Grade 6 Life Posttest
... What conclusion can Jacob make when he compares the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria in plant cells? A. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work together inside a plant cell. B. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work independently of one another. C. Light energy also drives the chemical reactions in ...
... What conclusion can Jacob make when he compares the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria in plant cells? A. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work together inside a plant cell. B. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work independently of one another. C. Light energy also drives the chemical reactions in ...
Grade 6 Life Posttest
... What conclusion can Jacob make when he compares the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria in plant cells? A. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work together inside a plant cell. B. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work independently of one another. C. Light energy also drives the chemical reactions in ...
... What conclusion can Jacob make when he compares the function of chloroplasts and mitochondria in plant cells? A. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work together inside a plant cell. B. Chloroplasts and mitochondria work independently of one another. C. Light energy also drives the chemical reactions in ...
8 - Hatboro
... The bladder technique was developed by Anthony Atala of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine in Winston-Salem, North Carolina. Researchers take healthy cells from a patient's diseased bladder, cause them to multiply profusely in petri dishes, then apply them to a balloon-shaped scaffo ...
... The bladder technique was developed by Anthony Atala of the Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine in Winston-Salem, North Carolina. Researchers take healthy cells from a patient's diseased bladder, cause them to multiply profusely in petri dishes, then apply them to a balloon-shaped scaffo ...
Question 37. - VCE
... From your studies in biology this year, it would be reasonable to assume that these two cells A. each have a nucleus to control their activity. B. would have a high surface area to volume ratio to maximize the uptake of oxygen. C. would each contain 46 chromosomes. D. would be able to divide and dev ...
... From your studies in biology this year, it would be reasonable to assume that these two cells A. each have a nucleus to control their activity. B. would have a high surface area to volume ratio to maximize the uptake of oxygen. C. would each contain 46 chromosomes. D. would be able to divide and dev ...
2006, Biology
... B. They are cycled through ecosystems. C. They are replaced by volcanic eruptions. D. They are produced constantly from nutrients. ...
... B. They are cycled through ecosystems. C. They are replaced by volcanic eruptions. D. They are produced constantly from nutrients. ...
1.4 packet
... In this activity, you will build a paper chain according to specific steps to explore the advantages of specialization. Many of the tasks that are performed in the human body require multiple steps. Different cells may perform different steps in the process. In this activity, you will first build th ...
... In this activity, you will build a paper chain according to specific steps to explore the advantages of specialization. Many of the tasks that are performed in the human body require multiple steps. Different cells may perform different steps in the process. In this activity, you will first build th ...
Biology Notes-Teacher (chapters 7, 8, 9)
... ATP energy and carrier proteins to pump these molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. - used to accumulate nutrients, or remove toxic materials or wastes Most cells use 40% of their energy on active transport; kidney cells use 90% of their energy o ...
... ATP energy and carrier proteins to pump these molecules from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high solute concentration. - used to accumulate nutrients, or remove toxic materials or wastes Most cells use 40% of their energy on active transport; kidney cells use 90% of their energy o ...
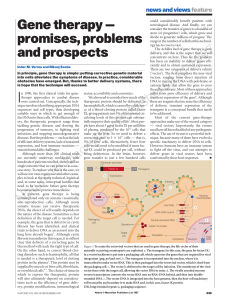
Gene therapy
... fibres. So perhaps successful animal models will prove inadequate when the same protocols are extended to humans. Moreover, these models are based on inbred animals — the outbred human population, with individual variation, will add yet another degree of complexity. The haematopoietic (bloodproducin ...
... fibres. So perhaps successful animal models will prove inadequate when the same protocols are extended to humans. Moreover, these models are based on inbred animals — the outbred human population, with individual variation, will add yet another degree of complexity. The haematopoietic (bloodproducin ...
The Cell - Twig World
... by mitosis compare to the original cell? The cells produced, called daughter cells, are genetically identical containing exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell. In humans, a cell with 46 chromosomes creates two cells, each with 46 identical chromosomes. This is achieved b ...
... by mitosis compare to the original cell? The cells produced, called daughter cells, are genetically identical containing exactly the same number and type of chromosomes as the parent cell. In humans, a cell with 46 chromosomes creates two cells, each with 46 identical chromosomes. This is achieved b ...
BIOL-2401-Holes-chapt03_holes_lecture
... provide a mitotic clock • Cells divide to provide a more favorable surface area to volume relationship • Growth factors and hormones stimulate cell division • Hormones stimulate mitosis of smooth muscle cells in uterus • Epidermal growth factor stimulates growth of new skin ...
... provide a mitotic clock • Cells divide to provide a more favorable surface area to volume relationship • Growth factors and hormones stimulate cell division • Hormones stimulate mitosis of smooth muscle cells in uterus • Epidermal growth factor stimulates growth of new skin ...
Grade 6 Life Pretest
... 9. All cells use similar processes to maintain homeostasis. However, there is one process that plants cells, but NOT animal cells, use to maintain homeostasis. This process is shown in the diagram below. ...
... 9. All cells use similar processes to maintain homeostasis. However, there is one process that plants cells, but NOT animal cells, use to maintain homeostasis. This process is shown in the diagram below. ...
Word Roots - Jennifer`s e
... con- = with; -vect = carried (convection: the mass movement of warmed air or liquid to or from the surface of a body or object) conjug- = together (conjugation: in bacteria, the transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined) contra- = against (contraception: the prevention of pregnan ...
... con- = with; -vect = carried (convection: the mass movement of warmed air or liquid to or from the surface of a body or object) conjug- = together (conjugation: in bacteria, the transfer of DNA between two cells that are temporarily joined) contra- = against (contraception: the prevention of pregnan ...
Z00-302(1.1)
... fit inside the nucleus. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells each have genomes, which is what we call the entire set of an organism's genetic and hereditary information. Genomes are entirely encoded in either the DNA or the RNA. In the case of eukaryotes, multiple linear pieces of DNA comprise its ...
... fit inside the nucleus. Both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells each have genomes, which is what we call the entire set of an organism's genetic and hereditary information. Genomes are entirely encoded in either the DNA or the RNA. In the case of eukaryotes, multiple linear pieces of DNA comprise its ...
Chapter 3 (Cells Review)
... provide a mitotic clock • Cells divide to provide a more favorable surface area to volume relationship • Growth factors and hormones stimulate cell division • Hormones stimulate mitosis of smooth muscle cells in uterus • Epidermal growth factor stimulates growth of new skin ...
... provide a mitotic clock • Cells divide to provide a more favorable surface area to volume relationship • Growth factors and hormones stimulate cell division • Hormones stimulate mitosis of smooth muscle cells in uterus • Epidermal growth factor stimulates growth of new skin ...
fundamental unit of life biology
... 5. Some enzymatic activity is also known to occur within the cell wall. 6. The cell wall gives the rigidity to the plant cell. 7. It maintains the shape of the plant cell. 8. It protects the internal organelles from external injuries. PLASMA MEMBRANE :It is the outer covering of most of the animal c ...
... 5. Some enzymatic activity is also known to occur within the cell wall. 6. The cell wall gives the rigidity to the plant cell. 7. It maintains the shape of the plant cell. 8. It protects the internal organelles from external injuries. PLASMA MEMBRANE :It is the outer covering of most of the animal c ...
Winter 2016 USC Stem Cell Newsletter
... “I love what I do, and I want to keep being a scientist as long as I can. It’s a privilege to get to do this.” ...
... “I love what I do, and I want to keep being a scientist as long as I can. It’s a privilege to get to do this.” ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... Lysosomes break down cellular waste products, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and other macromolecules into simple compounds, which are then transferred back into the cytoplasm as new cell-building materials. • Lysosomes are often made from the membrane of the golgi bodies. ...
... Lysosomes break down cellular waste products, fats, carbohydrates, proteins, and other macromolecules into simple compounds, which are then transferred back into the cytoplasm as new cell-building materials. • Lysosomes are often made from the membrane of the golgi bodies. ...
Prepared by Ms. Bowie Biology 11 Exam Preparation Notes Page 1
... environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules. Transport proteins, such as globular proteins, transport molecules across cell membranes through facilitated diffusion. Glycoproteins have a carbohydrate chain attached to them. They are embedded in the cell me ...
... environment through the use of hormones, neurotransmitters and other signaling molecules. Transport proteins, such as globular proteins, transport molecules across cell membranes through facilitated diffusion. Glycoproteins have a carbohydrate chain attached to them. They are embedded in the cell me ...
A. Why is cell division important?
... 2. However, bacteria do not have a nucleus so they can’t use mitosis. Instead, bacteria reproduce asexually by fission. 3. During fission, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides into two identical organisms. ...
... 2. However, bacteria do not have a nucleus so they can’t use mitosis. Instead, bacteria reproduce asexually by fission. 3. During fission, an organism whose cells do not contain a nucleus copies its genetic material and then divides into two identical organisms. ...
Unit 7A Cells
... The amoeba is a protozoan that belongs to the Kingdom Protista. The name amoeba comes from the Greek word amoibe, which means change. (Amoeba is also spelled amoeba.) Protists are microscopic unicellular organisms that don't fit into the other kingdoms. Some protozoans are considered plant-like whil ...
... The amoeba is a protozoan that belongs to the Kingdom Protista. The name amoeba comes from the Greek word amoibe, which means change. (Amoeba is also spelled amoeba.) Protists are microscopic unicellular organisms that don't fit into the other kingdoms. Some protozoans are considered plant-like whil ...
Chapter 1 - The Science of Biology - holyoke
... Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid Cholesterol embedded in the membrane makes it stronger and less fluid ...
... Phospholipids are not bonded to each other, which makes the double layer fluid Cholesterol embedded in the membrane makes it stronger and less fluid ...
Glossary
... inhibiting the firing of the sinoatrial node. (9.3) acoelomates animals with three cell layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm), but no body cavities such as cnidaria and flatworms. (13.3) acquired immune response a response through which the body’s resistance to a specific pathogen is built up ov ...
... inhibiting the firing of the sinoatrial node. (9.3) acoelomates animals with three cell layers (ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm), but no body cavities such as cnidaria and flatworms. (13.3) acquired immune response a response through which the body’s resistance to a specific pathogen is built up ov ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.