AP Chapter Five Outline
... OH-, when dissolved in water C. Electrolytes 1. Strong electrolytes are either ionic compounds (salts or strong bases) or molecular compounds that are strong acids and ionize completely in aqueous solutions. 2. Weak electrolytes are molecular compounds that are weak acids or bases and establish equi ...
... OH-, when dissolved in water C. Electrolytes 1. Strong electrolytes are either ionic compounds (salts or strong bases) or molecular compounds that are strong acids and ionize completely in aqueous solutions. 2. Weak electrolytes are molecular compounds that are weak acids or bases and establish equi ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
Slide 1
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
The challenge is to make an X-ray beam bright enough
... As the name indicates, X-ray crystallography is traditionally all about crystals. Von Laue realized that beams of X-rays bouncing off the regular arrays of atoms in a crystal would interfere with one another to produce a pattern of light and dark spots or bands. This phenomenon is now called Bragg d ...
... As the name indicates, X-ray crystallography is traditionally all about crystals. Von Laue realized that beams of X-rays bouncing off the regular arrays of atoms in a crystal would interfere with one another to produce a pattern of light and dark spots or bands. This phenomenon is now called Bragg d ...
Chemistry Standard Course of Study -- Detailed - UNCG GK-12
... Analyze and interpret data. Explain observations. Make inferences and predictions. Use questions and models to determine the relationships between variables in investigations. Identify how scientists share findings. ...
... Analyze and interpret data. Explain observations. Make inferences and predictions. Use questions and models to determine the relationships between variables in investigations. Identify how scientists share findings. ...
Particle Size Enlargement - Systematic Reviews in Pharmacy
... with solvent mixture, so during agitation of the solvent system, the crystals are formed. The drawback of this system is that it provide low yield because the drug shows significant solubility in the crystallization solvent due to co-solvency effect. This method is not applicable for water-insoluble ...
... with solvent mixture, so during agitation of the solvent system, the crystals are formed. The drawback of this system is that it provide low yield because the drug shows significant solubility in the crystallization solvent due to co-solvency effect. This method is not applicable for water-insoluble ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... Electrolysis y10 What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct ...
... Electrolysis y10 What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct ...
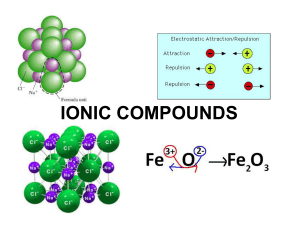
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
... ion is its oxidation number. (sometimes called oxidation state) ...
Atomic Concepts
... 6. Non polar covalent bond- equal sharing of electrons; diatomics (HOFBrINCl’s) 7. Metallic Bonding- “sea of mobile electrons;” metals only 8. Triple bond- three pairs of electrons shared; double bond- two pairs shared 9. Shape and distribution of charge decides molecular polarity ...
... 6. Non polar covalent bond- equal sharing of electrons; diatomics (HOFBrINCl’s) 7. Metallic Bonding- “sea of mobile electrons;” metals only 8. Triple bond- three pairs of electrons shared; double bond- two pairs shared 9. Shape and distribution of charge decides molecular polarity ...
Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
... Note: The hydrogen atom has the atomic number of 1 therefore contains 1 electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 ...
... Note: The hydrogen atom has the atomic number of 1 therefore contains 1 electron. This electron is found in the first orbital and has room to gain 1 more electron if it comes in contact with another atom. This would then completely fill the first orbital. Nitrogen’s atom has the atomic number of 7 ...
Syracuse University
... courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to succ ...
... courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to succ ...
The ocean is a mixture.
... Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
... Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. What makes an element reactive? ...
Classification of
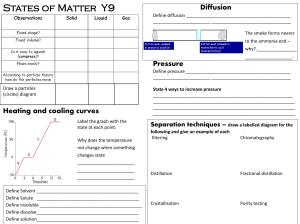
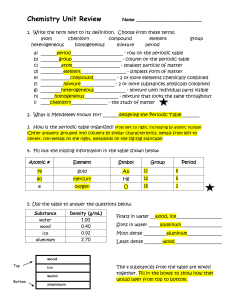
... _______period_______________________ - row on the periodic table ________group______________________ - column on the periodic table _________atom_____________________ - smallest particle of matter __________element____________________ - simplest form of matter _____________compound__________ - 2 or ...
... _______period_______________________ - row on the periodic table ________group______________________ - column on the periodic table _________atom_____________________ - smallest particle of matter __________element____________________ - simplest form of matter _____________compound__________ - 2 or ...
AP Chem -‐ Unit 1 Part 1 AP Chemistry 2016
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
... After completion of unit 1 I will be able to… • Identify an element or determine its purity using mass percent calculations. • Use mole relationships to convert between moles, mass and particles. • ...
GC-Final-Review-2014
... 6. A solution of KCl at 85º C contains 50g of dissolved solute in 100 cm3 water. The solution is allowed to cool. At what new temperature would crystals begin to start forming? 7. How do gases and solids differ in solubility when raising or lowering the temperature of the solution? ...
... 6. A solution of KCl at 85º C contains 50g of dissolved solute in 100 cm3 water. The solution is allowed to cool. At what new temperature would crystals begin to start forming? 7. How do gases and solids differ in solubility when raising or lowering the temperature of the solution? ...
Mineral Introduction
... • A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in orderly, repeating patterns. • A crystal system is a group of crystals that have similar atomic arrangements and therefore similar external crystal shapes. • There are six major crystal systems, which classify minerals according to their crys ...
... • A crystal is a solid in which the atoms are arranged in orderly, repeating patterns. • A crystal system is a group of crystals that have similar atomic arrangements and therefore similar external crystal shapes. • There are six major crystal systems, which classify minerals according to their crys ...
Mineral:
... were once living • “Non Example”: Coal – it is organic because it comes from plants that lived millions of years ago. ...
... were once living • “Non Example”: Coal – it is organic because it comes from plants that lived millions of years ago. ...
Topic/Objective: Full Name: Class: Period: _____ Date: Tutor Use
... An element is matter that is made up of the atoms that have the same number of _protons _ in their nucleus. But not all atoms of the same element are the same. Some elements have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, these are called ___isotopes__. Most su ...
... An element is matter that is made up of the atoms that have the same number of _protons _ in their nucleus. But not all atoms of the same element are the same. Some elements have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in the nucleus, these are called ___isotopes__. Most su ...
9.1-10.5 Organic Chemistry
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
... Number the parent chain carbon atoms, starting from the end closest to the branch(es) so that the numbers are the lowest possible Identify any branches and their location number on the parent chain (us the suffix –yl for branches) If more than one of the same branch exist, use a multiplier (di, tri) ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... G. Covalent-Network Compounds 1. Some covalent molecules do not exist of individual molecules. They instead are part of a 3 dimensional network. 2. When this occurs the lowest ratio is given and then named just as binary covalent compounds are. H. Acids and Salts 1. An acid is a distinct type of com ...
... G. Covalent-Network Compounds 1. Some covalent molecules do not exist of individual molecules. They instead are part of a 3 dimensional network. 2. When this occurs the lowest ratio is given and then named just as binary covalent compounds are. H. Acids and Salts 1. An acid is a distinct type of com ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures.
... • Pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. – Pure substance- a substance in which there is only one type of particle (atom or molecule) ...
... • Pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. – Pure substance- a substance in which there is only one type of particle (atom or molecule) ...
semester two review sheet
... 1. Define the following terms: polarity, surface tension, vapor pressure, specific heat, and capillary action. 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. ...
... 1. Define the following terms: polarity, surface tension, vapor pressure, specific heat, and capillary action. 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. ...
Chemical Reactions
... the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
... the chemical reaction • Law of conservation of mass (or matter)- mass is neither created or destroyed in ordinary chemical or physical changes • Subscript - number (representing atoms) written below and to the right of a chemical symbol ...
Summer Assignment Ch. 2-5
... This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you do review on your own, the questions that follow should help you focus on the most important points. Concept 2.1 Matter consists of chemical elements i ...
... This chapter covers the basics that you may have learned in your chemistry class. Whether your teacher goes over this chapter, or assigns it for you do review on your own, the questions that follow should help you focus on the most important points. Concept 2.1 Matter consists of chemical elements i ...
Matter and Measurement Ppt.
... (Homo: Same) Solution • A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. Many homogeneous mixtures are commonly referred to as solutions. • All components are all in the same phase. • Particles are uniform in size (atoms or molecules) • Can not be separated by physic ...
... (Homo: Same) Solution • A homogeneous mixture has the same uniform appearance and composition throughout. Many homogeneous mixtures are commonly referred to as solutions. • All components are all in the same phase. • Particles are uniform in size (atoms or molecules) • Can not be separated by physic ...