kb) Form
... • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different types - euchromatin (where most of the active genes are) and heterochromatin (no active genes). Some regions of genome can switch between these 2 states (facultative heterochromatin) ...
... • See figures 24-23, 24-24, table 24-3 in Lehninger • Chromatin is of 2 different types - euchromatin (where most of the active genes are) and heterochromatin (no active genes). Some regions of genome can switch between these 2 states (facultative heterochromatin) ...
Biology Assessment #3:
... 3. What is crossing over and when does it occur? 4. How does sexual reproduction increase variation within a species? 5. Why is there little variation in asexually reproducing organisms? 6. Identify the number of chromosomes in human haploid cells, diploid cells, sex cells, gametes, and somatic cell ...
... 3. What is crossing over and when does it occur? 4. How does sexual reproduction increase variation within a species? 5. Why is there little variation in asexually reproducing organisms? 6. Identify the number of chromosomes in human haploid cells, diploid cells, sex cells, gametes, and somatic cell ...
Micro Quiz #3R Stu F2011 - the Biology Scholars Program Wiki
... 4. AT-rich DNA strands will denature (separate) at a(n): A. Higher temperature than GC-rich DNA B. Identical temperature as GC-rich DNA C. Similar temperature as GC-rich DNA, with minor variations D. Lower temperature than GC-rich DNA E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or ...
... 4. AT-rich DNA strands will denature (separate) at a(n): A. Higher temperature than GC-rich DNA B. Identical temperature as GC-rich DNA C. Similar temperature as GC-rich DNA, with minor variations D. Lower temperature than GC-rich DNA E. Temperature dependent upon whether it is from a prokaryote or ...
What are the potential benefits to knowing more - B
... social and familial impact Genetic testing available directly to consumers ...
... social and familial impact Genetic testing available directly to consumers ...