SECTION 1 PRODUCT AND COMPANY INFORMATION Terbium (III
... SARA 313 COMPONENTS: This material does not contain any chemical components with know CAS numbers that exceed the threshold (De Minimis) reporting levels established by SARA Title III, Section 313. SARA 302 COMPONENTS: No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA T ...
... SARA 313 COMPONENTS: This material does not contain any chemical components with know CAS numbers that exceed the threshold (De Minimis) reporting levels established by SARA Title III, Section 313. SARA 302 COMPONENTS: No chemicals in this material are subject to the reporting requirements of SARA T ...
Precipitate Lab Report Power Point with Answers
... If the results of putting 2 aqueous solutions together results in the formation of 2 new aqueous solutions, without a precipitate forming, no reaction really occurred. Rather you just mixed the two solutions together, making a homogenous mixture (the same throughout, mixed with no new properties). W ...
... If the results of putting 2 aqueous solutions together results in the formation of 2 new aqueous solutions, without a precipitate forming, no reaction really occurred. Rather you just mixed the two solutions together, making a homogenous mixture (the same throughout, mixed with no new properties). W ...
Utah - Wavefunction, Inc.
... matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, the total amount of energy and matter in it remains constant. Many reactions attain a state of equilibrium. Many ordinary activities, such as baking, involve chemical re ...
... matter how they are rearranged; the total mass stays the same. Although energy can be absorbed or released in a chemical reaction, the total amount of energy and matter in it remains constant. Many reactions attain a state of equilibrium. Many ordinary activities, such as baking, involve chemical re ...
File
... These reactions involve the formation of a small molecule (such as H2O, NH3, or HCl) The small molecule is said to be “condensed out” of the reaction. The monomer molecules bond at the site where atoms are removed from their functional groups. To form a condensation polymer, the monomer molecules mu ...
... These reactions involve the formation of a small molecule (such as H2O, NH3, or HCl) The small molecule is said to be “condensed out” of the reaction. The monomer molecules bond at the site where atoms are removed from their functional groups. To form a condensation polymer, the monomer molecules mu ...
I. Crystal nucleation and growth
... II. Textures and relations related to crystallization order As we discussed previously, crystals form in a specific sequence that depends on the magma initial composition. Crystal growing in the melt develop their own crystalline shapes (euhedral), whereas crystals developing at a latter stage are l ...
... II. Textures and relations related to crystallization order As we discussed previously, crystals form in a specific sequence that depends on the magma initial composition. Crystal growing in the melt develop their own crystalline shapes (euhedral), whereas crystals developing at a latter stage are l ...
Scientific Principles: Chemical Properties
... • Are held together by the strong attraction of the positive and negative charges of the ions • Are neutral compounds • Are formed between metals and ...
... • Are held together by the strong attraction of the positive and negative charges of the ions • Are neutral compounds • Are formed between metals and ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... 1. Complete this test review and then study! 2. Text book pages that relate to this material: Unit 3 – p. 109 – 135 and 139 – 168 (the second half of the unit focuses on the second half of Unit 3 in the textbook) 3. Notes are always posted on the website – look in Unit 2.2 4. Remember, the “Unit Enr ...
... 1. Complete this test review and then study! 2. Text book pages that relate to this material: Unit 3 – p. 109 – 135 and 139 – 168 (the second half of the unit focuses on the second half of Unit 3 in the textbook) 3. Notes are always posted on the website – look in Unit 2.2 4. Remember, the “Unit Enr ...
Lecture 25 – The Solid State: types of crystals, lattice energies and
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
... It should be realized that the value of any ionic radius only serves as a useful but approximate size of the ion.. The fact that the ionic radius of Na+ is 0.98Å does not mean that the electron cloud of the ion never extends beyond this value. It is significant because when it is added together with ...
Chemistry
... Relative high density Relative incompressibility Dissolving ability Ability to diffuse Tendency to evaporate and boil Tendency to solidify ...
... Relative high density Relative incompressibility Dissolving ability Ability to diffuse Tendency to evaporate and boil Tendency to solidify ...
Structural properties - Département de Physique
... In this lecture, we aim at providing a conceptual basis to understand modern experimental techniques used to investigate the structural, electronic and magnetic properties of condensed matter: scattering experiments (X-rays, neutrons, electrons), spectroscopic techniques (XAFS, ARPES, NMR), magnetom ...
... In this lecture, we aim at providing a conceptual basis to understand modern experimental techniques used to investigate the structural, electronic and magnetic properties of condensed matter: scattering experiments (X-rays, neutrons, electrons), spectroscopic techniques (XAFS, ARPES, NMR), magnetom ...
Chapter 1: Quiz Review - Wetaskiwin Composite High School
... 12. Why are most pure molecular substance non-conductors of electricity? A. They are made of ions C. They are made of neutral molecules B. They are made of uncharged neutrons D. Their positive and negative molecules cancel out 13. What does the low melting point of a molecular compound suggest about ...
... 12. Why are most pure molecular substance non-conductors of electricity? A. They are made of ions C. They are made of neutral molecules B. They are made of uncharged neutrons D. Their positive and negative molecules cancel out 13. What does the low melting point of a molecular compound suggest about ...
High School Chemistry Essential Questions
... 2. What observations about chemical systems and chemical interactions lead us to form the physical, graphical, and mathematical models that we use to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? 3. How do we use the physical models, s ...
... 2. What observations about chemical systems and chemical interactions lead us to form the physical, graphical, and mathematical models that we use to represent, analyze, and communicate structure and relationships in chemical systems and chemical interactions? 3. How do we use the physical models, s ...
Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Solids 21 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
... the type of chemical bond. To a certain degree, the crystalline structure provides an indication of the type of binding; however, AgCl and NaCl oder CaCl2 and MgF2 have the same structure but different melting entropies ...
... the type of chemical bond. To a certain degree, the crystalline structure provides an indication of the type of binding; however, AgCl and NaCl oder CaCl2 and MgF2 have the same structure but different melting entropies ...
Unit 2.2 Test Review Key
... Know how read a chemical formula – what do the subscripts and coefficients mean? How can you tell which elements are present. Know the Law of Conservation of Mass and how it is applied to chemical reactions Know what makes a compound organic or not Know the difference between physical and chemical p ...
... Know how read a chemical formula – what do the subscripts and coefficients mean? How can you tell which elements are present. Know the Law of Conservation of Mass and how it is applied to chemical reactions Know what makes a compound organic or not Know the difference between physical and chemical p ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE abbr
... Elements with similar properties were placed in the same group. Left blank spots where possible undiscovered elements would logically fit based on mass, physical and chemical properties. ...
... Elements with similar properties were placed in the same group. Left blank spots where possible undiscovered elements would logically fit based on mass, physical and chemical properties. ...
Chemistry - School District of Springfield Township
... the lower the energy level, the closer to the nucleus the level is located. o Electrons absorb energy and move to a higher energy level or they give off energy (in the form of photons of light) and move to a lower energy level. o This is the basis for the electromagnetic spectrum and the Quantum The ...
... the lower the energy level, the closer to the nucleus the level is located. o Electrons absorb energy and move to a higher energy level or they give off energy (in the form of photons of light) and move to a lower energy level. o This is the basis for the electromagnetic spectrum and the Quantum The ...
Rocks and Minerals
... Mineral: naturally occurring solid formed by inorganic process, has crystal structure, definite chemical composition Crystal: repeating pattern of mineral’s particles forming a solid Inorganic: form from materials that were not living Luster: describes how light reflected from mineral surface Streak ...
... Mineral: naturally occurring solid formed by inorganic process, has crystal structure, definite chemical composition Crystal: repeating pattern of mineral’s particles forming a solid Inorganic: form from materials that were not living Luster: describes how light reflected from mineral surface Streak ...
2/22 Lecture Slides
... AP2 – Due March 1st (next Wednesday) Next quiz will be from Homework Set 2 (after Exam 1) Lab reports (glassware resubmission – due 2/27; Cl lab report – due 3/8) ...
... AP2 – Due March 1st (next Wednesday) Next quiz will be from Homework Set 2 (after Exam 1) Lab reports (glassware resubmission – due 2/27; Cl lab report – due 3/8) ...
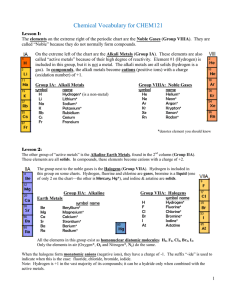
Vocabulary CHEM121
... Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not have a charge like polyatomic ions, but are neutra ...
... Bases: anything giving OH- when dissolved in water Salts: all other ionic materials Formulas of molecular/covalent compounds: Non-metals can combine with other non-metals to form molecules. Molecules are covalently bonded groups of atoms—they do not have a charge like polyatomic ions, but are neutra ...
Flexbook - What is Matter?
... This website provides a review about matter and the categories of matter. • http://www.thetech.org/exhibits/online/topics/50a.html ...
... This website provides a review about matter and the categories of matter. • http://www.thetech.org/exhibits/online/topics/50a.html ...
chemical bonds - geraldinescience
... • The forces that hold together the atoms in molecules are called chemical bonds. • Chemical bonds form because of the attraction between positive and negative charges. • Atoms form chemical bonds by either sharing or transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Scientists can study interactio ...
... • The forces that hold together the atoms in molecules are called chemical bonds. • Chemical bonds form because of the attraction between positive and negative charges. • Atoms form chemical bonds by either sharing or transferring electrons from one atom to another. • Scientists can study interactio ...