Chapter 2 – Exam style questions Q1. Bk Ch2 Exam MQ1 Which of
... Carbon dioxide is a raw material and a limiting factor for photosynthesis; the more carbon dioxide that is available the greater the expected rate of photosynthesis. The rate of photosynthesis is higher for the plant exposed to the 10% oxygen concentration compared to the plant exposed to 30% oxygen ...
... Carbon dioxide is a raw material and a limiting factor for photosynthesis; the more carbon dioxide that is available the greater the expected rate of photosynthesis. The rate of photosynthesis is higher for the plant exposed to the 10% oxygen concentration compared to the plant exposed to 30% oxygen ...
Perth Academy N5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Homework Booklet
... 3. Sperm production in humans is controlled by two hormones, P and Q. As levels of P rise, sperm production increases. As levels of Q rise, sperm production decreases. Which of the graphs below shows the changes in hormone levels of a man whose sperm production is decreasing? ...
... 3. Sperm production in humans is controlled by two hormones, P and Q. As levels of P rise, sperm production increases. As levels of Q rise, sperm production decreases. Which of the graphs below shows the changes in hormone levels of a man whose sperm production is decreasing? ...
This page should automatically redirect. If nothing is
... shaped like a series of letter C's. The open ends of the C's are held together by the trachealis muscle. The cartilage provides a rigid support so that the tracheal wall does not collapse inward and obstruct the air passageway, and, because the open parts of the C's face the esophagus, the latter ca ...
... shaped like a series of letter C's. The open ends of the C's are held together by the trachealis muscle. The cartilage provides a rigid support so that the tracheal wall does not collapse inward and obstruct the air passageway, and, because the open parts of the C's face the esophagus, the latter ca ...
New Negative Potential Body Energizer
... “Earl Sutherland, USA receive the 1971 Nobel Prize for his discoveries concerning the mechanism of the action of hormones. He showed that the signal used to communicate between cells (the 1st. messenger) is converted to a signal inside the cell (the 2nd. Messenger). This signal occurs in the cell me ...
... “Earl Sutherland, USA receive the 1971 Nobel Prize for his discoveries concerning the mechanism of the action of hormones. He showed that the signal used to communicate between cells (the 1st. messenger) is converted to a signal inside the cell (the 2nd. Messenger). This signal occurs in the cell me ...
© Centura Foods Ltd
... oxygen into their cells is rapid enough For transport across the whole body, diffusion would be much too slow Large organisms have evolved transport systems (e.g. blood circulatory systems) that carry oxygen from outside the body to the cells inside ...
... oxygen into their cells is rapid enough For transport across the whole body, diffusion would be much too slow Large organisms have evolved transport systems (e.g. blood circulatory systems) that carry oxygen from outside the body to the cells inside ...
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
... 1. The tubes leading to the lungs may be narrow so less air gets through them. 2. The structure of the alveoli can break down. This results in alveoli which have a smaller surface area for gas exchange. 3. Some people are paralysed in an accident or by disease so they can not breathe. Two main ways: ...
... 1. The tubes leading to the lungs may be narrow so less air gets through them. 2. The structure of the alveoli can break down. This results in alveoli which have a smaller surface area for gas exchange. 3. Some people are paralysed in an accident or by disease so they can not breathe. Two main ways: ...
Part I - Spring Branch ISD
... trace the pathway of food as it travels through the organs of the digestive system beginning in the mouth. Be able to identify the structures of the digestive system. ...
... trace the pathway of food as it travels through the organs of the digestive system beginning in the mouth. Be able to identify the structures of the digestive system. ...
Life Science Unit I Name: Date: 1. Eukaryotic cells are
... tissues. The algae produce food for the anemones while the anemones provide a place for the algae to live. ...
... tissues. The algae produce food for the anemones while the anemones provide a place for the algae to live. ...
14 Stem Cell Differentiation
... different types of cells all arise from a single fertilized egg cell. Yet that is what happens during embryo development. Initially, all the cells in the embryo are alike. But as they divide, they become more specialized and produce their own characteristic proteins. Cells that have the ability to p ...
... different types of cells all arise from a single fertilized egg cell. Yet that is what happens during embryo development. Initially, all the cells in the embryo are alike. But as they divide, they become more specialized and produce their own characteristic proteins. Cells that have the ability to p ...
14 Stem Cell Differentiation
... different types of cells all arise from a single fertilized egg cell. Yet that is what happens during embryo development. Initially, all the cells in the embryo are alike. But as they divide, they become more specialized and produce their own characteristic proteins. Cells that have the ability to p ...
... different types of cells all arise from a single fertilized egg cell. Yet that is what happens during embryo development. Initially, all the cells in the embryo are alike. But as they divide, they become more specialized and produce their own characteristic proteins. Cells that have the ability to p ...
CELLS AND HEREDITY
... use of a carrier molecule but follows the rules of simple diffusion – the molecules will move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The carrier molecule speeds up the diffusion process. The cell does not expend energy in this process. Active transport is another tra ...
... use of a carrier molecule but follows the rules of simple diffusion – the molecules will move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. The carrier molecule speeds up the diffusion process. The cell does not expend energy in this process. Active transport is another tra ...
you need to know and some!
... Enzymes – produces as in humans. Peristasis can go in reverse in the ...
... Enzymes – produces as in humans. Peristasis can go in reverse in the ...
MAINTENANCE INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES ALIMENTARY
... Air enters the body through tiny holes called spiracles. They control how much air is allowed into the insect body. These spiracles open into tubes called trachea, which in turn branch into tinier tracheoles. This branching gets the tracheoles within a few cell diameters of each cell. This is import ...
... Air enters the body through tiny holes called spiracles. They control how much air is allowed into the insect body. These spiracles open into tubes called trachea, which in turn branch into tinier tracheoles. This branching gets the tracheoles within a few cell diameters of each cell. This is import ...
Biology response 5 yeast
... The key to the simplicity of using yeast in cell cycle and Cancer research is that yeast cells are simple and haploid (one copy of each chromosome). Saccharomyces cerevisiae, budding yeast; is a simple cell that divides by budding. This yeast has a short G2 phase. It is usually found as Brewer's or ...
... The key to the simplicity of using yeast in cell cycle and Cancer research is that yeast cells are simple and haploid (one copy of each chromosome). Saccharomyces cerevisiae, budding yeast; is a simple cell that divides by budding. This yeast has a short G2 phase. It is usually found as Brewer's or ...
Page 18 - Educast
... They are granules, rich in ribonucleic acid (RNA). They serve as sites where proteins are synthesized hence called protein factories of cell. They are found free in cytoplasm as well as attached on the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum. ...
... They are granules, rich in ribonucleic acid (RNA). They serve as sites where proteins are synthesized hence called protein factories of cell. They are found free in cytoplasm as well as attached on the surface of rough endoplasmic reticulum. ...
Notes on Unit 4 – Nature`s Principles
... different species that help each other with various functions. Be able to draw and label the parts of these cells. The following structures are found in prokaryotes: o Nucleoid region – holds the circular shaped single bacterial chromosome (DNA) without a nuclear envelope o Plasmid – small, circul ...
... different species that help each other with various functions. Be able to draw and label the parts of these cells. The following structures are found in prokaryotes: o Nucleoid region – holds the circular shaped single bacterial chromosome (DNA) without a nuclear envelope o Plasmid – small, circul ...
What is a Cell?
... the stage. Don’t say it looks bigger…look closely! What happened? Why do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to ...
... the stage. Don’t say it looks bigger…look closely! What happened? Why do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to ...
25.4 Absorption of Water and Mineral Salts by
... • Plasma (functions) o To transport digested food substances form the small intestines to other parts of the body. o To transport carbon dioxide and waste products formed in cells to the excretory organs for removal. o To transport other substances such as enzymes and special chemicals called hormon ...
... • Plasma (functions) o To transport digested food substances form the small intestines to other parts of the body. o To transport carbon dioxide and waste products formed in cells to the excretory organs for removal. o To transport other substances such as enzymes and special chemicals called hormon ...
District Mid-Term Examination
... The company compares the data given to similar investigations. The company sends out the data to another researcher to investigate. The company performs the same investigation and compares results. The company tests many types of pesticides and draws its own conclusion. ...
... The company compares the data given to similar investigations. The company sends out the data to another researcher to investigate. The company performs the same investigation and compares results. The company tests many types of pesticides and draws its own conclusion. ...
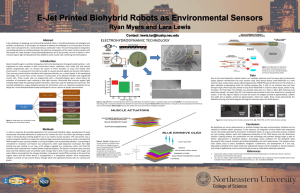
Abstract
... Recent breakthroughs in synthetic biology have led to the development of programmable bacteria— cells engineered to sense analytes in their environment (toxins, explosives, nitric oxide, pH) and execute specific programmed tasks. To harness the power of these microbes to assay and modify their envir ...
... Recent breakthroughs in synthetic biology have led to the development of programmable bacteria— cells engineered to sense analytes in their environment (toxins, explosives, nitric oxide, pH) and execute specific programmed tasks. To harness the power of these microbes to assay and modify their envir ...
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
... Blood is made up of plasma and blood cells. What is plasma? What is the function of white blood cells? Where in the body are white blood cells produced? Some people may have the blood group B Positive (B+). What factor is present in their blood that makes it positive? (v) The heart pumps blood aroun ...
... Blood is made up of plasma and blood cells. What is plasma? What is the function of white blood cells? Where in the body are white blood cells produced? Some people may have the blood group B Positive (B+). What factor is present in their blood that makes it positive? (v) The heart pumps blood aroun ...
C - Aptagen
... Microscopy of Internalized Polyclonal Aptamer Library (+) target receptor expressing cells ...
... Microscopy of Internalized Polyclonal Aptamer Library (+) target receptor expressing cells ...
Flashcard pictures hsa
... • Describe what an enzyme is, label and explain the lock and key model, and tell what conditions would make the enzyme not work properly – Include: catalyst, enzyme substrate complex, enzyme, substrate, product, and denature ...
... • Describe what an enzyme is, label and explain the lock and key model, and tell what conditions would make the enzyme not work properly – Include: catalyst, enzyme substrate complex, enzyme, substrate, product, and denature ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.