bilaminarand trilaminar discs2011-09-11 07:034.1 MB
... High columnar cells adjacent to the amniotic cavity. ...
... High columnar cells adjacent to the amniotic cavity. ...
2nd week of Development
... 2. Layer of multinucleated zone without distinct cell bounderies called syncytotrophblast or syncitium Extraembryonic structures • The embryonic disc gives rise to the germ layers that form all the tissues and organs of the embryo. • Extraembryonic structures forming during the second week are the a ...
... 2. Layer of multinucleated zone without distinct cell bounderies called syncytotrophblast or syncitium Extraembryonic structures • The embryonic disc gives rise to the germ layers that form all the tissues and organs of the embryo. • Extraembryonic structures forming during the second week are the a ...
1 Sample Canadian DAT Reading Comprehension
... the fertilized egg, or zygote. Repeated mitotic divisions result in many cells that differentiate to form the tissues and organs of the developing individual or embryo. Soon after an egg is fertilized, the singlecelled zygote becomes two cells, the two divide into four, and so on. This process of cl ...
... the fertilized egg, or zygote. Repeated mitotic divisions result in many cells that differentiate to form the tissues and organs of the developing individual or embryo. Soon after an egg is fertilized, the singlecelled zygote becomes two cells, the two divide into four, and so on. This process of cl ...
L2 Cleavage to gastrulation
... The zygote goes through different stages of development by specific morphogenetic processes. Cleavage, a series of mitotic divisions produces a morula Blastulation forms the blastula which hatches from the zona pellucida and implants in the wall of the uterus. Gastrulation transforms the flat ...
... The zygote goes through different stages of development by specific morphogenetic processes. Cleavage, a series of mitotic divisions produces a morula Blastulation forms the blastula which hatches from the zona pellucida and implants in the wall of the uterus. Gastrulation transforms the flat ...
Diversity – Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia
... • Blastomeres – smaller cells from original fertlized egg • Morula – cluster of cells after 5-7 divisions – Blastocoel – fluid formed cavity within the morula • Blastula – formed around the blastocoel • Cytoplasmic determinants will determine how these cells divide. Morula ...
... • Blastomeres – smaller cells from original fertlized egg • Morula – cluster of cells after 5-7 divisions – Blastocoel – fluid formed cavity within the morula • Blastula – formed around the blastocoel • Cytoplasmic determinants will determine how these cells divide. Morula ...
Animal Development Notes
... The blastocyst is _______________________ from its shell. As the hatching proceeds the blastula will implant into the _____________________. The ____________________ forms and the embryo is nourished by its mother. Implantation Implantation of the blastula occurs in the upper third of the ____ ...
... The blastocyst is _______________________ from its shell. As the hatching proceeds the blastula will implant into the _____________________. The ____________________ forms and the embryo is nourished by its mother. Implantation Implantation of the blastula occurs in the upper third of the ____ ...
Chapter 22: Development and Aging
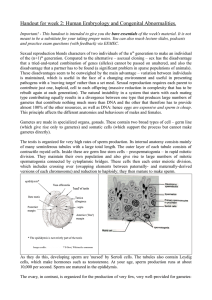
... extraembryonic membranes: 1) The amnion envelops the embryo/fetus in a protective amniotic fluid. ...
... extraembryonic membranes: 1) The amnion envelops the embryo/fetus in a protective amniotic fluid. ...
File
... Day 8 – The blastocyst is partially embedded in the endometrium. The side of the embryo containing the inner cell mass is the embryonic pole and opposite of it is the abembryonic pole. The trophoblast (outer cell mass) differentiates into an inner cytotrophoblast (mononuclear cells) and outer syncyt ...
... Day 8 – The blastocyst is partially embedded in the endometrium. The side of the embryo containing the inner cell mass is the embryonic pole and opposite of it is the abembryonic pole. The trophoblast (outer cell mass) differentiates into an inner cytotrophoblast (mononuclear cells) and outer syncyt ...
Handout for week 2: Human Embryology and Congenital
... making a motor neuron vs an interneuron, or for example making bone vs muscle. These cells will make signals of their own, and by these cellular conversations the internal complexity of the embryo pulls itself up 'by its own bootstraps'. Some of this also involves cell migrations, particularly of th ...
... making a motor neuron vs an interneuron, or for example making bone vs muscle. These cells will make signals of their own, and by these cellular conversations the internal complexity of the embryo pulls itself up 'by its own bootstraps'. Some of this also involves cell migrations, particularly of th ...
embryology PAP 2 Fertilization and implantation
... •formed by fusion of adjacent lacunae •filled with maternal blood and cellular debris ...
... •formed by fusion of adjacent lacunae •filled with maternal blood and cellular debris ...
Second Week of Development
... Yolk sac: a thin, exocoelomic membrane that forms from the hypoblast, formerly called the blastocyst cavity In humans, is small, relatively empty, and progressively decreases in size Several important functions include supplying nutrients during the second and third weeks of development, provi ...
... Yolk sac: a thin, exocoelomic membrane that forms from the hypoblast, formerly called the blastocyst cavity In humans, is small, relatively empty, and progressively decreases in size Several important functions include supplying nutrients during the second and third weeks of development, provi ...
1 - Lone Star College
... Embryo usually begins the process of implantation If implantation is successful, the female is clinically pregnant An ectopic pregnancy occurs if the embryo implants in the uterine tube The trophoblast begins to secrete HCG Acts like LH Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone and the endome ...
... Embryo usually begins the process of implantation If implantation is successful, the female is clinically pregnant An ectopic pregnancy occurs if the embryo implants in the uterine tube The trophoblast begins to secrete HCG Acts like LH Stimulates corpus luteum to secrete progesterone and the endome ...
Gastrulation - GEOCITIES.ws
... into the mesoderm and rolls up to form the brain and spinal cord The notochord elongates and stretches the embryo lengthwise The mesoderm cells that form the vertebrae condense around the notochord More mesoderm condenses along the sides of the notochord forming somites— blocks of tissue that ...
... into the mesoderm and rolls up to form the brain and spinal cord The notochord elongates and stretches the embryo lengthwise The mesoderm cells that form the vertebrae condense around the notochord More mesoderm condenses along the sides of the notochord forming somites— blocks of tissue that ...
Chapter 28 - apsubiology.org
... Amnion (inner membrane) envelops and protects embryo amnion – epiblast cells form a transparent membrane filled with amniotic fluid – a maternal plasma filtrate amniotic fluid comes from maternal blood, and, later, fetal urine adds to it amniotic fluid acts as a liquid shock absorber to prote ...
... Amnion (inner membrane) envelops and protects embryo amnion – epiblast cells form a transparent membrane filled with amniotic fluid – a maternal plasma filtrate amniotic fluid comes from maternal blood, and, later, fetal urine adds to it amniotic fluid acts as a liquid shock absorber to prote ...
Document
... chromosomal sex, and (c) initiation of cleavage. Cleavage is a series of mitotic divisions that results in an increase in cells, blastomeres, which become smaller with each division. After three divisions, blastomeres undergo compaction to become a tightly grouped ball of cells with inner and outer ...
... chromosomal sex, and (c) initiation of cleavage. Cleavage is a series of mitotic divisions that results in an increase in cells, blastomeres, which become smaller with each division. After three divisions, blastomeres undergo compaction to become a tightly grouped ball of cells with inner and outer ...
Chapter 41 Animal Development
... • After 1 week, the morula becomes a blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells with an inner cell mass on one side ...
... • After 1 week, the morula becomes a blastocyst, a hollow ball of cells with an inner cell mass on one side ...
Implantation2008-11-04 07:213.1 MB
... Begins about 30 hours after fertilization There is rapid increase in number of cells. The cells, blastomeres, become smaller with each division Normally occurs as the zygote passes along the uterine tube to the uterus During cleavage, zygote lies within the zona pellucida ...
... Begins about 30 hours after fertilization There is rapid increase in number of cells. The cells, blastomeres, become smaller with each division Normally occurs as the zygote passes along the uterine tube to the uterus During cleavage, zygote lies within the zona pellucida ...
Ch 47 Animal Development Abbreviated
... 4. Compare the formaBon of a blastula and gastrulaBon in a sea urchin, a frog, and a chick 5. List and explain the funcBons of the extraembryonic membranes ...
... 4. Compare the formaBon of a blastula and gastrulaBon in a sea urchin, a frog, and a chick 5. List and explain the funcBons of the extraembryonic membranes ...
Embryology • Important as a process, the way the organism
... the mesoderm winds up subdividing into 3 portions. A central region called chordamesoderm and lateral mesoderm –somite. Initially as the animal begins to develop, the somites are segmentally arranged. That is, the mesoderm actually develops as a series anteroposterior sequential structures called so ...
... the mesoderm winds up subdividing into 3 portions. A central region called chordamesoderm and lateral mesoderm –somite. Initially as the animal begins to develop, the somites are segmentally arranged. That is, the mesoderm actually develops as a series anteroposterior sequential structures called so ...
Chapter 47
... between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just completed the second surrounded by the fertilization by the fertilization envelope. cleavage division. envelope. The blastocoel cavity The nucleus is visible in the has begun to form. ...
... between the two cells that have multicellular ball that is still cleavage division, surrounded just completed the second surrounded by the fertilization by the fertilization envelope. cleavage division. envelope. The blastocoel cavity The nucleus is visible in the has begun to form. ...
Embryonic and Fetal Development
... The transformation from a single cell to an amazingly beautiful baby (to their mom and dad, at least) in 40 weeks is one the most amazing processes in biology. It’s cool for any organism, but we’re human so of course we must be anthropocentric. This time period consists of incredible growth, prolife ...
... The transformation from a single cell to an amazingly beautiful baby (to their mom and dad, at least) in 40 weeks is one the most amazing processes in biology. It’s cool for any organism, but we’re human so of course we must be anthropocentric. This time period consists of incredible growth, prolife ...
Unit 3 part 4 PPT
... will become the lining of the digestive system. • The blastopore is the future anus of the embryo. ...
... will become the lining of the digestive system. • The blastopore is the future anus of the embryo. ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.