Animal Development
... Yolk laden cells in vegetal hemisphere. Blastula wall more than one cell thick. ...
... Yolk laden cells in vegetal hemisphere. Blastula wall more than one cell thick. ...
Stephanie Bobbitt - jeffyoshimura.com
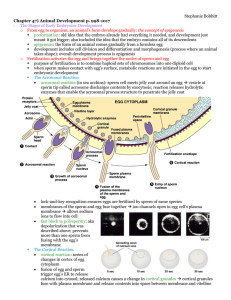
... mesenchyme cells; other cells flatten to make a plate that buckles inward (process is called invagination) buckled plate’s cells are rearranged that transforms the invagination into a deep pouch called the archenteron (open end of this is called the blastopore and will later become the anus) an ...
... mesenchyme cells; other cells flatten to make a plate that buckles inward (process is called invagination) buckled plate’s cells are rearranged that transforms the invagination into a deep pouch called the archenteron (open end of this is called the blastopore and will later become the anus) an ...
Embryo
... developing young within the female reproductive tract. Human pregnancy – averages 266 days (38 weeks) from fertilization or – 40 weeks (9 months) from the start of the last menstrual period. ...
... developing young within the female reproductive tract. Human pregnancy – averages 266 days (38 weeks) from fertilization or – 40 weeks (9 months) from the start of the last menstrual period. ...
LabStarfishDevelopment
... Estimate the number of cells in this embryo: ______________ How does the size of these cells compare with the size of the original zygote? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ At this ...
... Estimate the number of cells in this embryo: ______________ How does the size of these cells compare with the size of the original zygote? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ At this ...
Fertilization and Development
... Where do stem cells come from? • Stem cells are the body’s master cells, they are undifferentiated and can become any cell in your body. • Early stem cells are found in the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. Once the inner cell mass is removed from the blastocyst, the stem cells are placed in a cu ...
... Where do stem cells come from? • Stem cells are the body’s master cells, they are undifferentiated and can become any cell in your body. • Early stem cells are found in the inner cell mass of the blastocyst. Once the inner cell mass is removed from the blastocyst, the stem cells are placed in a cu ...
Vocabulary List
... Asymmetry – Body plan w/ irregular shape, can’t be divided into equal halves Bilateral – Body plan where organism can be divided down length into right & left halves Cell wall- Rigid structure outside plasma membrane in some cells Chlorophyll- Green photosynthetic pigment Cilia- Microscopic hairs us ...
... Asymmetry – Body plan w/ irregular shape, can’t be divided into equal halves Bilateral – Body plan where organism can be divided down length into right & left halves Cell wall- Rigid structure outside plasma membrane in some cells Chlorophyll- Green photosynthetic pigment Cilia- Microscopic hairs us ...
Chapter 26
... internal body organization, bilateral symmetry, and cephalization. Early Development in Animals When sperm and egg unite a zygote is formed. Mitotic cell divisions begin, increasing the # of cells in the individual. A blastula is formed, which looks like a hollow sphere of cells. At this point an op ...
... internal body organization, bilateral symmetry, and cephalization. Early Development in Animals When sperm and egg unite a zygote is formed. Mitotic cell divisions begin, increasing the # of cells in the individual. A blastula is formed, which looks like a hollow sphere of cells. At this point an op ...
PHYLLUM CNIDARIA (11,000 spp, mostly marine) 4 Classes
... Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind Digestive Tract (no anus) Diploblastic (2 germ layers, ectoderm & endoderm) No mesoderm - instead MESOGLEA (a collogen glue w/ or w/o cells in it) Blastopore 6 mouth Cnidocytes ...
... Two body forms - POLYP (e.g. sea anemones) - MEDUSA (e.g., jellyfish) Radial symmetry, mouth surrounded by tentacles Blind Digestive Tract (no anus) Diploblastic (2 germ layers, ectoderm & endoderm) No mesoderm - instead MESOGLEA (a collogen glue w/ or w/o cells in it) Blastopore 6 mouth Cnidocytes ...
Cells and Cell Organelles assignment
... for your answers. Do not give your answers on this page but on a separate page (or on more than one page). This assignment is due at the beginning of your lab during the week of October 19th. This assignment counts the same as a ten-point lab test, and one point will be deducted from the grade on th ...
... for your answers. Do not give your answers on this page but on a separate page (or on more than one page). This assignment is due at the beginning of your lab during the week of October 19th. This assignment counts the same as a ten-point lab test, and one point will be deducted from the grade on th ...
Animal Development Lab
... At this point in the embryo’s development, all cells are nearly the same. They have not yet begun the process of differentiation that will result in cells specializing to carry out different functions. Once the hollow ball of cells (called the ____________________________) is complete, some of its c ...
... At this point in the embryo’s development, all cells are nearly the same. They have not yet begun the process of differentiation that will result in cells specializing to carry out different functions. Once the hollow ball of cells (called the ____________________________) is complete, some of its c ...
Chapter 8
... The embryos of birds, reptiles, and mammals develop within a fluid-filled sac that is contained within a shell or the uterus. Organisms with these adaptations form a monophyletic group called amniotes. Allows for embryo to develop away from water. ...
... The embryos of birds, reptiles, and mammals develop within a fluid-filled sac that is contained within a shell or the uterus. Organisms with these adaptations form a monophyletic group called amniotes. Allows for embryo to develop away from water. ...
The Reproductive System Part 2
... The process by which a sperm joins an egg is called fertilization. Once the sperm nucleus enters the egg, the egg's cell membrane changes, preventing other sperm from entering. ...
... The process by which a sperm joins an egg is called fertilization. Once the sperm nucleus enters the egg, the egg's cell membrane changes, preventing other sperm from entering. ...
Arch Nerve Muscles Skeleton
... • Formation of bilaminar disk • Formation of trilaminar disk (gastrulation) Embryonic period phase 2 • Formation of neural tube • Differentiation of mesoderm • Folding of embryo • Formation of pharyngeal arches ...
... • Formation of bilaminar disk • Formation of trilaminar disk (gastrulation) Embryonic period phase 2 • Formation of neural tube • Differentiation of mesoderm • Folding of embryo • Formation of pharyngeal arches ...
Kingdom Animalia - Clayton High School
... cells (gametes or sex cells) that through fertilization form a new ...
... cells (gametes or sex cells) that through fertilization form a new ...
Implantation
... gonadotrophin hormone which prevents the degeneration of the corpus luteum. It also stimulates the production of progesterone which in turn is important in sustaining the placenta. By the end of the 2nd week, the amount of this hormone will be sufficient to be detected in the maternal blood and urin ...
... gonadotrophin hormone which prevents the degeneration of the corpus luteum. It also stimulates the production of progesterone which in turn is important in sustaining the placenta. By the end of the 2nd week, the amount of this hormone will be sufficient to be detected in the maternal blood and urin ...
04 Early Development - Biology Courses Server
... This section will cover a series of lectures that will begin, in a serious way, our exploration of human development. We will consider the developmental stages critical to the first month of development as we follow the zygote along its developmental path to its arrival at the basic vertebrate body ...
... This section will cover a series of lectures that will begin, in a serious way, our exploration of human development. We will consider the developmental stages critical to the first month of development as we follow the zygote along its developmental path to its arrival at the basic vertebrate body ...
Reproductive System, Day 4 (Professor Powerpoint)
... The space between the villi & the decidua basalis Maternal blood vessels release blood into the space, this bathes the chorionic villi This allows nutrients to diffuse in, but no mixing of blood As the fetus extends away, the allantois develops into the umbilical cord with blood vessels lead ...
... The space between the villi & the decidua basalis Maternal blood vessels release blood into the space, this bathes the chorionic villi This allows nutrients to diffuse in, but no mixing of blood As the fetus extends away, the allantois develops into the umbilical cord with blood vessels lead ...
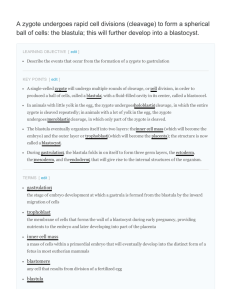
A zygote undergoes rapid cell divisions (cleavage)
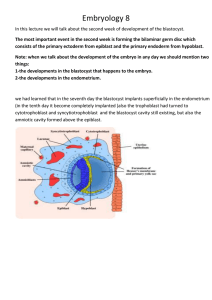
... cells in the blastula arrange themselves in two layers: the inner cell mass and an outer layer called the trophoblast . The inner cell mass is also known as the embryoblast; this mass of cells will go on to form the embryo. At this stage of development, the inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem ...
... cells in the blastula arrange themselves in two layers: the inner cell mass and an outer layer called the trophoblast . The inner cell mass is also known as the embryoblast; this mass of cells will go on to form the embryo. At this stage of development, the inner cell mass consists of embryonic stem ...
Embryology 8
... When these vacuoles fuse, they form large lacunae, and this phase of trophoblast development is thus known as the lacunar stage ...
... When these vacuoles fuse, they form large lacunae, and this phase of trophoblast development is thus known as the lacunar stage ...
Full Text - Quran and Medicine
... lacunae networks. At the same time, cytiotrphoblasts reproduce and form cell columns. These cell columns enter into syncytial tissues and get surrounded by the syncytial tissue. These columns, which form the primary villi, play role in placentation (13). ...
... lacunae networks. At the same time, cytiotrphoblasts reproduce and form cell columns. These cell columns enter into syncytial tissues and get surrounded by the syncytial tissue. These columns, which form the primary villi, play role in placentation (13). ...
Ch 10 Cell Growth and Division
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
Document
... Foregut – formed in front of yolk mass – differentiates into pharynx, oesophagus, stomach. Midgut – formed of yolk mass – differentiates into ...
... Foregut – formed in front of yolk mass – differentiates into pharynx, oesophagus, stomach. Midgut – formed of yolk mass – differentiates into ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.