Animal Development
... Yolk laden cells in vegetal hemisphere. Blastula wall more than one cell thick. ...
... Yolk laden cells in vegetal hemisphere. Blastula wall more than one cell thick. ...
Germ disc differentiation
... •As neural tube closes -Neural crest •Detach and migrate –Melanocytes – skin –Dorsal root ganglia ...
... •As neural tube closes -Neural crest •Detach and migrate –Melanocytes – skin –Dorsal root ganglia ...
Cleavage / Implantation
... Embryo: hypoblast Æ exocoelomic membrane = Hauser’s membrane Extraembryonic mesoderm from yolk sac ...
... Embryo: hypoblast Æ exocoelomic membrane = Hauser’s membrane Extraembryonic mesoderm from yolk sac ...
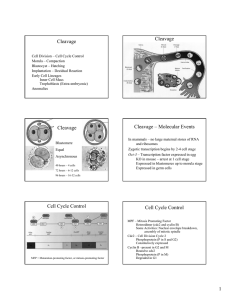
Cleavage Cleavage Cleavage Cleavage – Molecular Events Cell
... Embryo: hypoblast Æ exocoelomic membrane = Hauser’s membrane Extraembryonic mesoderm from yolk sac ...
... Embryo: hypoblast Æ exocoelomic membrane = Hauser’s membrane Extraembryonic mesoderm from yolk sac ...
Section 15.2 Reproductive Control
... The nervous system develops from the mesoderm section of the gastrula. The mesoderm cells join together to form a structure called the notochord. In the third week of development, a neural tube forms and the embryo is now called a neurula. The anterior part of the neural tube eventually forms into a ...
... The nervous system develops from the mesoderm section of the gastrula. The mesoderm cells join together to form a structure called the notochord. In the third week of development, a neural tube forms and the embryo is now called a neurula. The anterior part of the neural tube eventually forms into a ...
Fertilization
... cells in the region of the embryo once occupied by the middle of the gray crescent. This produces: ...
... cells in the region of the embryo once occupied by the middle of the gray crescent. This produces: ...
Biology Chapter 9 Starfish development LAB 2009
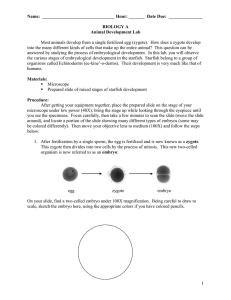
... Estimate the number of cells in this embryo: ______________ How does the size of these cells compare with the size of the original zygote? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ___ ...
... Estimate the number of cells in this embryo: ______________ How does the size of these cells compare with the size of the original zygote? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ___ ...
Name: Hour: ______ Date Due: BIOLOGY B Animal Development
... The outer layer of this form is called the ectoderm, and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. Label this layer on your sketch. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm, and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digestive proces ...
... The outer layer of this form is called the ectoderm, and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. Label this layer on your sketch. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm, and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digestive proces ...
Name: Hour: ______ Date Due: HONORS BIOLOGY B Animal
... The outer layer of this form is called the ectoderm, and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. Label this layer on your sketch. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm, and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digestive proces ...
... The outer layer of this form is called the ectoderm, and develops into the skin and nervous system of the animal. Label this layer on your sketch. The inner layer of this form is called the endoderm, and develops into the lining of the digestive tract and organs that are part of the digestive proces ...
Student worksheet for prokaryotic, animal and plant cells
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Comparison of prokaryotic, animal and plant cells 1. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. What is the other type of cell in this ...
... Student—please print this worksheet and complete it as you interact with the tutorial. The completed worksheet should be turned in to your assigned teacher. Tutorial: Comparison of prokaryotic, animal and plant cells 1. Plants and animals have eukaryotic cells. What is the other type of cell in this ...
2.germ disc differentiation(20160108).
... -Midgut: none -Hindgut: bladder,urethra •Surrounded by visceral lateral plate mesoderm ...
... -Midgut: none -Hindgut: bladder,urethra •Surrounded by visceral lateral plate mesoderm ...
Animal Classification, Phylogeny and Organization
... Bilateral symmetry Radial symmetry Cephalization ...
... Bilateral symmetry Radial symmetry Cephalization ...
2nd week of developement
... with the lacunae establishes the primordial uteroplacental circulation. ...
... with the lacunae establishes the primordial uteroplacental circulation. ...
Second Week of Development: Bilaminar Germ Disc
... a. Inner mononucleated cytotrphoblastic cells that divide by mitosis forming layer b. b. Outer multinucleated syncytiotrophblastic zone of fused cell losing their membrane, also called the syncytium. ...
... a. Inner mononucleated cytotrphoblastic cells that divide by mitosis forming layer b. b. Outer multinucleated syncytiotrophblastic zone of fused cell losing their membrane, also called the syncytium. ...
Second Week of evelopment: Bilaminar Germ Disc
... a. Inner mononucleated cytotrphoblastic cells that divide by mitosis forming layer b. b. Outer multinucleated syncytiotrophblastic zone of fused cell losing their membrane, also called the syncytium. ...
... a. Inner mononucleated cytotrphoblastic cells that divide by mitosis forming layer b. b. Outer multinucleated syncytiotrophblastic zone of fused cell losing their membrane, also called the syncytium. ...
Pregnancy
... sperm cell has made its way to an egg cell, burrowed into the egg, and the egg has changed so that no other sperm can enter the egg. It is at this stage that all of the genes of the baby are set. The next stage comes 3-4 days after fertilization where the dividing cells of the embryo form a circular ...
... sperm cell has made its way to an egg cell, burrowed into the egg, and the egg has changed so that no other sperm can enter the egg. It is at this stage that all of the genes of the baby are set. The next stage comes 3-4 days after fertilization where the dividing cells of the embryo form a circular ...
C. Egg - Cloudfront.net
... c. Allantois Blood vessels become umbilical cord d. Yolk sac Lacks yolk; first site of blood formation ...
... c. Allantois Blood vessels become umbilical cord d. Yolk sac Lacks yolk; first site of blood formation ...
intraembryonic mesoderm胚內中胚層
... 1. Notochordal canal--extends from primitive pit and extend within notochordal process. Notochordal process extends from primitive node to prochordal plate. 2. Floor of notochordal process fused with underlying endoderm. 3. Opening of the floor of notochordal process. Notochordal canal communicates ...
... 1. Notochordal canal--extends from primitive pit and extend within notochordal process. Notochordal process extends from primitive node to prochordal plate. 2. Floor of notochordal process fused with underlying endoderm. 3. Opening of the floor of notochordal process. Notochordal canal communicates ...
Human Embryology Development
... they do not all reach fallopian tubes. It takes approximately 3-5 days for the fertilized ovum to travel from the fallopian tube to uterus. • Cell division, or cleavage, occurs and the zygote gets smaller. The zygote develops into a fluid filled structure known as the blastocyst. ...
... they do not all reach fallopian tubes. It takes approximately 3-5 days for the fertilized ovum to travel from the fallopian tube to uterus. • Cell division, or cleavage, occurs and the zygote gets smaller. The zygote develops into a fluid filled structure known as the blastocyst. ...
Formation of the extra
... • Early development of the embryo • Gestation is often divided into three stages: (1) the ovum from 0–13 days, (2) the embryo from 14 days, when germ layers begin to form until 45 days, and (3) the fetus from 46 days until parturition. • The ovum begins to divide mitotically, a process known as clea ...
... • Early development of the embryo • Gestation is often divided into three stages: (1) the ovum from 0–13 days, (2) the embryo from 14 days, when germ layers begin to form until 45 days, and (3) the fetus from 46 days until parturition. • The ovum begins to divide mitotically, a process known as clea ...
Topic 2. Animal Architecture
... complete tube by forming a second opening to the outside it is then called the gut. ...
... complete tube by forming a second opening to the outside it is then called the gut. ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.