* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
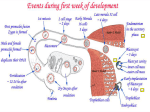
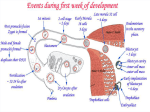
1 Second Week of Development: Bilaminar Germ Disc Day 8 – The blastocyst is partially embedded in the endometrium. The side of the embryo containing the inner cell mass is the embryonic pole and opposite of it is the abembryonic pole. The trophoblast (outer cell mass) differentiates into an inner cytotrophoblast (mononuclear cells) and outer syncytiotrophoblast (multinuclear cells), which are derived from fused cytotrophoblast cells. The inner cell mass differentiates into an upper layer known as the epiblast and a lower layer called the hypoblast (primitive endoderm, extraembryonic endoderm). During the 3rd week of embryonic development we will discuss the definitive or "intraembryonic" endoderm, derived from the epiblast. A small cavity appears in the epiblast and becomes the amniotic cavity. Epiblast cells adjacent to the cytotrophoblast are called amnioblasts. Day 9 – The blastocyst becomes more embedded into the endometrium. A fibrin plug covers the defect in endometrium. Especially at the embryonic pole, the trophoblast shows more vacuoles in its syncytial component. The vacuoles enlarge to become lacunae. At the abembryonic pole, flat cells form a thin membrane that lines the inside of the cytotrophoblast. These cells originate from the hypoblast and the membrane is called Heuser's (exocoelomic) membrane. This membrane is also described as extraembryonic endoderm or parietal endoderm. The cavity bounded by the hypoblast and Heuser's membrane is called the exocoelomic cavity or primitive (primary) yolk sac. Days 11 and 12 – The blastocyst is completely embedded in the endometrium. Syncytial cells erode maternal capillaries, allowing maternal blood to drain freely into open areas of the syncytiotrophoblast called sinusoids. Blood flowing through this area is the uteroplacental circulation. Meanwhile, transformed cells appear between the primary yolk sac [parietal endoderm, Heuser's (exocoelomic) membrane] and the cytotrophoblast, forming connective tissue called extraembryonic mesoderm. Cavities develop in the extraembryonic mesoderm as it expands. Coalescence of the cavities forms a new space, the extraembryonic coelom or chorionic cavity. The chorionic cavity encloses the primitive (primary) yolk sac and amniotic cavity. The connecting stalk (future umbilical cord) crosses the chorionic cavity, connecting the embryo to the placental area. Extraembryonic mesoderm lining the outside of the yolk sac is called extraembryonic splanchnopleuric mesoderm. Mesoderm lining the inside of the cytotrophoblast and outside of the amnion is extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm. The connecting stalk is, also, extraembryonic somatopleuric mesoderm. Like endoderm, there is, so to speak, "intraembryonic" mesoderm that is derived from cells of the epiblast. Soon, part of the splanchnopleuric mesoderm and part of the somatopleuric mesoderm will be incorporated into visceral (gut) and parietal (body wall) mesoderm, respectively. Cells of the endometrium and its stroma are becoming loaded with glycogen and lipids, plus the tissue is edematous: the decidua reaction. 2 Day 13 – Where there may still be a defect in the endometrium, leakage of blood from the uterus at this stage can produce "spotting," which is sometimes misinterpreted to be a menstrual period (day 28). Cells of the cytotrophoblast penetrate the syncytiotrophoblast. These columns of cytotrophoblastic cells surrounded by syncytium are called primary villi. Meanwhile, the hypoblast produces additional cells that line the inside of the exocoelomic membrane. This will become the secondary or definitive yolk sac. It is smaller than the primary yolk sac. Large portions of the exocoelomic (primary yolk sac) cavity are pinched off forming exocoelomic cysts in the chorionic cavity. Now, the extraembryonic mesoderm lining the inside of the cytotrophoblast is known as the chorionic plate. The connecting stalk, umbilical cord, is the only place where extraembryonic mesoderm crosses the chorionic cavity. Abnormal implantation Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) – This hormone is produce by the syncytiotrophoblast and in sufficient quantities by the end of the second week of pregnancy that it can be used for pregnancy testing. It also maintains the corpus luteum of pregnancy for a few months: if the corpus luteum is removed before the fourth month, abortion usually results. Hydatidiform mole – If for some reason a fertilized egg has no maternal genome present or two sperm fertilize a normal egg; the result is a hydatidiform mole. This appears as a "bag of grapes" and secretes very high levels of hCG, thus, giving the appearance of a normal pregnancy. All that is present is placental parts due to the fact that paternal genes are very important in making the placenta. If they become malignant it results in an invasive mole or choriocarcinoma. Ectopic pregnancy – This is a pregnancy that occurs outside the uterus, most frequently in the uterine tube. In these uterine tube cases, the embryo dies about the second month (6-7 weeks gestation) of gestation causing severe abdominal pain and hemorrhage that may be fatal. Questions 1. The outer cell mass differentiates into the ____________. a. trophoblast b. morula c. epiblast d. embryoblast 2. Amnioblasts are derived from the ____________. a. hypoblast b. cytotrophoblast c. syncytiotrophoblast d. epiblast 3 3. The cavity of the primitive yolk sac is also called the ___________. a. chorionic cavity b. amniotic cavity c. exocoelomic cavity d. lacunae 4. Extraembryonic mesoderm that adheres to the outside of the yolk sac is ______________. a. somatopleuric mesoderm b. cytotrophoblastic c. splanchnopleuric mesoderm d. the chorionic plate 5. Primary villi are projections of __________ that just start to penetrate the ___________. a. endometrium / syncytiotrophoblast b. cytotrophoblast / syncytiotrophoblast c. syncytiotrophoblast / endometrium d. extraembryonic mesoderm / umbilical cord 6. When _____________, it is probably an ectopic pregnancy. a. there are very high levels of hCG b. spotting about the 13th day of pregnancy c. pain during ovulation d. there is severe abdominal pain at about 6 or 7 weeks gestation