Biology - TeacherWeb
... 23. Explain the double helix structure. Two strands of chromosomes bonded together like a twisted ladder 24. Be able to write the complementary base pair to a DNA strand. 25. What is the purpose of DNA replication? For exact copy of genetic information from the parent cell. 26. Explain why DNA must ...
... 23. Explain the double helix structure. Two strands of chromosomes bonded together like a twisted ladder 24. Be able to write the complementary base pair to a DNA strand. 25. What is the purpose of DNA replication? For exact copy of genetic information from the parent cell. 26. Explain why DNA must ...
Mutations - TeacherWeb
... The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called insulin. The insulin protein is used to take up sugars from the bloo ...
... The genes in your DNA code for a specific ____________________. The ____________ and ____________ of amino acids will determine the ___________ and _________________ of the protein. The DNA sequence below codes for a protein called insulin. The insulin protein is used to take up sugars from the bloo ...
Chapter 6
... DNA, and U replaces C in RNA). A nucleotide is a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (ribose in RNA and deoyribose in DNA) and one to three phosphate molecules (Figure 6.1a). The nitrogenous bases can be grouped by structure (Figure 6.1b), into purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymin ...
... DNA, and U replaces C in RNA). A nucleotide is a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (ribose in RNA and deoyribose in DNA) and one to three phosphate molecules (Figure 6.1a). The nitrogenous bases can be grouped by structure (Figure 6.1b), into purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymin ...
BIOTECHNOLOGY
... H-bonds between the complementary base pairs. Produces what are called sticky ends (unpaired nucleotides at each end). ...
... H-bonds between the complementary base pairs. Produces what are called sticky ends (unpaired nucleotides at each end). ...
Nucleus
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
Nucleus - Maryville University
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
Genetics (4) - HCC Learning Web
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
... • Activation by ATP binds specific amino acid and provides necessary energy to join amino acid to growing protein molecule • Anticodon binds to complementary codon of ...
TruSight One Sequencing Panel Workflow
... of TruSight One Sequencing Panel allow us to perform these analyses using a streamlined laboratory workflow—as well as to offer a comprehensive, high-quality sequencing service. Stephen Abbs, Director of Genetics Laboratories, ...
... of TruSight One Sequencing Panel allow us to perform these analyses using a streamlined laboratory workflow—as well as to offer a comprehensive, high-quality sequencing service. Stephen Abbs, Director of Genetics Laboratories, ...
File
... and contains many sites which are recognized by restriction endonucleases (enzymes): one of a large number of nucleases (enzymes that degrade nucleic acids) that can cleave a DNA molecule at any site where a specific short sequence of nucleotides occurs. Restriction enzymes are extensively used in r ...
... and contains many sites which are recognized by restriction endonucleases (enzymes): one of a large number of nucleases (enzymes that degrade nucleic acids) that can cleave a DNA molecule at any site where a specific short sequence of nucleotides occurs. Restriction enzymes are extensively used in r ...
General Biology Program for Secondary
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that is present in humans and almost all other living organisms (Hermanson-Miller and Woodrow 8). DNA holds the genetic information that is inherited generation to generation. This genetic information is stored as a code made up of four bases: adenine, g ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a nucleic acid that is present in humans and almost all other living organisms (Hermanson-Miller and Woodrow 8). DNA holds the genetic information that is inherited generation to generation. This genetic information is stored as a code made up of four bases: adenine, g ...
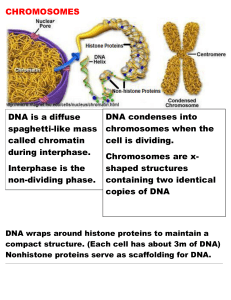
Chromosomes Notes
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... DNA wraps around histone proteins to maintain a compact structure. (Each cell has about 3m of DNA) Nonhistone proteins serve as scaffolding for DNA. ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ ...
Name Period _____ Date ______ SPRING MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 1. The indigenous people of Australia want to do an experiment to decrease the population size of non-native (invasive) cane toad species. There is a spray that claims to prevent maturity of specific type (dominant) of non-native toad eggs (therefore decreasing population size of the cane toad). a. ...
... 1. The indigenous people of Australia want to do an experiment to decrease the population size of non-native (invasive) cane toad species. There is a spray that claims to prevent maturity of specific type (dominant) of non-native toad eggs (therefore decreasing population size of the cane toad). a. ...
Name SIS # 1 Introductory Biochemistry BI 28 Third Midterm
... carefully before answering. Unless otherwise indicated, there is only one correct answer for each multiple choice question. Points are indicated by the question within brackets [ ]. There are no calculators or other electronic devices needed or allowed on this exam. Exams will be photocopied before ...
... carefully before answering. Unless otherwise indicated, there is only one correct answer for each multiple choice question. Points are indicated by the question within brackets [ ]. There are no calculators or other electronic devices needed or allowed on this exam. Exams will be photocopied before ...
Genetics IB Syllabus
... Topic 1.6 Cell division • Some genetic diseases are sex-linked. The pattern of inheritance is different with sex-linked genes due to their location on sex chromosomes. • Many genetic diseases have been identified in humans but most are very rare. Aims: • Radiation and mutagenic chemicals increase th ...
... Topic 1.6 Cell division • Some genetic diseases are sex-linked. The pattern of inheritance is different with sex-linked genes due to their location on sex chromosomes. • Many genetic diseases have been identified in humans but most are very rare. Aims: • Radiation and mutagenic chemicals increase th ...
8000 - International Commission on Missing Persons
... 20 individuals have been tried at the ICTY for crimes related to Srebrenica over the course of 12 cases. Of these, 14 individuals were convicted and one was acquitted. Three cases are ongoing: one is awaiting Trial Chamber judgment before the ICTY (Mladic), one case is on appeal before the Mechanism ...
... 20 individuals have been tried at the ICTY for crimes related to Srebrenica over the course of 12 cases. Of these, 14 individuals were convicted and one was acquitted. Three cases are ongoing: one is awaiting Trial Chamber judgment before the ICTY (Mladic), one case is on appeal before the Mechanism ...
DNA Detectives What is Your DNA Alias? The central dogma of
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
... We use four letters to code all the information contained in DNA: A, T, C and G. The letters are used in groups of three. A group is called a codon. DNA contains the information that is needed by your body to make proteins. The different proteins have specific functions, such as making our hearts, h ...
File
... • James Watson and Francis Crick were the first to discover the shape of DNA • DNA looks similar to a twisted ladder- the sides of the ladder are the same in all DNA molecules, but the rungs are what makes the variation. • Each rung is made up of a pair of chemicals called guanine, cytosine, thymine ...
... • James Watson and Francis Crick were the first to discover the shape of DNA • DNA looks similar to a twisted ladder- the sides of the ladder are the same in all DNA molecules, but the rungs are what makes the variation. • Each rung is made up of a pair of chemicals called guanine, cytosine, thymine ...
Lecture 1, Part I
... whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
... whose functions may include providing chromosomal structural integrity and regulating when, where, and in what quantity proteins are made (regulatory regions). • The terms exon and intron refer to coding (translated into a protein) and non-coding DNA, respectively. ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis
... With 64 possible codons Codon: consist of 3 consecutive nucleotides that specify a specific amino acid (3 bases long) Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides. The property of a protein is determined by the order in which different amino acids are joined toge ...
... With 64 possible codons Codon: consist of 3 consecutive nucleotides that specify a specific amino acid (3 bases long) Proteins are made by joining amino acids into long chains called polypeptides. The property of a protein is determined by the order in which different amino acids are joined toge ...
Grimmer presentation
... • Targeted re-sequencing (Targeted DNA Capture) • Gene regions identified by Genome Wide Association studies (GWAs) ...
... • Targeted re-sequencing (Targeted DNA Capture) • Gene regions identified by Genome Wide Association studies (GWAs) ...
Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... Intro to Heredity and Probability and Punnett Squares 1. ________________is the study of heredity. 2. Heredity is the passing of _______________ from parents to offspring 3. Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? ____________________________________ 4. What is a trait?____________________ ...
... Intro to Heredity and Probability and Punnett Squares 1. ________________is the study of heredity. 2. Heredity is the passing of _______________ from parents to offspring 3. Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? ____________________________________ 4. What is a trait?____________________ ...
Remember when we . . Students should be able to
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.