Key - Edquest
... The transportation of nutrients in plants is the role of the plant's tissue. Specialized tissue connects the roots to the leaves. The Phloem tissue transports ... water from the leaves to the air in a process called transpiration water from the roots to the leaves sugars, manufactured in the leaves ...
... The transportation of nutrients in plants is the role of the plant's tissue. Specialized tissue connects the roots to the leaves. The Phloem tissue transports ... water from the leaves to the air in a process called transpiration water from the roots to the leaves sugars, manufactured in the leaves ...
biology 103 final exam review sheet
... 22. Parts of a typical prokaryotic cell 23. Major components of eukaryotic cells 24. Know the functions of the organelles listed in the notes 25. Differences between plant and animal cells 26. Structure and functions of cell membranes 27. Types of proteins in cell membranes 28. Define the following ...
... 22. Parts of a typical prokaryotic cell 23. Major components of eukaryotic cells 24. Know the functions of the organelles listed in the notes 25. Differences between plant and animal cells 26. Structure and functions of cell membranes 27. Types of proteins in cell membranes 28. Define the following ...
Cells and Basketball
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
... When you shoot a basketball many parts of your body work together to help you make the shot! These different parts are made up of different tissues and cells. Each type of cell is specialized to perform its job in shooting a basketball. Cells can be specialized in their shape and the organelles that ...
Exam 7 Study Guide
... 41. 2nd line of defense (Non-specific patrol) Innate, general defense Patrolling proteins & cells- attack invaders that penetrate barriers. Leukocytes- neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer cells 42. Natural Killer Cells- release perforin protein causing cell to rupture. 43. Inflammator ...
... 41. 2nd line of defense (Non-specific patrol) Innate, general defense Patrolling proteins & cells- attack invaders that penetrate barriers. Leukocytes- neutrophils, macrophages, and natural killer cells 42. Natural Killer Cells- release perforin protein causing cell to rupture. 43. Inflammator ...
1 | Page Glossary: Atom: Molecule: Compound: Atomic number
... (in grams) quantity of equal to that elements atomic weight A substance that minimizes change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution fluid within cells o ...
... (in grams) quantity of equal to that elements atomic weight A substance that minimizes change in the acidity of a solution when an acid or base is added to the solution fluid within cells o ...
Chapter 2 Cells to Systems
... List five parts of all cells and their jobs. List the two parts that are only in plant cells. What are genes made of? What is the process of passing genes from one generation to the next called? ...
... List five parts of all cells and their jobs. List the two parts that are only in plant cells. What are genes made of? What is the process of passing genes from one generation to the next called? ...
Directed Reading: Exchange with the Environment
... Section: Exchange with the Environment 1. How is an organism’s cell like a factory? ...
... Section: Exchange with the Environment 1. How is an organism’s cell like a factory? ...
The Cell
... contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
... contain organelles that perform the functions needed for life. All cells must maintain homeostasis (balance). They function in a very narrow range of temperature, pH, O2, CO2, food and waste. ...
Slide 1
... A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function. There are 3 examples of tissue: • Muscular tissue, which can contract to bring about ...
... A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function. There are 3 examples of tissue: • Muscular tissue, which can contract to bring about ...
Histology
... • collagen remains and provides flexibility; matrix is mainly calcium phosphate and collagen • cell type: osteocytes § live within lacunae § have cytoplasmic processes that form a network between osteocytes; processes extend though tiny canals in the bone, or canaliculi § osteocytes remain alive ...
... • collagen remains and provides flexibility; matrix is mainly calcium phosphate and collagen • cell type: osteocytes § live within lacunae § have cytoplasmic processes that form a network between osteocytes; processes extend though tiny canals in the bone, or canaliculi § osteocytes remain alive ...
RED &WHITE BLOOD CELLS
... A very simple cell. Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
... A very simple cell. Major function is to transport oxygen to the tissues . And disposal of carbon dioxide and protons formed by the tissue metabolism. Is composed of a membrane surrounding the hemoglobin. Hb forms about 95% of the intracellular protein of the red cell. ...
4a Final Exam All
... 23. Protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because: a. they replicate inside human cells b. protozoan and helminth cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells c. they don't have ribosomes d. they have only simple reproductive structures e. they have prokaryotic r ...
... 23. Protozoan and helminthic diseases are difficult to treat because: a. they replicate inside human cells b. protozoan and helminth cells are structurally and functionally similar to human cells c. they don't have ribosomes d. they have only simple reproductive structures e. they have prokaryotic r ...
Cell Unit
... How would you divide your Halloween goodies into Kingdoms? Remember, we are trying to come up with only a few different types of classification groups. One possible way to divide the treats into kingdoms could be The Edible Kingdom, and The Non-Edible Kingdom. The word “edible” means that you can ea ...
... How would you divide your Halloween goodies into Kingdoms? Remember, we are trying to come up with only a few different types of classification groups. One possible way to divide the treats into kingdoms could be The Edible Kingdom, and The Non-Edible Kingdom. The word “edible” means that you can ea ...
Intermediate Filaments
... transport fluid or materials past them. The respiratory tract in humans is lined with cilia that keep inhaled dust, and harmful microorganisms from entering the lungs. Cilia are usually shorter and occur together in much greater numbers than flagella. In eukaryotic cells, cilia and flagella contain ...
... transport fluid or materials past them. The respiratory tract in humans is lined with cilia that keep inhaled dust, and harmful microorganisms from entering the lungs. Cilia are usually shorter and occur together in much greater numbers than flagella. In eukaryotic cells, cilia and flagella contain ...
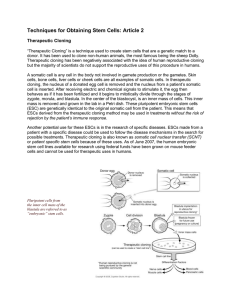
Techniques for Obtaining Stem Cells: Article 2 Therapeutic Cloning
... Therapeutic cloning has been negatively associated with the idea of human reproductive cloning but the majority of scientists do not support the reproductive uses of this procedure in humans. A somatic cell is any cell in the body not involved in gamete production or the gametes. Skin cells, bone ce ...
... Therapeutic cloning has been negatively associated with the idea of human reproductive cloning but the majority of scientists do not support the reproductive uses of this procedure in humans. A somatic cell is any cell in the body not involved in gamete production or the gametes. Skin cells, bone ce ...
What is a cell? - Epiphany Catholic School
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
... • controls materials moving into and out of the cell. • cytoplasm - region inside the cell that includes the fluid and all the organelles except for the nucleus. • organelle - small body in the cytoplasm • specialized to perform a specific function • DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)- genetic material tha ...
Unit 3 Review Study Guide
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
... Background Information: There are many different types of cells in the human body. None of these cells function on their own well. These cells are part of the larger organism that is called – human. Cells work together to form tissues. There are four main types of tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tis ...
Life Science: Cells
... transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells attack invading germs. All reproduce by mitosis, or cell division. A glitch in this process can lead to the growth of cancerous cells that crowd out healthy ones. Cells’ ability to replicate is what keeps every living thing alive. But when ...
... transporters of oxygen and carbon dioxide. White blood cells attack invading germs. All reproduce by mitosis, or cell division. A glitch in this process can lead to the growth of cancerous cells that crowd out healthy ones. Cells’ ability to replicate is what keeps every living thing alive. But when ...
Chapter Test B
... 2. Plants produce their own food by the process of ______________________. 3. Food molecules that are too large to pass easily through the cell membrane can enter the cell by ______________________. 4. Human body cells have 23 pairs of ______________________. 5. The process of cell division in a bac ...
... 2. Plants produce their own food by the process of ______________________. 3. Food molecules that are too large to pass easily through the cell membrane can enter the cell by ______________________. 4. Human body cells have 23 pairs of ______________________. 5. The process of cell division in a bac ...
Click Here for Science Words in Word DOC format
... Minerals – inorganic substances that are important for chemical reactions or as building materials in the body, Mitochondria – eukaryotic membrane-bound organelles that transform energy stored in food molecules; has a highly folded inner membrane that produces energy-storing molecules. Mitosis – per ...
... Minerals – inorganic substances that are important for chemical reactions or as building materials in the body, Mitochondria – eukaryotic membrane-bound organelles that transform energy stored in food molecules; has a highly folded inner membrane that produces energy-storing molecules. Mitosis – per ...
Science Words in Adobe Reader PDF format
... Minerals – inorganic substances that are important for chemical reactions or as building materials in the body, Mitochondria – eukaryotic membrane-bound organelles that transform energy stored in food molecules; has a highly folded inner membrane that produces energy-storing molecules. Mitosis – per ...
... Minerals – inorganic substances that are important for chemical reactions or as building materials in the body, Mitochondria – eukaryotic membrane-bound organelles that transform energy stored in food molecules; has a highly folded inner membrane that produces energy-storing molecules. Mitosis – per ...
Cells - Biloxi Public Schools
... Term 3---Cells Notes nucleus (nuclei) control center; “brain” contains the cell’s genetic material; DNA, chromosomes, traits chromosomes---genetic information of organisms nuclear surrounds the nucleus membrane thin structure that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell vacuole ...
... Term 3---Cells Notes nucleus (nuclei) control center; “brain” contains the cell’s genetic material; DNA, chromosomes, traits chromosomes---genetic information of organisms nuclear surrounds the nucleus membrane thin structure that separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell vacuole ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.