I. Introduction
... 2. Senescence is the result of the normal wear-and-tear of body parts over many years. 3. Major events of senescence include loss of memory and intellectual functions, loss of coordination and sensory functions, and decreased immune responses. 4. Death usually results from mechanical disturbances in ...
... 2. Senescence is the result of the normal wear-and-tear of body parts over many years. 3. Major events of senescence include loss of memory and intellectual functions, loss of coordination and sensory functions, and decreased immune responses. 4. Death usually results from mechanical disturbances in ...
Human Organ Systems
... 2. Students observe plant and animal cells. Make copies of Student Resource 1.3, What Do Cells Look Like? and distribute to students. Have groups observe the onion cells and cheek cells at the microscope stations you have set up. Explain that the yellowish-brown color of each cell’s nucleus is from ...
... 2. Students observe plant and animal cells. Make copies of Student Resource 1.3, What Do Cells Look Like? and distribute to students. Have groups observe the onion cells and cheek cells at the microscope stations you have set up. Explain that the yellowish-brown color of each cell’s nucleus is from ...
Mock Exam III
... a. Nervous and chemical signals. b. Medulla breathing center impulses. c. A drop in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid. d. Severe deficiencies of oxygen. e. All of the above. 19. Which of the following are similarities between open and closed circulatory systems? a. Pumping device that helps to move bloo ...
... a. Nervous and chemical signals. b. Medulla breathing center impulses. c. A drop in the pH of cerebrospinal fluid. d. Severe deficiencies of oxygen. e. All of the above. 19. Which of the following are similarities between open and closed circulatory systems? a. Pumping device that helps to move bloo ...
Cells and Systems
... 1. What are organelles? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. How do mitochondria provide cells with energy? _____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ ...
... 1. What are organelles? _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. How do mitochondria provide cells with energy? _____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________ ...
Red Blood Cells
... muscles force food all the way from the esophagus in the throat to the rectum, much as if toothpaste were being squeezed along its tube by some built-in power in the tube walls. These peristaltic waves are so powerful that they will move swallowed food even if you stand on your head! The stomach is ...
... muscles force food all the way from the esophagus in the throat to the rectum, much as if toothpaste were being squeezed along its tube by some built-in power in the tube walls. These peristaltic waves are so powerful that they will move swallowed food even if you stand on your head! The stomach is ...
Document
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions plants are grown in can be changed to promote growth. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: ■ interpret da ...
... Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil. The conditions plants are grown in can be changed to promote growth. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: ■ interpret da ...
Alexa Fluor® 700 Mouse Anti-Human
... This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test). An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest. Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols ...
... This reagent has been pre-diluted for use at the recommended Volume per Test. We typically use 1 × 10^6 cells in a 100-µl experimental sample (a test). An isotype control should be used at the same concentration as the antibody of interest. Please refer to www.bdbiosciences.com/pharmingen/protocols ...
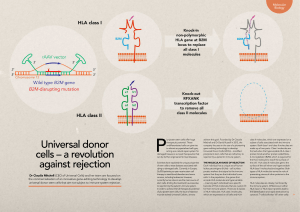
Universal donor cells – a revolution against rejection
... company focuses on the use of a pioneering gene-editing technology to develop Universal Donor Cells (UDCs) – modified pluripotent stem cells that are refractory to rejection by a patients’ immune system. ...
... company focuses on the use of a pioneering gene-editing technology to develop Universal Donor Cells (UDCs) – modified pluripotent stem cells that are refractory to rejection by a patients’ immune system. ...
301 Amy Young Three Definitions
... Erythrocytes live around 120 days in the bloodstream because of the wear and tear their membranes faces as they squeeze through capillaries (tiny blood vessels in the lungs). Worn out red blood cells are destroyed by macrophages (scavenger cells) in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow. When red blood ...
... Erythrocytes live around 120 days in the bloodstream because of the wear and tear their membranes faces as they squeeze through capillaries (tiny blood vessels in the lungs). Worn out red blood cells are destroyed by macrophages (scavenger cells) in the spleen, liver, and bone marrow. When red blood ...
Cells - Open Equal Free
... In plants and animals, atoms come together to form molecules, which come together to form all the parts of a cell. Cells are called the building blocks of life. A cell is the smallest living thing that can function on its own. Cells are the basic unit of all living things: plants, animals, fungi, a ...
... In plants and animals, atoms come together to form molecules, which come together to form all the parts of a cell. Cells are called the building blocks of life. A cell is the smallest living thing that can function on its own. Cells are the basic unit of all living things: plants, animals, fungi, a ...
water - Lisle CUSD 202
... membrane has a higher concentration of substances than the other side ...
... membrane has a higher concentration of substances than the other side ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems - E
... They are able to combine carbon dioxide and water by using the energy from light. By doing this they release oxygen and glucose. ...
... They are able to combine carbon dioxide and water by using the energy from light. By doing this they release oxygen and glucose. ...
CP biology mitosis notes
... cells come from a three-to-five-day-old cluster of cells. These cells are entirely undifferentiated and can form any type of cell in the human body. ...
... cells come from a three-to-five-day-old cluster of cells. These cells are entirely undifferentiated and can form any type of cell in the human body. ...
Cells, Tissues, Organs and Organ Systems
... They are able to combine carbon dioxide and water by using the energy from light. By doing this they release oxygen and glucose. ...
... They are able to combine carbon dioxide and water by using the energy from light. By doing this they release oxygen and glucose. ...
Diversity of Life Notes
... 1. Most viruses infect only specific kinds of cells. 2. Viruses are often carried to the host through the air 3. The virus and host cell must fit together exactly to begin a viral infection. 4. Bacteriophages attach to bacteria and inject their hereditary material. D. Fighting viruses ...
... 1. Most viruses infect only specific kinds of cells. 2. Viruses are often carried to the host through the air 3. The virus and host cell must fit together exactly to begin a viral infection. 4. Bacteriophages attach to bacteria and inject their hereditary material. D. Fighting viruses ...
LIVNG THING AND THEIR STRUCTURE
... grow. They need the right temperatures in their surroundings. Living things meet their needs by doing certain activities. Activities of living things Nutrition: All living things need food. Nutrition is how living things take and use food. Cells use foods to grow and make cells. o Respiration: Whe ...
... grow. They need the right temperatures in their surroundings. Living things meet their needs by doing certain activities. Activities of living things Nutrition: All living things need food. Nutrition is how living things take and use food. Cells use foods to grow and make cells. o Respiration: Whe ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.