Fluid compartments of the embryonic environment
... the exocoelomic cavity during the first trimester (Figure 5). This can be explained by the slow turnover of the coelomic fluid and/or the increased production of these proteins by fetal organs. In contrast, there is a physiological decrease in total maternal serum protein which occurs mainly during ...
... the exocoelomic cavity during the first trimester (Figure 5). This can be explained by the slow turnover of the coelomic fluid and/or the increased production of these proteins by fetal organs. In contrast, there is a physiological decrease in total maternal serum protein which occurs mainly during ...
Chapter 7 Structural Organisation in Animals Question
... Answer: When two or more organs perform a common function by their physical and/or chemical interaction they together form organ system. 3. Which tissue provide a covering or lining for some part of the body? Answer: Epithelial tissue. 4. What is simple epithelium? Answer: It is the epithelium which ...
... Answer: When two or more organs perform a common function by their physical and/or chemical interaction they together form organ system. 3. Which tissue provide a covering or lining for some part of the body? Answer: Epithelial tissue. 4. What is simple epithelium? Answer: It is the epithelium which ...
Organs - Allium-textile
... the more message it transmits through the neurons. The main purpose of the axon is to send impulses away from the cell body to neuron dendrite or other body cells called effecter cells-sound. A nerve impulse travels from a dendrite, to the cell body, and down the axon to thousands of branches called ...
... the more message it transmits through the neurons. The main purpose of the axon is to send impulses away from the cell body to neuron dendrite or other body cells called effecter cells-sound. A nerve impulse travels from a dendrite, to the cell body, and down the axon to thousands of branches called ...
DEVELOPMENT of the URINARY SYSTEM
... In week 5 the thoracic segments regress but the mesonephric kidney continues functioning until week 10 ...
... In week 5 the thoracic segments regress but the mesonephric kidney continues functioning until week 10 ...
Type of joint
... various planes and direction so the activities involved in ingestion, mastication and speech can be executed. Type of joint TMJ is a synovial joint, this joint permits significant movement and forms between glenoid fossa, articular eminence (parts of temporal bone) and condyle process (part of mandi ...
... various planes and direction so the activities involved in ingestion, mastication and speech can be executed. Type of joint TMJ is a synovial joint, this joint permits significant movement and forms between glenoid fossa, articular eminence (parts of temporal bone) and condyle process (part of mandi ...
Answers to Even Questions
... neurotransmitters (or neuromodulators): (i) they must be synthesized by presynaptic neurons; (ii) they have to reside within the synaptic terminals (enclosed in synaptic vesicles); (iii) they have to be released from the presynaptic terminals by way of a calcium-dependent mechanism; (iv) they have t ...
... neurotransmitters (or neuromodulators): (i) they must be synthesized by presynaptic neurons; (ii) they have to reside within the synaptic terminals (enclosed in synaptic vesicles); (iii) they have to be released from the presynaptic terminals by way of a calcium-dependent mechanism; (iv) they have t ...
Part III
... 2. What kind of cells did the first vascular plants have that were specialized to conduct water? 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about tracheids. a. They are hollow cells. b. They are connected end to end. c. Their thick cell walls resist pressure. d. They are the key cells of phl ...
... 2. What kind of cells did the first vascular plants have that were specialized to conduct water? 3. Circle the letter of each sentence that is true about tracheids. a. They are hollow cells. b. They are connected end to end. c. Their thick cell walls resist pressure. d. They are the key cells of phl ...
body_system_relationships_chart
... Circulatory System- Brings oxygen, hormones and nutrients to cells; fights infection; removes cell waste; helps regulate body temperature ...
... Circulatory System- Brings oxygen, hormones and nutrients to cells; fights infection; removes cell waste; helps regulate body temperature ...
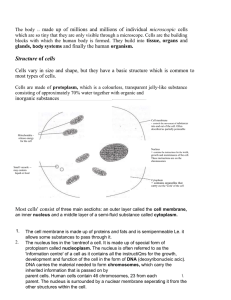
GCSE Biology Textbook sample
... • Cells differentiate to become specialised, and specialised cells are organised. • When cell division accelerates out of control, cancer develops. • Cells that are unspecialised in the embryo, and cells that remain unspecialised in us as adults, are called stem cells. • Stem cells could be us ...
... • Cells differentiate to become specialised, and specialised cells are organised. • When cell division accelerates out of control, cancer develops. • Cells that are unspecialised in the embryo, and cells that remain unspecialised in us as adults, are called stem cells. • Stem cells could be us ...
Microsoft Word 97 - 2003 Document
... Many chemical actions require higher temperatures to initiate them. Inside plant or animal bodies these higher temperatures are not possible. Instead, proteinbased enzymes are able to join or split molecules. The enzymes assume the role of catalysts in that they initiate and control rates of rea ...
... Many chemical actions require higher temperatures to initiate them. Inside plant or animal bodies these higher temperatures are not possible. Instead, proteinbased enzymes are able to join or split molecules. The enzymes assume the role of catalysts in that they initiate and control rates of rea ...
OCR Document
... . When the muscle is stimulated to contract, A TP is converted to another chemical compound, ADP (adenosine diphosphate), which releases the energy needed to be used during the phase of muscle contraction . During the oxidation of glycogen, a substance called pyruvic acid is formed . If plenty of ox ...
... . When the muscle is stimulated to contract, A TP is converted to another chemical compound, ADP (adenosine diphosphate), which releases the energy needed to be used during the phase of muscle contraction . During the oxidation of glycogen, a substance called pyruvic acid is formed . If plenty of ox ...
Study Material - Class- XI - Biology
... -Sporophyte forms spores which germinate to form protonema. eg. Funaria, Polytrichum etc. ...
... -Sporophyte forms spores which germinate to form protonema. eg. Funaria, Polytrichum etc. ...
Study Material - Class- XI- Biology
... -Sporophyte forms spores which germinate to form protonema. eg. Funaria, Polytrichum etc. ...
... -Sporophyte forms spores which germinate to form protonema. eg. Funaria, Polytrichum etc. ...
EXAMPLE Histology Compendium
... collagen fibers. This structural pattern provides support to areas subjected to stresses from many directions. As you grasp objects in your hand or pivot your The dermis of the skin is dense irregular connective tissue and is what foot, forces are placed across the skin from any of a number of direc ...
... collagen fibers. This structural pattern provides support to areas subjected to stresses from many directions. As you grasp objects in your hand or pivot your The dermis of the skin is dense irregular connective tissue and is what foot, forces are placed across the skin from any of a number of direc ...
Cnidarians - cloudfront.net
... Cnidarian Characteristics • Either polyp (tubular) or medusa (bell shaped) • Tentacles surround mouth • Only animal with cnidocytes (stinging cells) found in the tentacles • Nematocyst – coiled, harpoon-like stinger inside cnidocyte that shoots out ...
... Cnidarian Characteristics • Either polyp (tubular) or medusa (bell shaped) • Tentacles surround mouth • Only animal with cnidocytes (stinging cells) found in the tentacles • Nematocyst – coiled, harpoon-like stinger inside cnidocyte that shoots out ...
anatomy_lec16_12_4_2011 - Post-it
... Nose -Has pear-shaped cavity divided into two cavities by nesal septum . -held open by framework of bone & cartilage . -Nasal cavity extends between external -Nostril- opnining outside and internal -choana-opening into nasopharynx. ...
... Nose -Has pear-shaped cavity divided into two cavities by nesal septum . -held open by framework of bone & cartilage . -Nasal cavity extends between external -Nostril- opnining outside and internal -choana-opening into nasopharynx. ...
Accessory Organs of the Small Intestine
... sinusoid system for the secretion of substances into the blood. This association with the sinusoids also allows for the recovery of nutrients arriving from the digestive tract through the hepatic portal system. The hepatocytes store these nutrients and will release them into the blood as needed. Ex; ...
... sinusoid system for the secretion of substances into the blood. This association with the sinusoids also allows for the recovery of nutrients arriving from the digestive tract through the hepatic portal system. The hepatocytes store these nutrients and will release them into the blood as needed. Ex; ...
Sponges are sessile, feed by phagocytosis, and reproduce sexually
... However, sponge cells are capable of creeping along substrata via organizational plasticity. Under experimental conditions, researchers have shown that sponge cells spread on a physical support demonstrate a leading edge for directed movement. It has been speculated that this localized creeping move ...
... However, sponge cells are capable of creeping along substrata via organizational plasticity. Under experimental conditions, researchers have shown that sponge cells spread on a physical support demonstrate a leading edge for directed movement. It has been speculated that this localized creeping move ...
2. Parkinsons diseas and Movement Disorders. 1998
... Cerebrospinal Fluid System Choroid Plexus Lateral Ventricle The choroid plexus consists of convoluted vascular villi which invaginate from certain parts of the ventricular wall and protrude into the cavity of the ventricle. The part of the wall (lamina choroidea) A1 which lies on the medial surface ...
... Cerebrospinal Fluid System Choroid Plexus Lateral Ventricle The choroid plexus consists of convoluted vascular villi which invaginate from certain parts of the ventricular wall and protrude into the cavity of the ventricle. The part of the wall (lamina choroidea) A1 which lies on the medial surface ...
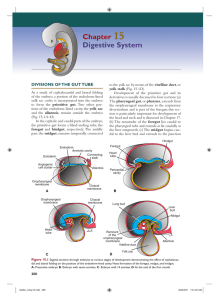
Chapter 15 Digestive System
... extends from the lower end of the esophagus to the cloacal region of the hindgut. In the region of the stomach, it forms the dorsal mesogastrium or greater omentum; in the region of the duodenum, it forms the dorsal mesoduodenum; and in the region of the colon, it forms the dorsal mesocolon. Dorsal ...
... extends from the lower end of the esophagus to the cloacal region of the hindgut. In the region of the stomach, it forms the dorsal mesogastrium or greater omentum; in the region of the duodenum, it forms the dorsal mesoduodenum; and in the region of the colon, it forms the dorsal mesocolon. Dorsal ...
the lymphatic system
... Lymphatic tissue contains many types of cells, the principal one being the lymphocyte. This white blood cell is made in the bone marrow. Once released into the bloodstream from the bone marrow, lymphocytes are further processed to make two functionally distinct types: the T-lymphocyte and the B-lymp ...
... Lymphatic tissue contains many types of cells, the principal one being the lymphocyte. This white blood cell is made in the bone marrow. Once released into the bloodstream from the bone marrow, lymphocytes are further processed to make two functionally distinct types: the T-lymphocyte and the B-lymp ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.