* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diversity – Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
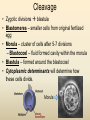
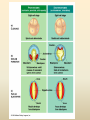
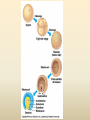
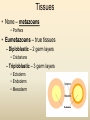
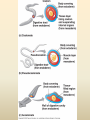
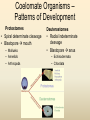
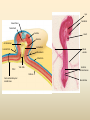
Diversity – Eukarya – Kingdom Animalia Chapter 32-34 Key Characteristics – Eukarya Kingdom Animalia • Nucleus and membrane bound organelles • Multicellular • Heterotrophic – Ingestion • NO cell walls – collagen – structural protein • Store carbs as glycogen • Nervous tissue and muscle tissue – except sponges (porifera) • Usually reproduce sexually w/ dominant diploid stage – Flagellated sperm Animal Development • Function – Zygote (unicellular) multicellular – Differentiation of cells within the multicellular unit • Tissues and organs and systems – Morphogenesis – animal taking shape Zygote 4 cell stage Early Blastula Late Blastula Cleavage • Zygotic divisions blastula • Blastomeres – smaller cells from original fertlized egg • Morula – cluster of cells after 5-7 divisions – Blastocoel – fluid formed cavity within the morula • Blastula – formed around the blastocoel • Cytoplasmic determinants will determine how these cells divide. Morula Cleavage Radial • 90 degree divisions • Direct alignment of cells • Deuterostomes – Indeterminate cleavage – Cells can become anything at this stage (twins) Spiral • Not 90 degree divisions • Cells aligned at an angle • Protostomes – Determinate cleavage – Cells fate is predetermined Gastrulation • Rearrangement of the blastula to form a 3 layered (germ layers) embryo with a gut • Blastula cells begin to infold forming the gut (digestive system) – Invagination forms archenteron (gut) – Blastopore anus (deuterostomes) – Blastopore mouth (protostomes) Symmetry • None – asymetrical – porifera • Radial – parts radiate in equal directions from the center of the organism. • Bilateral – left side and right side – Dorsal – Ventral – Anterior – Posterior Tissues • None – metazoans • Porifera • Eumetazoans – true tissues – Diploblastic – 2 germ layers • Cnidarians – Triploblastic – 3 germ layers • Ectoderm • Endoderm • Mesoderm Body Cavities • None – not triploblastic organisms – Porifera, Cniderians • Acoelomate – lack a body cavity – Plattyhelmenthes • Pseudocoelomate – fake body cavity – Rotifera, Nematoda • Coelomate – body cavity lined with mesoderm – Protostomes - Annelida, Arthropoda, Molluska, – Deuterostomes - Echinodermata, and Chordata Coelomate Organisms – Patterns of Development Protostomes • Spiral determinate cleavage • Blastopore mouth – Mollusks – Annelids – Arthropods Deuterostomes • Radial indeterminate cleavage • Blastopore anus – Echinodermata – Chordata Embryonic Germ Layers • Will form the tissues and organs of an adult triploblastic organism • Ectoderm – outer layer • Mesoderm – between ectoderm and endoderm • Endoderm – inner layer (lines digestive tract) Blastula Gastrula Ectoderm Endoderm Neuralation Lining of digestive and respiratory tract Neural Tube Brain and Spinal Cord (CNS) Mesoderm Notochord Vertebral Disks Somites Vertebrae Skeletal Muscle Eye Forebrain Neural tube Notochord Somite Heart Coelom Archenteron Endoderm Lateral fold Mesoderm Blood vessels Ectoderm YOLK Somites become bones Yolk stalk Yolk sac Form extraembryonic membranes Neural tube Embryonic Germ Layers Organogenesis Ectoderm • Skin - epidermis • Brain and Spinal cord (CNS) • Parts of eye and ear • Tooth enamel Mesoderm • • • • Skeletal system Muscle Dermis of skin Circulatory and lymphatic Systems • Excretory system • Reproductive system Endoderm • Inner digestive linings • Inner Respiratory tract • Liver • Pancreas • Bladder • Thymus • Thyroid and parathyroid