Prenatal Development - Southern Illinois University School
... • Cell begins to split via mitosis • By end of week there are more than 100 cells clustered in hollow, ball-like structure with 2 layers: • Inner = BLASTOCYST • Later develops into the embryo ...
... • Cell begins to split via mitosis • By end of week there are more than 100 cells clustered in hollow, ball-like structure with 2 layers: • Inner = BLASTOCYST • Later develops into the embryo ...
Animals…
... • Ectoderm cells develop into skin and nervous tissue • Endoderm cells develop into the lining of the digestive tract and the digestive organs • Mesoderm cells develop into muscles, circulatory system, excretory system, respiratory system. ...
... • Ectoderm cells develop into skin and nervous tissue • Endoderm cells develop into the lining of the digestive tract and the digestive organs • Mesoderm cells develop into muscles, circulatory system, excretory system, respiratory system. ...
Chapter 1 (C) Review
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
... a. a group of cells that work together to perform a specific job b. a group of tissues that belong to different systems c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs _____ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, ...
Intro to Animals
... fungi. • The multicellular bodies of animals are held together with the extracellular proteins, especially collagen. ...
... fungi. • The multicellular bodies of animals are held together with the extracellular proteins, especially collagen. ...
Morphogenesis
... The most important event in your life • Dynamic process of cellular movements which form the three primordial germ layers and the coelom • Morphogenetic movements depend on the amount and distribution of yolk. • Involves some type of involution. • Regulated by homeobox genes and their proteins - mor ...
... The most important event in your life • Dynamic process of cellular movements which form the three primordial germ layers and the coelom • Morphogenetic movements depend on the amount and distribution of yolk. • Involves some type of involution. • Regulated by homeobox genes and their proteins - mor ...
Fun with Cells with the Amoeba Sisters
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
... What does a cell contain within itself, apart from the jelly like cytoplasm? And what do they do? But, wait. There are basically 2 kinds of cells, right? One that is found in simple life forms like amoeba. And such cells are called as prokaryotes. And the other that is found in complex life forms l ...
Introduction to Animals Worksheet
... 6. A hollow ball of cells that forms after fertilization is called a [ blastula / mesoderm ] 7. In all animals except [ humans / sponges ] a zygote undergoes divisions to become a blastula. 8. The cells of animals are organized into functional units called [ blastula / tissues ] Matching: 9. ______ ...
... 6. A hollow ball of cells that forms after fertilization is called a [ blastula / mesoderm ] 7. In all animals except [ humans / sponges ] a zygote undergoes divisions to become a blastula. 8. The cells of animals are organized into functional units called [ blastula / tissues ] Matching: 9. ______ ...
filled-in vers.
... cells are slow… involution is delayed. Consequently, slightly different process accomplishes same ends. Lateral mesoderm moves in from sides and ventral area of blastopore heading for the head. ...
... cells are slow… involution is delayed. Consequently, slightly different process accomplishes same ends. Lateral mesoderm moves in from sides and ventral area of blastopore heading for the head. ...
2. Nervous system 1 - Meninges: Dura mater, subdural space
... Lateral plate mesoderm form limb, muscles, bone and connective tissue. Limb is initiated by mesoderm, then controlled by ectoderm Digit development: Feet and hands start as flat plat, then form the hand by killing cells in zone between fingers (apoptosis). Endoderm: form organ along with mesoderm. E ...
... Lateral plate mesoderm form limb, muscles, bone and connective tissue. Limb is initiated by mesoderm, then controlled by ectoderm Digit development: Feet and hands start as flat plat, then form the hand by killing cells in zone between fingers (apoptosis). Endoderm: form organ along with mesoderm. E ...
phases of embryonic development 4
... • As the embryo grows, the caudal eminence (tail region) projects over the cloacal membrane (future site of anus). • During folding, part of the endodermal germ layer is incorporated into the embryo as the hindgut (primordium of descending colon). • The terminal part of the hindgut soon dilates slig ...
... • As the embryo grows, the caudal eminence (tail region) projects over the cloacal membrane (future site of anus). • During folding, part of the endodermal germ layer is incorporated into the embryo as the hindgut (primordium of descending colon). • The terminal part of the hindgut soon dilates slig ...
Chapter 42 Review: Embryology and Stem Cells What are the three
... 14. Where do gene regulatory substances come from? How do they get distributed into the cells of the embryo? ...
... 14. Where do gene regulatory substances come from? How do they get distributed into the cells of the embryo? ...
phylum_porifera
... secreted by endoderm cells. - Some endoderm cells use phagocytosis to engulf large particles and digestion then occurs in the endoderm cell itself. Note: There is no need for an organ systems because there are only 2 layers of cells. Water can diffuse in and carbon can diffuse out. ...
... secreted by endoderm cells. - Some endoderm cells use phagocytosis to engulf large particles and digestion then occurs in the endoderm cell itself. Note: There is no need for an organ systems because there are only 2 layers of cells. Water can diffuse in and carbon can diffuse out. ...
What are the phases of prenatal neurodevelopment?
... and proliferate. The anterior end of the neural tube ultimately develops into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The posterior end of the neural tube ultimately develops into the cerebral ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord. ...
... and proliferate. The anterior end of the neural tube ultimately develops into the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. The posterior end of the neural tube ultimately develops into the cerebral ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord. ...
NEURAL TUBE
... • The openings in the tube, the cranial and caudal neuropores remain open until the fourth week when the cranial neuropore closes followed by the caudal neuropore. • The cells of the neural crest migrate laterally to form various tissues including the peripheral ganglia, the adrenal medulla, the me ...
... • The openings in the tube, the cranial and caudal neuropores remain open until the fourth week when the cranial neuropore closes followed by the caudal neuropore. • The cells of the neural crest migrate laterally to form various tissues including the peripheral ganglia, the adrenal medulla, the me ...
Development
... layers, thus maintaining the organizational structure specified in the ventricular layer.After their last division, cohort of migrating neurons (MN) first traverse the intermediate zone (IZ) and then the subplate zone (SP) where they have an opportunity to interact with ...
... layers, thus maintaining the organizational structure specified in the ventricular layer.After their last division, cohort of migrating neurons (MN) first traverse the intermediate zone (IZ) and then the subplate zone (SP) where they have an opportunity to interact with ...
chapter42_part1 - Lower Cape May Regional School District
... Processes of Development • Organ formation • The neural tube and notochord characteristic of all chordate embryos form early • Growth and tissue specialization • Many organs incorporate tissues derived from more than one germ layer • In some animals, a larva undergoes metamorphosis – a drastic remo ...
... Processes of Development • Organ formation • The neural tube and notochord characteristic of all chordate embryos form early • Growth and tissue specialization • Many organs incorporate tissues derived from more than one germ layer • In some animals, a larva undergoes metamorphosis – a drastic remo ...
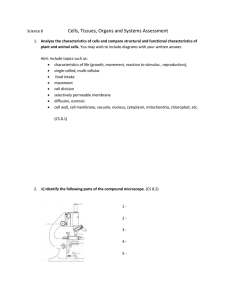
CS 8.1 - 8.4 Assessment Event
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
... B) Calculate the magnification of the following cell, which is shown under the high power field of view. (CS 8.2) ...
chapter42_part1wUnderline
... Processes of Development • Organ formation • The neural tube and notochord characteristic of all chordate embryos form early • Growth and tissue specialization • Many organs incorporate tissues derived from more than one germ layer • In some animals, a larva undergoes metamorphosis – a drastic remo ...
... Processes of Development • Organ formation • The neural tube and notochord characteristic of all chordate embryos form early • Growth and tissue specialization • Many organs incorporate tissues derived from more than one germ layer • In some animals, a larva undergoes metamorphosis – a drastic remo ...
Basic Baupläne—Architectural Styles of the Biosphere
... GASTRULA = invaginated blastula (pre- pluripotent) PLURIPOTENT = having more than one potential outcome. Often called stem cells that can differentiate into type of body tissues o Cell cleavage controls morphological development Direction of mitosis controls shape of “colony” of cells o Eukary ...
... GASTRULA = invaginated blastula (pre- pluripotent) PLURIPOTENT = having more than one potential outcome. Often called stem cells that can differentiate into type of body tissues o Cell cleavage controls morphological development Direction of mitosis controls shape of “colony” of cells o Eukary ...
Basic Bauplane
... • GASTRULA = invaginated blastula (pre- pluripotent) • PLURIPOTENT = having more than one potential outcome. Often called stem cells that can differentiate into type of body tissues o Cell cleavage controls morphological development • Direction of mitosis controls shape of “colony” of cells o Eukary ...
... • GASTRULA = invaginated blastula (pre- pluripotent) • PLURIPOTENT = having more than one potential outcome. Often called stem cells that can differentiate into type of body tissues o Cell cleavage controls morphological development • Direction of mitosis controls shape of “colony” of cells o Eukary ...
Semester 1 Exam Study Guide
... Virchow- Discovered that all cells come from living things; cell theory Janssen – first compound microscope ...
... Virchow- Discovered that all cells come from living things; cell theory Janssen – first compound microscope ...
Unit 1 From Single Cells
... called alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. 12. villi Nutrients move from the digestive system into the blood by traveling through villi, tiny tubes sticking out of the wall of the small intestine. 13. nephrons In the body’s excretory system, urea and water travel from the blood into th ...
... called alveoli, which are surrounded by capillaries. 12. villi Nutrients move from the digestive system into the blood by traveling through villi, tiny tubes sticking out of the wall of the small intestine. 13. nephrons In the body’s excretory system, urea and water travel from the blood into th ...
Development - mcguireswr
... each — one black, the other white. The odds of such a birth are about a million to one, experts said. Although occurrences of this nature sometimes occur when a woman conceives twins fathered by two different men, this was a much rarer case in which a single pairing produced twins with distinctly di ...
... each — one black, the other white. The odds of such a birth are about a million to one, experts said. Although occurrences of this nature sometimes occur when a woman conceives twins fathered by two different men, this was a much rarer case in which a single pairing produced twins with distinctly di ...
UNIT 5 Notes #3 - Phylum Cnidarian - Mr. Lesiuk
... movements and by flagellated cells in the endoderm. Thus the cavity is involved in both ___________________________________________________________________ 3) ____________________and______________________: -Both take place by ___________________________________that bathes the tissues. 4)NERVOUS: The ...
... movements and by flagellated cells in the endoderm. Thus the cavity is involved in both ___________________________________________________________________ 3) ____________________and______________________: -Both take place by ___________________________________that bathes the tissues. 4)NERVOUS: The ...
Human embryogenesis
Human embryogenesis is the process of cell division and cellular differentiation of the embryo that occurs during the early stages of development. In biological terms, human development entails growth from a one celled zygote to an adult human being. Fertilisation occurs when the sperm cell successfully enters and fuses with an egg cell (ovum). The genetic material of the sperm and egg then combine to form a single cell called a zygote and the germinal stage of prenatal development commences. Embryogenesis covers the first eight weeks of development and at the beginning of the ninth week the embryo is termed a fetus.Human embryology is the study of this development during the first eight weeks after fertilisation. The normal period of gestation (pregnancy) is nine months or 38 weeks.The germinal stage, refers to the time from fertilization, through the development of the early embryo until implantation is completed in the uterus. The germinal stage takes around 10 days.During this stage, the zygote, which is defined as an embryo because it contains a full complement of genetic material, begins to divide, in a process called cleavage. A blastocyst is then formed and implanted in the uterus. Embryogenesis continues with the next stage of gastrulation when the three germ layers of the embryo form in a process called histogenesis, and the processes of neurulation and organogenesis follow. The embryo is referred to as a fetus in the later stages of prenatal development, usually taken to be at the beginning of the ninth week. In comparison to the embryo, the fetus has more recognizable external features, and a more complete set of developing organs. The entire process of embryogenesis involves coordinated spatial and temporal changes in gene expression, cell growth and cellular differentiation. A nearly identical process occurs in other species, especially among chordates.