An introduction to animal diversity
... The blastula is typically a hollow ball of cells around a cavity called the blastocoel. Most animals also undergo gastrulation, in which one end of the embryo folds inward to form two layers of embryonic tissue, ectoderm and endoderm; eventually fills in the blastocoel to form the gastrula. ...
... The blastula is typically a hollow ball of cells around a cavity called the blastocoel. Most animals also undergo gastrulation, in which one end of the embryo folds inward to form two layers of embryonic tissue, ectoderm and endoderm; eventually fills in the blastocoel to form the gastrula. ...
Cells and Systems Review Outine
... Matter moves into/out of the cell through the process of _____________________. Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
... Matter moves into/out of the cell through the process of _____________________. Osmosis Because the cell membrane allows SOME matter to move in and out – it is said to be ________________________. Cells combine together to form tissue. 4 types of animal tissue: ...
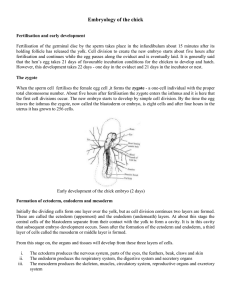
embryology of the chick
... When the sperm cell fertilises the female egg cell ,it forms the zygote - a one-cell individual with the proper total chromosome number. About five hours after fertilisation the zygote enters the isthmus and it is here that the first cell divisions occur. The new embryo starts to develop by simple c ...
... When the sperm cell fertilises the female egg cell ,it forms the zygote - a one-cell individual with the proper total chromosome number. About five hours after fertilisation the zygote enters the isthmus and it is here that the first cell divisions occur. The new embryo starts to develop by simple c ...
Sexual Reproduction - Mr Schmitt
... Embryonic development is the early development of an organism - in humans, it is the first two months after fertilization Stages ...
... Embryonic development is the early development of an organism - in humans, it is the first two months after fertilization Stages ...
The fluid that is ejaculated at the time of orgasm Contains
... between the future caudal end of the embryonic disc and the chorion The connecting stalk forms a pathway along which vascular anastomoses of embryonic disk establish communication with those of the chorion ...
... between the future caudal end of the embryonic disc and the chorion The connecting stalk forms a pathway along which vascular anastomoses of embryonic disk establish communication with those of the chorion ...
Animal Kingdom Webquest
... 15. (http://mansfield.osu.edu/~sabedon/campbl32.htm) In organisms that are triploblastic and contain the mesodermal layer of cells, this mesoderm layer can interact with the endoderm layer in one of three ways to create three distinct groups of organisms. Describe them: i. acoelomates: _____________ ...
... 15. (http://mansfield.osu.edu/~sabedon/campbl32.htm) In organisms that are triploblastic and contain the mesodermal layer of cells, this mesoderm layer can interact with the endoderm layer in one of three ways to create three distinct groups of organisms. Describe them: i. acoelomates: _____________ ...
Reproductive System, Day 5 (Professor Powerpoint)
... The space between the villi & the decidua basalis Maternal blood vessels release blood into the space, this bathes the chorionic villi This allows nutrients to diffuse in, but no mixing of blood As the fetus extends away, the allantois develops into the umbilical cord with blood vessels lead ...
... The space between the villi & the decidua basalis Maternal blood vessels release blood into the space, this bathes the chorionic villi This allows nutrients to diffuse in, but no mixing of blood As the fetus extends away, the allantois develops into the umbilical cord with blood vessels lead ...
functions of the circulatory system
... FUNCTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system has seven major functions: ...
... FUNCTIONS OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM The circulatory system has seven major functions: ...
Document
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
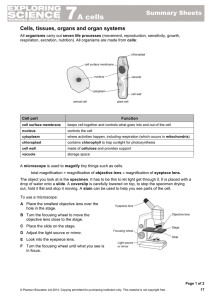
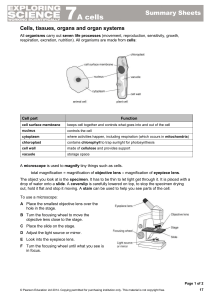
7A cells
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
KS3 Science
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
... Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems All organisms carry out seven life processes (movement, reproduction, sensitivity, growth, respiration, excretion, nutrition). All organisms are made from cells: ...
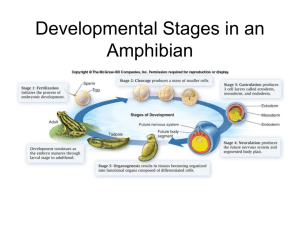
Animal Development
... – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the uterine wall • At this point, it is called a blastocyst (same as blastula) ...
... – The embryo floats free for several days, nourished by fluids from glands in the uterine wall • At this point, it is called a blastocyst (same as blastula) ...
key terms lab 9
... Endoskeleton. Internal skeleton composed of calcium carbonate plates just beneath the surface of the skin. Hydrostatic skeleton. A skeletal system composed of fluid held under pressure in a closed body compartment; the main skeleton of most cnidarians, flatworms, nematodes, and annelids. indetermina ...
... Endoskeleton. Internal skeleton composed of calcium carbonate plates just beneath the surface of the skin. Hydrostatic skeleton. A skeletal system composed of fluid held under pressure in a closed body compartment; the main skeleton of most cnidarians, flatworms, nematodes, and annelids. indetermina ...
Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of
... Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of the nervous system ...
... Computational modeling of an early evolutionary stage of the nervous system ...
Animal development PDF
... • The sharp rise in Ca2+ in the egg’s cytosol increases the rates of cellular respiration and protein synthesis by the egg cell • With these rapid changes in metabolism, the egg is said to be activated • The sperm nucleus merges with the egg nucleus and cell division begins ...
... • The sharp rise in Ca2+ in the egg’s cytosol increases the rates of cellular respiration and protein synthesis by the egg cell • With these rapid changes in metabolism, the egg is said to be activated • The sperm nucleus merges with the egg nucleus and cell division begins ...
R 28.1
... Programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is also an important part of developing individual structures such as individual fingers or toes. The human body has five levels of organization. • Specialized cells are characterized by their specific structures and functions. • A tissue is a group of similar ce ...
... Programmed cell death, or apoptosis, is also an important part of developing individual structures such as individual fingers or toes. The human body has five levels of organization. • Specialized cells are characterized by their specific structures and functions. • A tissue is a group of similar ce ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... • Presence of a body cavity Multicellular with tissues in 2 layers: Placozoa and Porifera Multicellular, tissues in 2 layers, radial symmetry: Cnidaria, Ctenophora ...
... • Presence of a body cavity Multicellular with tissues in 2 layers: Placozoa and Porifera Multicellular, tissues in 2 layers, radial symmetry: Cnidaria, Ctenophora ...
intro to animals
... pieces and each piece can develop into an adult animal __regeneration___ a new organism can regenerate, or regrow, from a lost body part if the part contains enough genetic information ___parthenogenesis___ a female animal produces eggs that develop without being fertilized - Early Development o ...
... pieces and each piece can develop into an adult animal __regeneration___ a new organism can regenerate, or regrow, from a lost body part if the part contains enough genetic information ___parthenogenesis___ a female animal produces eggs that develop without being fertilized - Early Development o ...
Week 2 of development
... Neuroectoderm consists of : 1. Neural plate> neural tube>>brain and spinal cord. 2. Neural crest>>consists of pluripotent cells which migrate to all areas and give rise to formation of many organs and tissues. ...
... Neuroectoderm consists of : 1. Neural plate> neural tube>>brain and spinal cord. 2. Neural crest>>consists of pluripotent cells which migrate to all areas and give rise to formation of many organs and tissues. ...
anidevlt - CowanScience
... embryo proper Trophoblast – outer cells forming the wall of the blastula – forms the placenta ...
... embryo proper Trophoblast – outer cells forming the wall of the blastula – forms the placenta ...
Pathophysiology of Disease
... produce new trophoblastic cells to increase the mass of the syncytiotrophoblast Syncytiotrophoblast-rapidly expanding mass of cells that produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Fingerlike processes of the syncytiotrophoblast extend through the endometrial epithelium and invade the connective tis ...
... produce new trophoblastic cells to increase the mass of the syncytiotrophoblast Syncytiotrophoblast-rapidly expanding mass of cells that produce human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). Fingerlike processes of the syncytiotrophoblast extend through the endometrial epithelium and invade the connective tis ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.