Diffusion and Human body
... The cell is the basic functional unit of all living things. If one is to understand what is happening within an organism, it is necessary to study what is happening to the individual cells within the organism .The cell membrane, sometimes referred to as the plasma membrane, is a phospholipid bilayer ...
... The cell is the basic functional unit of all living things. If one is to understand what is happening within an organism, it is necessary to study what is happening to the individual cells within the organism .The cell membrane, sometimes referred to as the plasma membrane, is a phospholipid bilayer ...
Unit 2 Homework
... why this is the case. (1) 4. Construct a table to compare the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries. (6) 5. What is the name given to the red blood pigment haemoglobin when it combines with oxygen? (1) Total 13 marks ...
... why this is the case. (1) 4. Construct a table to compare the structure and function of arteries, veins and capillaries. (6) 5. What is the name given to the red blood pigment haemoglobin when it combines with oxygen? (1) Total 13 marks ...
Biology Mid Year Exam Revision
... Aerobic Respiration The process of releasing energy from food in cells. Aerobic respiration ‐ uses oxygen. All chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. ...
... Aerobic Respiration The process of releasing energy from food in cells. Aerobic respiration ‐ uses oxygen. All chemical reactions inside cells are controlled by enzymes. ...
SelfAssessment 1 – Cells
... The cell membrane consists of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. Passive transport is with the concentration gradient and does not require energy. The importance of diffusion in cells as the movement of molecules along a concentration gradient. Osmosis as the movement of water ...
... The cell membrane consists of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. Passive transport is with the concentration gradient and does not require energy. The importance of diffusion in cells as the movement of molecules along a concentration gradient. Osmosis as the movement of water ...
Six Grade Science Vocabulary
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
... concentration of white blood cells found in lymph nodes. A network of organs and tissues that collect the fluid that leaks from blood and returns it to blood vessels; includes lymph nodes, lymph vessels, and lymph; the place where certain white blood cells mature. A cell organelle that contains dige ...
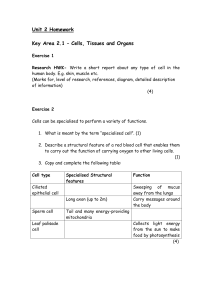
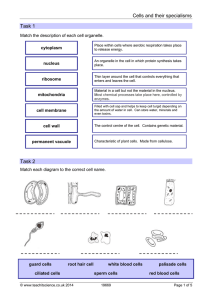
Cells and their specialisms Task 1 Task 2
... Material in a cell but not the material in the nucleus. Most chemical processes take place here, controlled by enzymes. The control centre of the cell. Contains genetic material. An organelle in the cell in which protein synthesis takes place. Place within cells where aerobic respiration takes place ...
... Material in a cell but not the material in the nucleus. Most chemical processes take place here, controlled by enzymes. The control centre of the cell. Contains genetic material. An organelle in the cell in which protein synthesis takes place. Place within cells where aerobic respiration takes place ...
Background - WordPress.com
... which a relationship between the HEPES and bicarbonate exists for differing CO2 levels, although, HEPES alone can maintain pH in the absence of exogenous CO2. ...
... which a relationship between the HEPES and bicarbonate exists for differing CO2 levels, although, HEPES alone can maintain pH in the absence of exogenous CO2. ...
Important Properties of Water
... Osmosis = the diffusion of water across a differentially permeable membrane. There are three possible conditions in regards to a cell's water concentration relative to its environment: 1. Isotonic = The solute concentration is the same on either side of the cell membrane. This is the condition o ...
... Osmosis = the diffusion of water across a differentially permeable membrane. There are three possible conditions in regards to a cell's water concentration relative to its environment: 1. Isotonic = The solute concentration is the same on either side of the cell membrane. This is the condition o ...
... atoms and can be arranged into large molecular structures such as chromosomes, proteins, and membranes. Some of these proteins may be grouped together to become the organelles that make up your cells. • Organelle – Cells also have a set of "little organs", called organelles, that are adapted and/or ...
1 Light Microscopes Electron Microscopes • The simplest form of
... Red blood cells contain haemoglobin and are responsible for carrying oxygen around the body; the fact that they are small in size allows them to pass through narrow capillaries. Red blood cells do not contain a nucleus and other organelles this means that there is more space inside the cell for haem ...
... Red blood cells contain haemoglobin and are responsible for carrying oxygen around the body; the fact that they are small in size allows them to pass through narrow capillaries. Red blood cells do not contain a nucleus and other organelles this means that there is more space inside the cell for haem ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Packet
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
Keystone Exam Review Power Point
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
Biology Keystone Exam Review Power Point
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is a la ...
UNIT 3 -CELLS, HISTOLOGY, INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... The serous membrane covering the heart is known as the _______________, whereas that covering the lungs is called the _______________. The serous membrane over abdominal organs is the _____________. The portion of serous membranes that covers organs (viscera ) is called the ______________ layer; tha ...
... The serous membrane covering the heart is known as the _______________, whereas that covering the lungs is called the _______________. The serous membrane over abdominal organs is the _____________. The portion of serous membranes that covers organs (viscera ) is called the ______________ layer; tha ...
Unit 4 Tissue Assignment
... The serous membrane covering the heart is known as the _______________, whereas that covering the lungs is called the _______________. The serous membrane over abdominal organs is the _____________. The portion of serous membranes that covers organs (viscera ) is called the ______________ layer; tha ...
... The serous membrane covering the heart is known as the _______________, whereas that covering the lungs is called the _______________. The serous membrane over abdominal organs is the _____________. The portion of serous membranes that covers organs (viscera ) is called the ______________ layer; tha ...
Holiday Packet 2
... a. The red blood cells will absorb water and increase in size. b. The red blood cells will lose water and decrease in size. c. The red blood cells will first absorb water, then lose water and maintain their normal size. d. The red blood cells will first lose water, then absorb water, and finally dou ...
... a. The red blood cells will absorb water and increase in size. b. The red blood cells will lose water and decrease in size. c. The red blood cells will first absorb water, then lose water and maintain their normal size. d. The red blood cells will first lose water, then absorb water, and finally dou ...
• B2.1.1 Cells and cell structure • B2.1.2 Dissolved substances No
... Characteristics are passed on from one generation to the next in both plants and animals. Simple genetic diagrams can be used to show this. There are ethical considerations in treating genetic disorders. Higher Tier - construct genetic diagrams of monohybrid crosses and predict the outcomes of monoh ...
... Characteristics are passed on from one generation to the next in both plants and animals. Simple genetic diagrams can be used to show this. There are ethical considerations in treating genetic disorders. Higher Tier - construct genetic diagrams of monohybrid crosses and predict the outcomes of monoh ...
are
... Brief electrical pulses that create a temporary hole in the plasma membrane through which DNA can enter ...
... Brief electrical pulses that create a temporary hole in the plasma membrane through which DNA can enter ...
Biology Review Answers
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is ...
... Due to the fact that they are highly charged molecules (and “hate” the nonpolar cell membrane and can’t pass through it) and are trying to move against a concentration gradient (from low high), sodium and potassium ions require a protein and energy to move across the cell membrane. Glucose is ...
Metric System
... Salt and water can be in a variety of _______________________________ which make the water more or less salty. diffusion: the movement of molecules in a ______________________ from an area of ___________________ concentration to an area of _________________________ concentration. ...
... Salt and water can be in a variety of _______________________________ which make the water more or less salty. diffusion: the movement of molecules in a ______________________ from an area of ___________________ concentration to an area of _________________________ concentration. ...
chapter28_Sections 1
... through extracellular fluid is limited • Vertebrates developed a circulatory system to transport substances ...
... through extracellular fluid is limited • Vertebrates developed a circulatory system to transport substances ...
Regents Packet Green
... Once again units of measurement must be written with the title. 3. The independent variable is always plotted on the x-axis. 4. The dependent variable is always plotted on the y-axis. 5. The x and y axis must be numbered. a. These numbers must increase by a uniform increment (that is you must count ...
... Once again units of measurement must be written with the title. 3. The independent variable is always plotted on the x-axis. 4. The dependent variable is always plotted on the y-axis. 5. The x and y axis must be numbered. a. These numbers must increase by a uniform increment (that is you must count ...
Benchmark SC.F.1.2.4: The student knows that similar cells
... • All living organisms are made up of cells • “building blocks of life” • Mold on bread, your dog, pine trees, etc. are all made up of cells • Cells are so small, they need to be magnified to be seen • Microscopes are used to magnify cells ...
... • All living organisms are made up of cells • “building blocks of life” • Mold on bread, your dog, pine trees, etc. are all made up of cells • Cells are so small, they need to be magnified to be seen • Microscopes are used to magnify cells ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.