PORIFERA/CNIDARIA LABORATORY Phylum Porifera Class
... to a substrate. After a nematocyst is released, its cnidoblast cell dies. New cnidoblast cells and nematocysts are therefore continually being produced. Despite the difference in shape between polyps and medusae, the internal structure of these two body forms is very similar. Each has a central coel ...
... to a substrate. After a nematocyst is released, its cnidoblast cell dies. New cnidoblast cells and nematocysts are therefore continually being produced. Despite the difference in shape between polyps and medusae, the internal structure of these two body forms is very similar. Each has a central coel ...
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
... weakened immune system, diabetes, and hyperglycemia. These problems occur because refined sugars are absorbed too quickly and force the body to work extra hard to keep a healthy balance of sugar in the blood. All that extra sugar gets turned into fat! When you eat too much sugar, it causes a rapid s ...
... weakened immune system, diabetes, and hyperglycemia. These problems occur because refined sugars are absorbed too quickly and force the body to work extra hard to keep a healthy balance of sugar in the blood. All that extra sugar gets turned into fat! When you eat too much sugar, it causes a rapid s ...
The Basic Unit of Life
... All living things are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life. It is'the smallest thing that can be called "alive." Most living things that you have seen are made of many cells. Depending on their size, plants and animals are made of thousands, millions, billions, or even trillions of cells. ...
... All living things are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life. It is'the smallest thing that can be called "alive." Most living things that you have seen are made of many cells. Depending on their size, plants and animals are made of thousands, millions, billions, or even trillions of cells. ...
Lec 09 - Structure-Circulatory System
... Circulation in insects is maintained by a system of muscular pumps moving haemolymph through compartments separated by fibromuscular septa or membranes. The main pump is the pulsatile dorsal vessel (`heart'). The anterior part may be called aorta and the posterior part the heart. The dorsal vessel i ...
... Circulation in insects is maintained by a system of muscular pumps moving haemolymph through compartments separated by fibromuscular septa or membranes. The main pump is the pulsatile dorsal vessel (`heart'). The anterior part may be called aorta and the posterior part the heart. The dorsal vessel i ...
The Cranial Cavity
... established that we divide the cranial cavity into supratentorial and infratentorial regions. ...
... established that we divide the cranial cavity into supratentorial and infratentorial regions. ...
[edit] Reproduction
... spermatozoon and an egg, which occurs through fusion of their plasma membranes. After a spermatozoon comes in contact with an egg, the acrosome, which is a prominence at the anterior tip of the spermatozoa, undergoes a series of well-defined structural changes. A structure within the acrosome, calle ...
... spermatozoon and an egg, which occurs through fusion of their plasma membranes. After a spermatozoon comes in contact with an egg, the acrosome, which is a prominence at the anterior tip of the spermatozoa, undergoes a series of well-defined structural changes. A structure within the acrosome, calle ...
Tissues Part B PPT
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
lab1 - Java JAVAC
... 2. Submucosa: connective tissue deep to the mucosa 3. Adventitia: outermost layer, has C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage ...
... 2. Submucosa: connective tissue deep to the mucosa 3. Adventitia: outermost layer, has C-shaped rings of hyaline cartilage ...
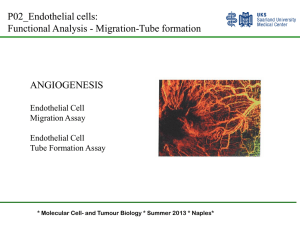
Microvascular Endothelial Cells
... Onto the allantoic membrane of the chicken Embryo and angiogenesis is analyzed Matrigel Plug Assay: A chilled mixture of cells/Matrigel HC is injected Subcutaneously. In the body, the plug will be broken down over Time (10-14 d) Invasion of vessels into plug starts at day 2-3 ...
... Onto the allantoic membrane of the chicken Embryo and angiogenesis is analyzed Matrigel Plug Assay: A chilled mixture of cells/Matrigel HC is injected Subcutaneously. In the body, the plug will be broken down over Time (10-14 d) Invasion of vessels into plug starts at day 2-3 ...
Skeleton to Initial Groups
... appendage; air chambers in one layer with filaments; involucres apical & clam-like; W Epidermis commonly smooth & lacking bulging trigones; ventral scales various; air chambers of thalli in multiple layers; carpocephala elevated. Archegonia & carpocephala arising from an dorsal crypt behind the apex ...
... appendage; air chambers in one layer with filaments; involucres apical & clam-like; W Epidermis commonly smooth & lacking bulging trigones; ventral scales various; air chambers of thalli in multiple layers; carpocephala elevated. Archegonia & carpocephala arising from an dorsal crypt behind the apex ...
lecture 1 - Nose, Nasal cavity & Paranasal sinuses & Pharynx 2013
... Extends from the base of the skull to level of the 6th cervical vertebra, where it is continuous with the esophagus The anterior wall is deficient and shows (from above downward): Posterior nasal apertures. Opening of the oral cavity. Laryngeal inlet. The muscles arranged in circular and ...
... Extends from the base of the skull to level of the 6th cervical vertebra, where it is continuous with the esophagus The anterior wall is deficient and shows (from above downward): Posterior nasal apertures. Opening of the oral cavity. Laryngeal inlet. The muscles arranged in circular and ...
The Special Senses
... • ***NOTE: Touch is not part of special senses, it is part of the NERVOUS SYSTEM ...
... • ***NOTE: Touch is not part of special senses, it is part of the NERVOUS SYSTEM ...
The Respiratory System
... primary bronchi are external to the lungs, while the rest of the bronchial tree is embedded in lung tissues. • diameters of the tubes from primary bronchi to tertiary bronchi are large, so that support with cartilage rings is necessary. These tubes contain columnar cells which prevent diffusion, so ...
... primary bronchi are external to the lungs, while the rest of the bronchial tree is embedded in lung tissues. • diameters of the tubes from primary bronchi to tertiary bronchi are large, so that support with cartilage rings is necessary. These tubes contain columnar cells which prevent diffusion, so ...
Chapter 4b
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
File
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
Nose, Nasal cavity & Paranasal sinuses & Pharynx
... Extends from the base of the skull to level of the 6th cervical vertebra, where it is continuous with the esophagus The anterior wall is deficient and shows (from above downward): Posterior nasal apertures. Opening of the oral cavity. Laryngeal inlet. The muscles arranged in circular and ...
... Extends from the base of the skull to level of the 6th cervical vertebra, where it is continuous with the esophagus The anterior wall is deficient and shows (from above downward): Posterior nasal apertures. Opening of the oral cavity. Laryngeal inlet. The muscles arranged in circular and ...
Connective Tissue
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
... (k) Others: blood Description: Red and white blood cells in a fluid matrix (plasma). Plasma Function: Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances. Location: Contained within blood vessels. ...
Chapter 16 *Lecture PowerPoint Sense Organs
... General Properties of Receptors • Sensory receptors transmit four kinds of information: modality, location, intensity, duration • Modality—type of stimulus or the sensation it produces – Vision, hearing, taste – Labeled line code: all action potentials are identical. Each nerve pathway from sensory ...
... General Properties of Receptors • Sensory receptors transmit four kinds of information: modality, location, intensity, duration • Modality—type of stimulus or the sensation it produces – Vision, hearing, taste – Labeled line code: all action potentials are identical. Each nerve pathway from sensory ...
Chapter 16 - Saladin
... General Properties of Receptors • Sensory receptors transmit four kinds of information: modality, location, intensity, duration • Modality—type of stimulus or the sensation it produces – Vision, hearing, taste – Labeled line code: all action potentials are identical. Each nerve pathway from sensory ...
... General Properties of Receptors • Sensory receptors transmit four kinds of information: modality, location, intensity, duration • Modality—type of stimulus or the sensation it produces – Vision, hearing, taste – Labeled line code: all action potentials are identical. Each nerve pathway from sensory ...
12. Appendicular & limb2009-06
... The upper limb buds are visible by day 26 or 27 and the lower limb buds are appear a day or 2 later. Limb buds elongate by the proliferation of the mesenchyme. The upper limb buds appear low on the embryo’s trunk because of the early development of the cranial half of the embryo. The upper limb buds ...
... The upper limb buds are visible by day 26 or 27 and the lower limb buds are appear a day or 2 later. Limb buds elongate by the proliferation of the mesenchyme. The upper limb buds appear low on the embryo’s trunk because of the early development of the cranial half of the embryo. The upper limb buds ...
b) Anatomy and Physiology - Association for Respiratory
... not possible with a complex multicellular organism, so that a more sophisticated gas exchange system has been developed. In the human, this has been divided into two subsystems – the lungs and pulmonary circulation which form the external respiratory system, and the cells, which form the internal re ...
... not possible with a complex multicellular organism, so that a more sophisticated gas exchange system has been developed. In the human, this has been divided into two subsystems – the lungs and pulmonary circulation which form the external respiratory system, and the cells, which form the internal re ...
Basic Human Anatomy - The Brookside Associates
... Introduction to Basic Human Anatomy is a distance learning product that is based on the Correspondence Subcourse MD0006 of the U.S. Army Medical Department Center and School. This presentation was produced by the Brookside Associates, Ltd., which is privately-held and not connected to any government ...
... Introduction to Basic Human Anatomy is a distance learning product that is based on the Correspondence Subcourse MD0006 of the U.S. Army Medical Department Center and School. This presentation was produced by the Brookside Associates, Ltd., which is privately-held and not connected to any government ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.



![[edit] Reproduction](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004262089_1-11e1f262a9daa1eb642481be5091f0d7-300x300.png)