Remember when we . . Students should be able to
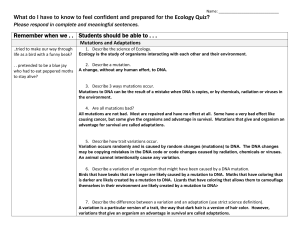
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
... Ecology is the study of organisms interacting with each other and their environment. ...
Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... Intro to Heredity and Probability and Punnett Squares 1. ________________is the study of heredity. 2. Heredity is the passing of _______________ from parents to offspring 3. Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? ____________________________________ 4. What is a trait?____________________ ...
... Intro to Heredity and Probability and Punnett Squares 1. ________________is the study of heredity. 2. Heredity is the passing of _______________ from parents to offspring 3. Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? ____________________________________ 4. What is a trait?____________________ ...
My Genetics, DNA and Evolution Term Summary! [PDF
... of chromosomes in a diploid human cell, the first 22 are called autosomal chromosomes and the 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes (either XX=female or XY=male). DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is one of 2 types of nucleic acid (the other is RNA). DNA consists of 2 strands attached together by molecules ...
... of chromosomes in a diploid human cell, the first 22 are called autosomal chromosomes and the 23rd pair are the sex chromosomes (either XX=female or XY=male). DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is one of 2 types of nucleic acid (the other is RNA). DNA consists of 2 strands attached together by molecules ...
Particle bombardment
... Advantage: there is no need to establish callus or suspension culture first. Explants (embryos) were directly electroporated. ...
... Advantage: there is no need to establish callus or suspension culture first. Explants (embryos) were directly electroporated. ...
federal circuit holds claims to isolated dna and to
... that isolated DNA is patent eligible because it ...
... that isolated DNA is patent eligible because it ...
LESSON 4 Genetics: STUDY GUIDE
... • Describe the events of DNA replication. (pg. 350) • Differentiate DNA replication in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes. (pg. 352) ...
... • Describe the events of DNA replication. (pg. 350) • Differentiate DNA replication in prokaryotes with that of eukaryotes. (pg. 352) ...
Document
... Search for genetic material: James Watson joined the unit (its first biologist) and began by trying to crystallize myoglobin for Kendrew. The unsuccess of this left much time for discussion with Crick, whose office he was sharing, and the topic of DNA structure naturally arose – particularly how to ...
... Search for genetic material: James Watson joined the unit (its first biologist) and began by trying to crystallize myoglobin for Kendrew. The unsuccess of this left much time for discussion with Crick, whose office he was sharing, and the topic of DNA structure naturally arose – particularly how to ...
Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between
... 28. If a solution is hypotonic to the cell, which of the following will happen a. Nothing. The phospholipid membrane stops the solutes from moving. b. The water moves into the cell because it has a greater number of solutes. c. ...
... 28. If a solution is hypotonic to the cell, which of the following will happen a. Nothing. The phospholipid membrane stops the solutes from moving. b. The water moves into the cell because it has a greater number of solutes. c. ...
Karyn Sykes January 24, 2009 LLOG 1: Immortal Genes: Running in
... Why were the impacts of these discoveries in Biology so profound? Tom Brock’s discovery of hyperthermophiles led to three profound discoveries in the field of Biology. The first discovery that was made was a whole new domain of species. The name of the kingdom is called Archaea. This discovery was s ...
... Why were the impacts of these discoveries in Biology so profound? Tom Brock’s discovery of hyperthermophiles led to three profound discoveries in the field of Biology. The first discovery that was made was a whole new domain of species. The name of the kingdom is called Archaea. This discovery was s ...
HW#2 (first draft)
... (ii) Imagine that the double-stranded DNA template for a PCR reaction has two blocks of sequence of 70bp that are identical (a perfect repeat, indicated by the rectangles below), separated by a stretch of normal, unique DNA sequence of about 800bp. You use 25nt long primers complementary to sequence ...
... (ii) Imagine that the double-stranded DNA template for a PCR reaction has two blocks of sequence of 70bp that are identical (a perfect repeat, indicated by the rectangles below), separated by a stretch of normal, unique DNA sequence of about 800bp. You use 25nt long primers complementary to sequence ...
Mock Exam 3 Chapters 14-18 Anthony Todd http
... a. Both old strands are kept together and the two new strands pair up b. One old strand pairs up with one new strand c. Parts of the new and old strands mix together to form the new DNA d. It is destroyed by the cell and two new strands of DNA are destroyed 26. Which of the following is paired incor ...
... a. Both old strands are kept together and the two new strands pair up b. One old strand pairs up with one new strand c. Parts of the new and old strands mix together to form the new DNA d. It is destroyed by the cell and two new strands of DNA are destroyed 26. Which of the following is paired incor ...
2.5.15 Summary - Intermediate School Biology
... A molecule of DNA consists of a double helical structure ...
... A molecule of DNA consists of a double helical structure ...
3687317_mlbio10_Ch13_TestA_3rd.indd
... Use the diagram below to answer the following questions on the lines provided. ...
... Use the diagram below to answer the following questions on the lines provided. ...
Answers to End-of-Chapter Questions – Brooker et al ARIS site
... Recombinant DNA technology: The use of laboratory techniques to isolate and manipulate fragments of DNA. Recombinant DNA: Any DNA molecule that has been manipulated so that it contains DNA from two or more sources. 2. Explain how using one restriction enzyme to cut both a plasmid and a gene of inter ...
... Recombinant DNA technology: The use of laboratory techniques to isolate and manipulate fragments of DNA. Recombinant DNA: Any DNA molecule that has been manipulated so that it contains DNA from two or more sources. 2. Explain how using one restriction enzyme to cut both a plasmid and a gene of inter ...
ABOUT-BREAST-CANCER
... compared to other patients suffering from breast cancer. [5] BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination which involves 1 major pathway of double stranded DNA repair. In comparison to BRCA1, BRCA2 does not have any impact on multiple DNA repair or in other words to nonhomologous end joining. The specifi ...
... compared to other patients suffering from breast cancer. [5] BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination which involves 1 major pathway of double stranded DNA repair. In comparison to BRCA1, BRCA2 does not have any impact on multiple DNA repair or in other words to nonhomologous end joining. The specifi ...
Chapter 9 Genetics Chromosome Genes • DNA RNA Protein Flow of
... F+ and F- - the former are the donor cells and the latter are the recipient cells. The donor cells have an F plasmid – sex pili and DNA Transfer. Conjugation in this case is a transfer of the F plasmid from the donor to the recipient. ...
... F+ and F- - the former are the donor cells and the latter are the recipient cells. The donor cells have an F plasmid – sex pili and DNA Transfer. Conjugation in this case is a transfer of the F plasmid from the donor to the recipient. ...
Biology Lecture 2 – Genes
... o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mRNA/rRNA/tRNA o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes not actively transcribed o Genome: entire DNA sequence of an organism — human: 26k-38k genes, ~1% codes for protei ...
... o Gene: DNA that codes for a single polypeptide/mRNA/rRNA/tRNA o Euchromatin: region of DNA containing genes being actively transcribed o Heterochromatin: region of DNA containing genes not actively transcribed o Genome: entire DNA sequence of an organism — human: 26k-38k genes, ~1% codes for protei ...
The Secret Code of Life: - Richmond School District
... effects if it occurs within a gene as the triplet sequence will be disrupted – ii) Deletion: 1 or 2 bases are deleted to DNA at one place (not in multiples of 3 – why is that?) • These mutations can cause serious effects as well if it occurs within a gene as the triplet sequence is disrupted – Iii) ...
... effects if it occurs within a gene as the triplet sequence will be disrupted – ii) Deletion: 1 or 2 bases are deleted to DNA at one place (not in multiples of 3 – why is that?) • These mutations can cause serious effects as well if it occurs within a gene as the triplet sequence is disrupted – Iii) ...
WWTBAM Review C8 test - Week of 1/12-1/15
... bases on only one strand of the double helix. What would you use to figure out the sequence on the other strand? ...
... bases on only one strand of the double helix. What would you use to figure out the sequence on the other strand? ...
chapter_3_2007
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
... – Determine what activities will occur in a protein. – Enzymes and hormones Carrier proteins – Transport molecules from one place to another. – Lipoproteins ...
Set 2
... cell to split its contents equally between the two new cells. Prior to this division, the parent cell duplicates its DNA and when the split takes place each new cell receives a complete exact copy of the DNA, of the parent. In multi-cellular organisms the process that produces two new cells with the ...
... cell to split its contents equally between the two new cells. Prior to this division, the parent cell duplicates its DNA and when the split takes place each new cell receives a complete exact copy of the DNA, of the parent. In multi-cellular organisms the process that produces two new cells with the ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;12)(p36;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Myeloid disorders: one chronic myelogenous leukemia with t(9;22) and one refractory anemiia with excee of blasts in transformation. ...
... Myeloid disorders: one chronic myelogenous leukemia with t(9;22) and one refractory anemiia with excee of blasts in transformation. ...
6.G Meiosis Graphic Organizer 6.H Genetic Variation
... _____8. John has one recessive allele for blue eyes (b) and one dominant allele for brown eyes (B). Amy also has one recessive allele for blue eyes and one dominant allele for brown eyes. What phenotype is an offspring of John and Amy most likely to express? a. Bb b. BB c. blue eyes d. brown eyes 6. ...
... _____8. John has one recessive allele for blue eyes (b) and one dominant allele for brown eyes (B). Amy also has one recessive allele for blue eyes and one dominant allele for brown eyes. What phenotype is an offspring of John and Amy most likely to express? a. Bb b. BB c. blue eyes d. brown eyes 6. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Studies of genomes have also revealed how genes act together to produce a functioning organism through an unusually complex network of interactions among genes and their products. • To determine which genes are transcribed under different situations, researchers isolate mRNA from particular cells ...
... • Studies of genomes have also revealed how genes act together to produce a functioning organism through an unusually complex network of interactions among genes and their products. • To determine which genes are transcribed under different situations, researchers isolate mRNA from particular cells ...
Nucleic acid double helix

In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its tertiary structure. The term entered popular culture with the publication in 1968 of The Double Helix: A Personal Account of the Discovery of the Structure of DNA, by James Watson.The DNA double helix polymer of nucleic acids, held together by nucleotides which base pair together. In B-DNA, the most common double helical structure, the double helix is right-handed with about 10–10.5 base pairs per turn. This translates into about 20-21 nucleotides per turn. The double helix structure of DNA contains a major groove and minor groove. In B-DNA the major groove is wider than the minor groove. Given the difference in widths of the major groove and minor groove, many proteins which bind to B-DNA do so through the wider major groove.























