Unit 1 revision - Groby Bio Page
... What affects the rate of diffusion? Concentration gradient, area of the exchange surface and thickness of the exchange surface What is facilitated diffusion? Diffusion through protein channels in the plasma membrane. These channels are selective. Alternatively, it can be through carrier proteins tha ...
... What affects the rate of diffusion? Concentration gradient, area of the exchange surface and thickness of the exchange surface What is facilitated diffusion? Diffusion through protein channels in the plasma membrane. These channels are selective. Alternatively, it can be through carrier proteins tha ...
BASIC INTRO TAXONOMY CELL THEORY PROKARYOTES
... Volume increases more rapidly than the surface area. Do you think a large cell or a small cell is more efficient? ...
... Volume increases more rapidly than the surface area. Do you think a large cell or a small cell is more efficient? ...
Animal Structure and FUNction
... Lymphocytes form from stem cells in bone marrow or in the liver of a fetus L’s that migrate from the marrow to the thymus develop into T cells L’s that remain in the bone marrow and mature there are called B cells L’s that bear receptors for molecules already present in the body are either r ...
... Lymphocytes form from stem cells in bone marrow or in the liver of a fetus L’s that migrate from the marrow to the thymus develop into T cells L’s that remain in the bone marrow and mature there are called B cells L’s that bear receptors for molecules already present in the body are either r ...
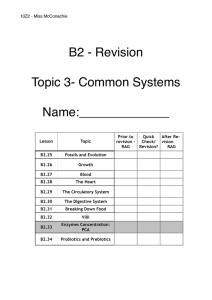
b2- revision booklet topic 3
... The fossil record is incomplete and has many gaps. These gaps mean that scientists must interpret how organisms change over time from incomplete data. How might this lead some people to believe in divine intelligence and not evolution?! ...
... The fossil record is incomplete and has many gaps. These gaps mean that scientists must interpret how organisms change over time from incomplete data. How might this lead some people to believe in divine intelligence and not evolution?! ...
Exam 1
... 35. In the reaction (H2O + CO2 H2CO3), increasing the concentration of H2O would A. decrease the concentration of H2CO3. B. increase the concentration of CO2. C. have no effect on either CO2 or H2CO3 concentrations. *D. increase the concentration of H2CO3. 36. In an enzymatic reaction, when temper ...
... 35. In the reaction (H2O + CO2 H2CO3), increasing the concentration of H2O would A. decrease the concentration of H2CO3. B. increase the concentration of CO2. C. have no effect on either CO2 or H2CO3 concentrations. *D. increase the concentration of H2CO3. 36. In an enzymatic reaction, when temper ...
Cell - Del Mar College
... DNA containing region • Nucleus in eukaryotic cells • Nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells ...
... DNA containing region • Nucleus in eukaryotic cells • Nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells ...
Document
... DNA containing region • Nucleus in eukaryotic cells • Nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells ...
... DNA containing region • Nucleus in eukaryotic cells • Nucleoid region in prokaryotic cells ...
Review Guide for Body Systems and Cells Test
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
... Key Concept 3: The skeletal system holds organs in place, provides a structural support for the body and its muscles, stores minerals and contains materials to make new blood cells. Key Concept 4: The muscular system allows the body to move when attached to bone, and allows movement in internal orga ...
File - Wildcat Biology Review
... Sickle cell anemia: recessive genetic disorder in which red blood cells take on an unusual shape, leading to other problems with the blood (African American – associated with malaria affected regions) Huttington’s disease: Dominant genetic disorder in which a protein is produced abnormally, leading ...
... Sickle cell anemia: recessive genetic disorder in which red blood cells take on an unusual shape, leading to other problems with the blood (African American – associated with malaria affected regions) Huttington’s disease: Dominant genetic disorder in which a protein is produced abnormally, leading ...
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
... Our cell membranes are in charge of what enters and exits the cell. Dissolved substances and very small molecules (i.e. oxygen, glucose, amino acids and water) can move in and out of cells by diff ...
... Our cell membranes are in charge of what enters and exits the cell. Dissolved substances and very small molecules (i.e. oxygen, glucose, amino acids and water) can move in and out of cells by diff ...
Cells Practice Test - Crossroads Academy
... 45) To the first decimal place, how many billion years ago did life arise on Earth? ANSWER: 46) What is the plural of genus? 47) What is the meaning of the scientific term, endosymbiosis? ANSWER: 48) What are the three taxonomical Domains? ANSWER: 49) Proteins are most directly made from a temporar ...
... 45) To the first decimal place, how many billion years ago did life arise on Earth? ANSWER: 46) What is the plural of genus? 47) What is the meaning of the scientific term, endosymbiosis? ANSWER: 48) What are the three taxonomical Domains? ANSWER: 49) Proteins are most directly made from a temporar ...
Class - Educast
... Plant cells are surrounded by a non living and rigid coat called cell wall. The cell wall is not a living part of the cell. Cell walls are significantly thicker than plasma membranes. It is responsible for the shape of plants and controls the growth rate of plant cells. Walls are a layered stru ...
... Plant cells are surrounded by a non living and rigid coat called cell wall. The cell wall is not a living part of the cell. Cell walls are significantly thicker than plasma membranes. It is responsible for the shape of plants and controls the growth rate of plant cells. Walls are a layered stru ...
Slide 1
... In unicellular organisms- collections of genetically identical cells that live together in a closely connected group- example: VOLVOX- a colonial algae In a Unicellular Organism, one cell carries out all of the functions of life. In a Multicellular Organism, cells are Specialized to perform one or a ...
... In unicellular organisms- collections of genetically identical cells that live together in a closely connected group- example: VOLVOX- a colonial algae In a Unicellular Organism, one cell carries out all of the functions of life. In a Multicellular Organism, cells are Specialized to perform one or a ...
Ultimate AP BIOLOGY REVIE - Page County Public Schools
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) can be used during Gel Electrophoresis but can also be used to sequence DNA › PCR will amplify the gene to be studied › PCR will allow scientist to study genetic ...
... Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) can be used during Gel Electrophoresis but can also be used to sequence DNA › PCR will amplify the gene to be studied › PCR will allow scientist to study genetic ...
1. - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
1. - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... • Cells are the basic unit of structure for all living things. • Cells are the basic unit of function for all living things. • All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
Topic 1.1 Why are cells important?
... uch of this unit focuses on how cells function, divide, and work together. But before you read any further, take a moment to think about one very important question: Why should we learn about cells? The answer is that studying cells helps us understand how organisms, including humans, function. Afte ...
... uch of this unit focuses on how cells function, divide, and work together. But before you read any further, take a moment to think about one very important question: Why should we learn about cells? The answer is that studying cells helps us understand how organisms, including humans, function. Afte ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... 2. A concentration gradient is the difference in concentrations. 3. Diffusional equilibrium is the condition of having a uniform concentration of substances throughout a solution. 4. Substances diffuse down a concentration gradient. 5. Two conditions that allow a substance to diffuse across a membra ...
... 2. A concentration gradient is the difference in concentrations. 3. Diffusional equilibrium is the condition of having a uniform concentration of substances throughout a solution. 4. Substances diffuse down a concentration gradient. 5. Two conditions that allow a substance to diffuse across a membra ...
Chapter 3: Cells
... 2. A concentration gradient is the difference in concentrations. 3. Diffusional equilibrium is the condition of having a uniform concentration of substances throughout a solution. 4. Substances diffuse down a concentration gradient. 5. Two conditions that allow a substance to diffuse across a membra ...
... 2. A concentration gradient is the difference in concentrations. 3. Diffusional equilibrium is the condition of having a uniform concentration of substances throughout a solution. 4. Substances diffuse down a concentration gradient. 5. Two conditions that allow a substance to diffuse across a membra ...
Blood Cell Formation
... Attracted by bacterial products and are first line of defense in inflammatory response ...
... Attracted by bacterial products and are first line of defense in inflammatory response ...
cells - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... Tell two of the parts of the cell theory. *All living things are made of cells. *Cells are the basic units of structure & function in an organism * Cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... Tell two of the parts of the cell theory. *All living things are made of cells. *Cells are the basic units of structure & function in an organism * Cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Chapter 1: Cells, Reproduction, and Heredity
... Lesson 4 - How Are Traits Inherited? 62 – Dominant and Recessive Factors Traits of the first generation had only one kind of trait. The traits of their offspring, always had a ratio of 3:1. One factor stays hidden in the first generation, but seen in the second generation. Some factors are stronger ...
... Lesson 4 - How Are Traits Inherited? 62 – Dominant and Recessive Factors Traits of the first generation had only one kind of trait. The traits of their offspring, always had a ratio of 3:1. One factor stays hidden in the first generation, but seen in the second generation. Some factors are stronger ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.