Section 2
... • In animals, fertilization is the union of haploid female and male gametes to form a single diploid zygote. Gametes • In most animals, the sperm cell is specialized for movement. • The egg is typically large, with a store of cytoplasm and yolk. Fertilization • The sperm’s cell membrane fuses with t ...
... • In animals, fertilization is the union of haploid female and male gametes to form a single diploid zygote. Gametes • In most animals, the sperm cell is specialized for movement. • The egg is typically large, with a store of cytoplasm and yolk. Fertilization • The sperm’s cell membrane fuses with t ...
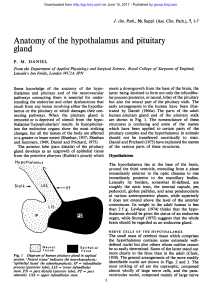
Anatomy of the hypothalamus and pituitary
... 1966). Much remains to be learned from careful shown diagrammatically in Fig. 1. The epithelial cells morphological studies of the human hypothalamus, forming the anterior lobe of the gland, or pars especially from brains in which lesions have occurred distalis, secrete their hormones directly into ...
... 1966). Much remains to be learned from careful shown diagrammatically in Fig. 1. The epithelial cells morphological studies of the human hypothalamus, forming the anterior lobe of the gland, or pars especially from brains in which lesions have occurred distalis, secrete their hormones directly into ...
22-Nasal Cavity
... endings sensitive to the reception of smell The lower part of the nasal cavity is lined with respiratory mucous membrane A large plexus of veins in the submucous connective tissue is present in the respiratory region ...
... endings sensitive to the reception of smell The lower part of the nasal cavity is lined with respiratory mucous membrane A large plexus of veins in the submucous connective tissue is present in the respiratory region ...
Invertebrates
... Arthropods and mollusks for example have an open circulatory system. In this type of system, there is neither a true heart or capillaries as are found in humans. Instead of a heart there are blood vessels that act as pumps to force the blood along. The closed circulatory system of a few mollusks and ...
... Arthropods and mollusks for example have an open circulatory system. In this type of system, there is neither a true heart or capillaries as are found in humans. Instead of a heart there are blood vessels that act as pumps to force the blood along. The closed circulatory system of a few mollusks and ...
body. This system
... gametes, are made by the male and female reproductive systems. • Male gametes are called sperm. • Female gametes are called ova, or eggs. • A sperm joins with an egg in a reproductive process called fertilization. ...
... gametes, are made by the male and female reproductive systems. • Male gametes are called sperm. • Female gametes are called ova, or eggs. • A sperm joins with an egg in a reproductive process called fertilization. ...
2-Development of cerebrum & cerebellum.Final
... Describe briefly the development of the cerebrum. Describe briefly the development of the ...
... Describe briefly the development of the cerebrum. Describe briefly the development of the ...
Respiratory
... 1. Pulmonary ventilation – moving air into and out of the lungs 2. External respiration – gas exchange between the lungs and the blood 3. Transportation – transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues 4. Internal respiration – gas exchange between systemic blood vessels and ti ...
... 1. Pulmonary ventilation – moving air into and out of the lungs 2. External respiration – gas exchange between the lungs and the blood 3. Transportation – transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lungs and tissues 4. Internal respiration – gas exchange between systemic blood vessels and ti ...
Chapter 6 Stems I. External forms of a Woody Twig
... A. Attachments of leaves to a twig 1. Alternate (one leaf) 2. Opposite (two leaves) 3. Whorled (3 or more leaves) B. Special Regions on Twigs 1. Nodes: area of stem where a leaf or leaves is (are) attached 2. Internodes: region of stem between nodes 3. Axils: angle between a petiole and the stem ...
... A. Attachments of leaves to a twig 1. Alternate (one leaf) 2. Opposite (two leaves) 3. Whorled (3 or more leaves) B. Special Regions on Twigs 1. Nodes: area of stem where a leaf or leaves is (are) attached 2. Internodes: region of stem between nodes 3. Axils: angle between a petiole and the stem ...
Homeostasis and feedback loops
... A feedback loop is a cycle of events by which a variable is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitered and revaluated to ensure it is kept within narrow limits. What are the three basic components of a feedback loop? The basic components of a feedback loop include (1) A receptor which de ...
... A feedback loop is a cycle of events by which a variable is continually monitored, evaluated, changed, remonitered and revaluated to ensure it is kept within narrow limits. What are the three basic components of a feedback loop? The basic components of a feedback loop include (1) A receptor which de ...
Connective Tissue
... • Tissue repair involves two major processes: • Regeneration: replace damaged tissue with the same type of tissue • Fibrosis: production of fibrous connective tissue called scar tissue • Which process occurs depends on the location and severity of the tissue damage Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education ...
... • Tissue repair involves two major processes: • Regeneration: replace damaged tissue with the same type of tissue • Fibrosis: production of fibrous connective tissue called scar tissue • Which process occurs depends on the location and severity of the tissue damage Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education ...
1 ANATOMY RS#9 August 14, 2008 JR Churchill, Ph.D. 9:00
... The proteoglycan family of proteins is large and varied in structure and function. Grouping them together is similar to grouping all phosphorylated proteins together, however some general features make it convenient to consider them as a group. They are major constituents of cartilage, loose CT and ...
... The proteoglycan family of proteins is large and varied in structure and function. Grouping them together is similar to grouping all phosphorylated proteins together, however some general features make it convenient to consider them as a group. They are major constituents of cartilage, loose CT and ...
homework for the week of August 22, 2016
... 2. What cavities belong to the dorsal and ventral regions? 3. The cranial cavity holds what organs? 4. What is the difference between negative and positive feedback? 5. What is the function of the lymphatic ...
... 2. What cavities belong to the dorsal and ventral regions? 3. The cranial cavity holds what organs? 4. What is the difference between negative and positive feedback? 5. What is the function of the lymphatic ...
Flatworms Phylum: PLATYHELMINTHES
... process called fission. The anterior and posterior ends hold a surface and the midsection constricts. This results in two new flatworms, one from the anterior end of the original flatworm and the other from the posterior end of the original ...
... process called fission. The anterior and posterior ends hold a surface and the midsection constricts. This results in two new flatworms, one from the anterior end of the original flatworm and the other from the posterior end of the original ...
nasal cavity paranasal sinuses
... Sagittal Sinus. This can be a route of transmission of infection to the cranial cavity. ...
... Sagittal Sinus. This can be a route of transmission of infection to the cranial cavity. ...
The Worms - Cloudfront.net
... Tapeworms The largest tapeworms can grow up to 58ft long You can become contaminated by eating infected food They harm what they are living in by stealing vital nutrients. (House episode) ...
... Tapeworms The largest tapeworms can grow up to 58ft long You can become contaminated by eating infected food They harm what they are living in by stealing vital nutrients. (House episode) ...
EAR
... middle ear with the atmospheric pressure. It is a pathway of infection from the throat to the tympanic cavity and mastoid air cells. Nerve supply : tympanic plexus. ...
... middle ear with the atmospheric pressure. It is a pathway of infection from the throat to the tympanic cavity and mastoid air cells. Nerve supply : tympanic plexus. ...
Points to take note for Biology - Learning Made Simple Singapore
... - This is because left ventricle wall need to produce a larger force to pump oxygenated blood at higher pressure and speed to reach all parts of body. - Right ventricle only need to produce smaller force to pump deoxygenated blood at lower pressure and speed to reach lungs to allow sufficient time f ...
... - This is because left ventricle wall need to produce a larger force to pump oxygenated blood at higher pressure and speed to reach all parts of body. - Right ventricle only need to produce smaller force to pump deoxygenated blood at lower pressure and speed to reach lungs to allow sufficient time f ...
TI-IJE YXRIPHERAL EERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE
... organism; first, actions i n relation to the external world (somatic), and second, internal activities having to do with the processes of nutrition, etc. (visceral). In each case there is the double activity on the part of the nervous system, sensory and motor, making in all four primary functional ...
... organism; first, actions i n relation to the external world (somatic), and second, internal activities having to do with the processes of nutrition, etc. (visceral). In each case there is the double activity on the part of the nervous system, sensory and motor, making in all four primary functional ...
Pelvis and Contents
... Oogonia begin Meiosis I are called primary oocytes (2n) Meiosis I is stalled before birth During ovulation, Meiosis I completed and Meiosis II begins Once Meiosis II begins, begins primary oocytes now called secondary oocytes (n) ...
... Oogonia begin Meiosis I are called primary oocytes (2n) Meiosis I is stalled before birth During ovulation, Meiosis I completed and Meiosis II begins Once Meiosis II begins, begins primary oocytes now called secondary oocytes (n) ...
Biology XI Support Material 2016
... 2-Biodiversity: Large variety of organisms. 3- Nomenclature: Scientific naming of organisms . 4-Identification: Correct description of organism prior to nomenclature. 5-Classification: Grouping of organisms in to categories on the basis of similarities & differences. 6-Taxon: Concrete biological obj ...
... 2-Biodiversity: Large variety of organisms. 3- Nomenclature: Scientific naming of organisms . 4-Identification: Correct description of organism prior to nomenclature. 5-Classification: Grouping of organisms in to categories on the basis of similarities & differences. 6-Taxon: Concrete biological obj ...
Lymphatic System - American Academy
... 5. Bone marrow-soft tissue inside bones that makes red and white blood cells 6. lymphocytes-white blood cells part of the lymphatic system that fights infection 7. thymus-located just above the heart, where T cells develop further after the bone marrow 8. spleen-largest lymphatic organ, located in a ...
... 5. Bone marrow-soft tissue inside bones that makes red and white blood cells 6. lymphocytes-white blood cells part of the lymphatic system that fights infection 7. thymus-located just above the heart, where T cells develop further after the bone marrow 8. spleen-largest lymphatic organ, located in a ...
145 CHAPTER SUMMARY
... 9. Describe the criteria used to classify covering and lining epithelia. 10. Explain the functional classification of multicellular exocrine glands and supply an example for each class. 11. Provide examples from the body that illustrate four of the major functions of connective tissue. 12. Name the ...
... 9. Describe the criteria used to classify covering and lining epithelia. 10. Explain the functional classification of multicellular exocrine glands and supply an example for each class. 11. Provide examples from the body that illustrate four of the major functions of connective tissue. 12. Name the ...
for ICD-10
... by paralyzing the cilia. This causes mucus and bacteria to accumulate, leading to such secondary infections as sinusitis or bronchitis. The basal cells are small, nearly cuboidal cells thought to have some ability to differentiate into other cell types found within the epithelium. Cell differentiati ...
... by paralyzing the cilia. This causes mucus and bacteria to accumulate, leading to such secondary infections as sinusitis or bronchitis. The basal cells are small, nearly cuboidal cells thought to have some ability to differentiate into other cell types found within the epithelium. Cell differentiati ...
HEART internal structure
... • The left atrium is rather smaller than the right, but its walls are thicker, measuring about 3 mm it consists, like the right, • of two parts, a principal cavity and an auricula. – The principal cavity is cuboidal in form, and concealed, in front, by the pulmonary artery and aorta; in front and to ...
... • The left atrium is rather smaller than the right, but its walls are thicker, measuring about 3 mm it consists, like the right, • of two parts, a principal cavity and an auricula. – The principal cavity is cuboidal in form, and concealed, in front, by the pulmonary artery and aorta; in front and to ...
Answer Key: What Did You Learn
... In the fourth week of development, limb buds appear as small ridges along the lateral sides of the embryo. Upper limb buds appear early in the fourth week, and lower limb buds appear a few days later. The limb buds have a core of lateral plate mesoderm which forms bones, tendons, cartilage and conne ...
... In the fourth week of development, limb buds appear as small ridges along the lateral sides of the embryo. Upper limb buds appear early in the fourth week, and lower limb buds appear a few days later. The limb buds have a core of lateral plate mesoderm which forms bones, tendons, cartilage and conne ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.