Ch. 5 ppt - USD305.com
... collagen, add strength for holding body parts together. Elastic fibers (yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues. Reticular fibers are thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues. ...
... collagen, add strength for holding body parts together. Elastic fibers (yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues. Reticular fibers are thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues. ...
الشريحة 1
... Both REF & globulin unite in plasma and form EP. EP then stimulates bone marrow to produce RBCs. Erythropoietin accelerates nearly all stages of RBCs formation, i.e. it stimulates proliferation & differentiation of progenitor stem cells to produce mature RBCs. ...
... Both REF & globulin unite in plasma and form EP. EP then stimulates bone marrow to produce RBCs. Erythropoietin accelerates nearly all stages of RBCs formation, i.e. it stimulates proliferation & differentiation of progenitor stem cells to produce mature RBCs. ...
Ch. 5 ppt
... collagen, add strength for holding body parts together. Elastic fibers (yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues. Reticular fibers are thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues. ...
... collagen, add strength for holding body parts together. Elastic fibers (yellow fibers), made of the protein elastin, are stretchy and add flexibility to certain types of connective tissues. Reticular fibers are thin collagenous fibers that form supportive networks in a variety of tissues. ...
Photosynthesis
... Classified according to type of collagen and elastic fibers found in the matrix Cartilage cells (chondrocytes), lie in small chambers (lacunae) in the matrix ...
... Classified according to type of collagen and elastic fibers found in the matrix Cartilage cells (chondrocytes), lie in small chambers (lacunae) in the matrix ...
- bYTEBoss
... • In most vertebrates, a more complex, jointed skeleton develops – And the adult retains only remnants of the embryonic notochord which are the fluid filled cartilaginous discs between the centra of the vertebrae ...
... • In most vertebrates, a more complex, jointed skeleton develops – And the adult retains only remnants of the embryonic notochord which are the fluid filled cartilaginous discs between the centra of the vertebrae ...
Biology IGCSE FALL 2011_2012 - Biology
... vasoconstriction of arterioles supplying skin surface capillaries and the coordinating role of the brain Define drug as any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body Describe the medicinal use of antibiotics for the treatment of ...
... vasoconstriction of arterioles supplying skin surface capillaries and the coordinating role of the brain Define drug as any substance taken into the body that modifies or affects chemical reactions in the body Describe the medicinal use of antibiotics for the treatment of ...
Ch20 - CESA 10 Moodle
... By the eighth week, the trophoblast is now the chorion, a portion of which develops into the placenta. During this time, another membrane, the amnion, is developing around the embryo and will hold cushioning amniotic fluid. An umbilical cord containing two umbilical arteries and one vein forms. ...
... By the eighth week, the trophoblast is now the chorion, a portion of which develops into the placenta. During this time, another membrane, the amnion, is developing around the embryo and will hold cushioning amniotic fluid. An umbilical cord containing two umbilical arteries and one vein forms. ...
Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... By the eighth week, the trophoblast is now the chorion, a portion of which develops into the placenta. During this time, another membrane, the amnion, is developing around the embryo and will hold cushioning amniotic fluid. An umbilical cord containing two umbilical arteries and one vein forms. ...
... By the eighth week, the trophoblast is now the chorion, a portion of which develops into the placenta. During this time, another membrane, the amnion, is developing around the embryo and will hold cushioning amniotic fluid. An umbilical cord containing two umbilical arteries and one vein forms. ...
Blog resource: http://tinyurl
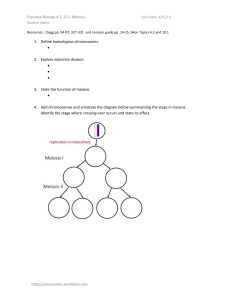
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
... 14. A diploid cell carries genes A and B. There are dominant and recessive alleles for these genes. The cell is heterozygous for both genes. a. What combination of gametes could be produced if there was no crossing over? AB or ____ ...
Ovaries and fallopian tube
... INFUNDIBULUM with its abdominal ostium, surrounded by fimbriæ, one of which, the OVARIAN FIMBRIA is attached to the ovary The tubal ostium is the point where the tubal canal meets the peritoneal cavity Uterine opening of the Fallopian tube is the entrance into the uterine cavity, the utero-tubal jun ...
... INFUNDIBULUM with its abdominal ostium, surrounded by fimbriæ, one of which, the OVARIAN FIMBRIA is attached to the ovary The tubal ostium is the point where the tubal canal meets the peritoneal cavity Uterine opening of the Fallopian tube is the entrance into the uterine cavity, the utero-tubal jun ...
GROSS ANATOMY Ovaries and fallopian tube
... INFUNDIBULUM with its abdominal ostium, surrounded by fimbriæ, one of which, the OVARIAN FIMBRIA is attached to the ovary The tubal ostium is the point where the tubal canal meets the peritoneal cavity Uterine opening of the Fallopian tube is the entrance into the uterine cavity, the utero-tubal jun ...
... INFUNDIBULUM with its abdominal ostium, surrounded by fimbriæ, one of which, the OVARIAN FIMBRIA is attached to the ovary The tubal ostium is the point where the tubal canal meets the peritoneal cavity Uterine opening of the Fallopian tube is the entrance into the uterine cavity, the utero-tubal jun ...
Nervous System PPT D
... • Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube—connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx – Equalizes pressure in the middle ear cavity with the external air pressure ...
... • Pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube—connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx – Equalizes pressure in the middle ear cavity with the external air pressure ...
TSM53 - The External, Middle, and Inner Ear
... The cochlea is a stacked bony spiral with two to three ‘levels’ containing the organs of hearing o The central bony column of the cochlea is called the modiolus o The cochlear nerve (branch of CNVIII) ascends the core of the modiolus o A bony shelf, the spiral lamina, projects laterally from the mod ...
... The cochlea is a stacked bony spiral with two to three ‘levels’ containing the organs of hearing o The central bony column of the cochlea is called the modiolus o The cochlear nerve (branch of CNVIII) ascends the core of the modiolus o A bony shelf, the spiral lamina, projects laterally from the mod ...
The uterus
... The mesonephric duct consist of large ovoid organ on each sides with the developing gonads on the medial side of its lower portion. Assuming that is female development, the two-paramesonephric duct extend caudally into urogenital sinus and develop to form the female genital organ while the wolfian d ...
... The mesonephric duct consist of large ovoid organ on each sides with the developing gonads on the medial side of its lower portion. Assuming that is female development, the two-paramesonephric duct extend caudally into urogenital sinus and develop to form the female genital organ while the wolfian d ...
Wk 12 Lec 2 notes Resp 1 2015
... The larynx A cartilaginous structure that surrounds the glottis, which is a narrow opening Cartilages of the Larynx ...
... The larynx A cartilaginous structure that surrounds the glottis, which is a narrow opening Cartilages of the Larynx ...
ANIMAL TISSUES
... Cells group together in the body to form tissues. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning. There are only four types of tissues that are dispers ...
... Cells group together in the body to form tissues. A tissue is an ensemble of cells, not necessarily identical, but from the same origin, that together carry out a specific function. These are called tissues because of their identical functioning. There are only four types of tissues that are dispers ...
Expression of axial and sonic hedgehog in wildtype and midline
... the pathways controlling the development of the notochord and Iloor plate. Previous reports of the expression patterns of ax I (zebrafish HNF-3f3, Strahle el al., 1993) and shh (Krauss el al., 1993) along the developing midline of gastrula and neurula stage zebrafish embryos are consistent with such ...
... the pathways controlling the development of the notochord and Iloor plate. Previous reports of the expression patterns of ax I (zebrafish HNF-3f3, Strahle el al., 1993) and shh (Krauss el al., 1993) along the developing midline of gastrula and neurula stage zebrafish embryos are consistent with such ...
Biology 6 – Test 3 Study Guide
... 2. They have thick layers of smooth muscle and lack valves. They can vasodilate and constrict. 3. They experience high blood pressure. ii. Veins and venules 1. Carry blood toward the heart. 2. They have thin layers of smooth muscle and have valves to prevent backflow Fig. 13.23). 3. They experience ...
... 2. They have thick layers of smooth muscle and lack valves. They can vasodilate and constrict. 3. They experience high blood pressure. ii. Veins and venules 1. Carry blood toward the heart. 2. They have thin layers of smooth muscle and have valves to prevent backflow Fig. 13.23). 3. They experience ...
Scaling up Delivery Guide
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
... understand the electrical and ‘mechanical’ activity of the heart. With the increasing size of the population, the need for food production is vital. Food production depends greatly on the environmental conditions the water levels and nutrient ability. The transport systems in plants are important fo ...
It was therefore considered desirable to trace its origin and fate. The
... nature. A critical examination reveals that not the entire fused margin of the placenta forms the meristematic strip. It is formed in the middle (PI. X , fig. 14). Each carpel is an inrolled leaf so that the tips are free to bear the ovules. True, it is that it is the fused product of the adjacent c ...
... nature. A critical examination reveals that not the entire fused margin of the placenta forms the meristematic strip. It is formed in the middle (PI. X , fig. 14). Each carpel is an inrolled leaf so that the tips are free to bear the ovules. True, it is that it is the fused product of the adjacent c ...
Page 1 of 61 EOC Practice Subject: Science, Grade: HS, Year
... Water hyacinth ( Eichornia crassipes ) is an example of a plant species that was introduced into this country without any natural enemies. Its typical habitats are bogs, marshes, and around lakes. What is the most likely impact of this plant on marsh ecosystems? It crowds out native plants. It provi ...
... Water hyacinth ( Eichornia crassipes ) is an example of a plant species that was introduced into this country without any natural enemies. Its typical habitats are bogs, marshes, and around lakes. What is the most likely impact of this plant on marsh ecosystems? It crowds out native plants. It provi ...
Palpebrae (Eyelids)
... The wall is composed of three tunics – fibrous, vascular, and sensory The internal cavity is filled with fluids called humors The lens separates the internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments ...
... The wall is composed of three tunics – fibrous, vascular, and sensory The internal cavity is filled with fluids called humors The lens separates the internal cavity into anterior and posterior segments ...
Urogenital System
... collecting tubule induces clusters of mesenchymal cells in the metanephrogenic blastema to form small metanephric vesicles ...
... collecting tubule induces clusters of mesenchymal cells in the metanephrogenic blastema to form small metanephric vesicles ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.