Human Anatomy and Physiology
... that are the major effectors of biological control systems. Glands: the effector may be a hormone secreted into the blood A hormone is a type of chemical messenger secreted into the blood by cells of the endocrine system (see Table 1–1) Hormones may act on many different cells simultaneously because ...
... that are the major effectors of biological control systems. Glands: the effector may be a hormone secreted into the blood A hormone is a type of chemical messenger secreted into the blood by cells of the endocrine system (see Table 1–1) Hormones may act on many different cells simultaneously because ...
10. Use a different colour for each stage of
... 3. The two upper chambers in the heart are A. the right ventricle and the left ventricle B. the right atrium and the left atrium C. the right ventricle and the right atrium D. the left ventricle and the left atrium ...
... 3. The two upper chambers in the heart are A. the right ventricle and the left ventricle B. the right atrium and the left atrium C. the right ventricle and the right atrium D. the left ventricle and the left atrium ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... 7. Two structures found in nucleoplasm are ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. The nucleolus is composed of _______________________________________ 9. The nucleolus is the site of__________________________________________ 10. Chromatin ...
... 7. Two structures found in nucleoplasm are ______________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 8. The nucleolus is composed of _______________________________________ 9. The nucleolus is the site of__________________________________________ 10. Chromatin ...
Hoerner EDAY 2
... important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remember things. Below I have placed a series of review questions regarding our Life Science unit. Please read through these pages ...
... important part of learning is reviewing to make sure that you still remember things. Below I have placed a series of review questions regarding our Life Science unit. Please read through these pages ...
unit 6. living things/biosphere
... INTERACTION WITH THE ENVIROMENT: All the processes which enable living things to react to changes in the environment. REPRODUCTION: refers to all the processes which enable living thing to create new living thing. There are two basic types: Asexual reproduction: involve one living thing. Sexual repr ...
... INTERACTION WITH THE ENVIROMENT: All the processes which enable living things to react to changes in the environment. REPRODUCTION: refers to all the processes which enable living thing to create new living thing. There are two basic types: Asexual reproduction: involve one living thing. Sexual repr ...
Science Notes
... -Red blood cells have cell membrane and cytoplasm that can be labelled as well -Red blood cells carry oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body. -The biconcave shape of the red blood cell is to increase surface area to volume ratio to increase the rate of oxygen diffusion. -An organ is made up of d ...
... -Red blood cells have cell membrane and cytoplasm that can be labelled as well -Red blood cells carry oxygen from lungs to all parts of the body. -The biconcave shape of the red blood cell is to increase surface area to volume ratio to increase the rate of oxygen diffusion. -An organ is made up of d ...
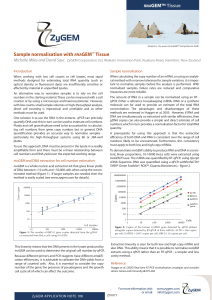
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... must apply to both low and high copy mRNAs. To demonstrate RNAGEM‘s ability to produce RNA and DNA in consistent, linear proportions, 10-10000 HeLa cells were extracted using RNAGEM Tissue. The mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR using qScript cDNA Supermix. DNA was quantified using a qPCR withPerfeCTA® ...
... must apply to both low and high copy mRNAs. To demonstrate RNAGEM‘s ability to produce RNA and DNA in consistent, linear proportions, 10-10000 HeLa cells were extracted using RNAGEM Tissue. The mRNA was quantified by RT-qPCR using qScript cDNA Supermix. DNA was quantified using a qPCR withPerfeCTA® ...
Oct 2310:58 AM Comparing Cells Lab Analysis Questions
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
... 1. Describe 3 differences between the plant cells and the animal cells you looked at. 2. Thinking about how the structure and arrangement of cells contributes to the functioning of the organism, propose reasons for the differences you mentioned. 3. Why do you think we stained the cheek cells but ...
Chapter 23
... 21. Define fetus. The fetus is the name given to the developing offspring from the end of the eighth week until birth. 22. List the major changes that occur during the fetal stage of development. In the third lunar month body growth is accelerated and the external reproductive organs appear as male ...
... 21. Define fetus. The fetus is the name given to the developing offspring from the end of the eighth week until birth. 22. List the major changes that occur during the fetal stage of development. In the third lunar month body growth is accelerated and the external reproductive organs appear as male ...
2.1-3
... • Produced in your body by absorption of energy in ultraviolet light in sunlight, xrays, by breakdown of harmful substances, & during normal metabolic reactions • Linked to many diseases -- cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer, atherosclerosis and arthritis • Damage may be slowed with antioxidants such as vi ...
... • Produced in your body by absorption of energy in ultraviolet light in sunlight, xrays, by breakdown of harmful substances, & during normal metabolic reactions • Linked to many diseases -- cancer, diabetes, Alzheimer, atherosclerosis and arthritis • Damage may be slowed with antioxidants such as vi ...
Note - WordPress.com
... Everything small enough to diffuse out of the glomerulus includes glucose, salts, vitamins, waste such as urea, and other small molecules Filtrate travels into the proximal tube Secretion is active and highly selective Occurs in proximal and distal tubules Uptake of certain drugs and toxic molecules ...
... Everything small enough to diffuse out of the glomerulus includes glucose, salts, vitamins, waste such as urea, and other small molecules Filtrate travels into the proximal tube Secretion is active and highly selective Occurs in proximal and distal tubules Uptake of certain drugs and toxic molecules ...
What is a cell?
... Organism, organelle, multicellular , unicellular, cell 1. A(n)______is the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms. 2. A(n)______ is any living thing that carries out its own life processes. 3. Organisms made up of just one cell are called ________ organisms. 4.Organisms mad ...
... Organism, organelle, multicellular , unicellular, cell 1. A(n)______is the smallest functional and structural unit of all living organisms. 2. A(n)______ is any living thing that carries out its own life processes. 3. Organisms made up of just one cell are called ________ organisms. 4.Organisms mad ...
Check In: WHAT ARE CELLS?
... 6. Are all animals made of only one cell or are they made of many cells? ...
... 6. Are all animals made of only one cell or are they made of many cells? ...
Unit IV- Nervous System
... Unit XI - excretion 1. Define excretion - the process of eliminating waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials. It is an essential process in all forms of life. It contrasts secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell. ...
... Unit XI - excretion 1. Define excretion - the process of eliminating waste products of metabolism and other non-useful materials. It is an essential process in all forms of life. It contrasts secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks after leaving the cell. ...
Cells of the Respiratory System
... how the sticky mucus traps many pathogens and particles and facilitates removal from the body. Yet the mucus does not trap all inhaled particles. Particles that make it to the level of the alveoli are typically removed by alveolar macrophages through the process of phagocytosis. ...
... how the sticky mucus traps many pathogens and particles and facilitates removal from the body. Yet the mucus does not trap all inhaled particles. Particles that make it to the level of the alveoli are typically removed by alveolar macrophages through the process of phagocytosis. ...
Lab on chip for rapid diagnosis of infectious diseases
... and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses or civil protection measures. ...
... and microbiological tests, the future areas of application also comprise environmental analyses or civil protection measures. ...
Tissues: Living Communities
... the basement membrane from the connective tissue. Absorbed substances and waste products produced by epithelium diffuse down through basement membrane to the connective tissue. ...
... the basement membrane from the connective tissue. Absorbed substances and waste products produced by epithelium diffuse down through basement membrane to the connective tissue. ...
Immunological Methods AppendixIII
... CFSE is partitioned equally among daughter cells with each division. These properties allows simultaneous analysis of cell number, position, as well as division status. • Fluorochromes compatible with fluorescein can be used to probe other cellular properties. Dilution of CFSE with cell division ...
... CFSE is partitioned equally among daughter cells with each division. These properties allows simultaneous analysis of cell number, position, as well as division status. • Fluorochromes compatible with fluorescein can be used to probe other cellular properties. Dilution of CFSE with cell division ...
BIO 1101 - Makerere University Courses
... This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this course, learners are expected to be able to: 1. Describe ...
... This course is designed to acquaint biology student-teachers with knowledge about the cell theory and origin of life. It also describes the functions, structures and division processes of biological cells. COURSE OBJECTIVES By the end of this course, learners are expected to be able to: 1. Describe ...
Topic 1 – Measurement and graphing
... Control variables: The size of the body, the launcher, the amount of water. Hypothesis: If the number of fins increases, then the rocket will fly higher. ...
... Control variables: The size of the body, the launcher, the amount of water. Hypothesis: If the number of fins increases, then the rocket will fly higher. ...
Differentiation and containment of derived pancreatic beta cells
... States, according to the American Diabetes Association. Currently, the only permanent cure for T1D is a pancreatic or islet transplant. With a large shortage of available donors, our work is progressing research towards alternative therapies by differentiating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) ...
... States, according to the American Diabetes Association. Currently, the only permanent cure for T1D is a pancreatic or islet transplant. With a large shortage of available donors, our work is progressing research towards alternative therapies by differentiating induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) ...
Question Bank 1
... Active transport – movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the molecule used in cell processes as a supply of energy; it is produced by cells during cellular respi ...
... Active transport – movement of matter into, or out of, a cell which requires energy from the cell; usually this involves movement against the concentration gradient Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) – the molecule used in cell processes as a supply of energy; it is produced by cells during cellular respi ...
Goal 6: Cell Theory Review Guide
... 11. Mature human red blood cells have no nucleus or mitochondria. How does the lack of these organelles affect these cells? Human RBCs have nuclei in the beginning of their life but get ride of them as they mature in order to provide more space for hemoglobin. They also lose their other organelles s ...
... 11. Mature human red blood cells have no nucleus or mitochondria. How does the lack of these organelles affect these cells? Human RBCs have nuclei in the beginning of their life but get ride of them as they mature in order to provide more space for hemoglobin. They also lose their other organelles s ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.