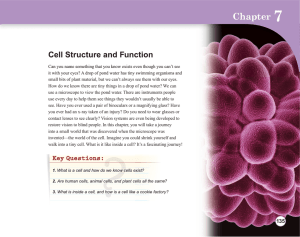
The Human Body: An Orientation
... The Stages of Mitosis • Prophase—the first and longest stage of mitosis • Early prophase—chromatin threads condense into chromosomes • Chromosomes are made up of two threads called chromatids (sister chromatids) • Chromatids are held together by the centromere • Centriole pairs separate from one ano ...
... The Stages of Mitosis • Prophase—the first and longest stage of mitosis • Early prophase—chromatin threads condense into chromosomes • Chromosomes are made up of two threads called chromatids (sister chromatids) • Chromatids are held together by the centromere • Centriole pairs separate from one ano ...
AS Module 1 - heckgrammar.co.uk
... • Cohesion. Water molecules "stick together" due to their hydrogen bonds, so water has high cohesion. This explains why long columns of water can be sucked up tall trees by transpiration without breaking. It also explains surface tension, which allows small animals to walk on water. • Ionisation. Wh ...
... • Cohesion. Water molecules "stick together" due to their hydrogen bonds, so water has high cohesion. This explains why long columns of water can be sucked up tall trees by transpiration without breaking. It also explains surface tension, which allows small animals to walk on water. • Ionisation. Wh ...
Module 1 Notes
... cohesion. This explains why long columns of water can be sucked up tall trees by transpiration without breaking. It also explains surface tension, which allows small animals to walk on water. Ionisation. When many salts dissolve in water they ionise into discrete positive and negative ions (e.g. N ...
... cohesion. This explains why long columns of water can be sucked up tall trees by transpiration without breaking. It also explains surface tension, which allows small animals to walk on water. Ionisation. When many salts dissolve in water they ionise into discrete positive and negative ions (e.g. N ...
Student Edition Sample Chapter (3MB PDF)
... more about living things? 3. Who was the first to discover cells? 4. Draw a timeline that shows the dates, discoveries, and scientists involved in the development of the cell theory. 5. What are the four statements of the cell theory? 6. What are specialized cells? List three examples. 7. What are f ...
... more about living things? 3. Who was the first to discover cells? 4. Draw a timeline that shows the dates, discoveries, and scientists involved in the development of the cell theory. 5. What are the four statements of the cell theory? 6. What are specialized cells? List three examples. 7. What are f ...
Histology
... a. Microvilli are cylindrical, cell-surface projections, 80 nm wide and 1-2 .m long, which increase the cell surface area for absorbing materials from the lumen. b. Stereocilia are long microvilli present in the male reproductive tract and in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. They are simil ...
... a. Microvilli are cylindrical, cell-surface projections, 80 nm wide and 1-2 .m long, which increase the cell surface area for absorbing materials from the lumen. b. Stereocilia are long microvilli present in the male reproductive tract and in the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear. They are simil ...
Unit 1 Biology 3
... Examination of cells using various microscopes reveals much about their internal organisation. Each living cell is a small compartment with an outer boundary known as the cell membrane or plasma membrane. Inside each living cell is a fluid, known as cytosol, that consists mainly of water containing ...
... Examination of cells using various microscopes reveals much about their internal organisation. Each living cell is a small compartment with an outer boundary known as the cell membrane or plasma membrane. Inside each living cell is a fluid, known as cytosol, that consists mainly of water containing ...
Cell Structure & Function
... structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. A. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. B. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. C. Explain that ce ...
... structure and function of cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. A. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. B. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria) to basic cell functions. C. Explain that ce ...
Structural Organization in Animals
... The heart is made of specialized muscle tissue with some similarities to both smooth and skeletal muscle. It is involuntary and mononucleate as is smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle is striated like skeletal muscle which means that it has microscopically visible myofilaments arranged in parallel with the ...
... The heart is made of specialized muscle tissue with some similarities to both smooth and skeletal muscle. It is involuntary and mononucleate as is smooth muscle. Cardiac muscle is striated like skeletal muscle which means that it has microscopically visible myofilaments arranged in parallel with the ...
An Introduction to Biology - Emory
... Is the world of living things in disorder without being organized? As it isn’t, any living things do seem to have hierarchical organization. Any living thing falls under a hierarchical level. The representation of level in order to have easier picture of the sense of hierarchy is called hierarchy of ...
... Is the world of living things in disorder without being organized? As it isn’t, any living things do seem to have hierarchical organization. Any living thing falls under a hierarchical level. The representation of level in order to have easier picture of the sense of hierarchy is called hierarchy of ...
Circulating blood cells function as a surveillance system for damaged tissue in Drosophila larvae. PNAS 105 , 10017-10022.
... to be an ancestral function of the immune system (2) but has not been studied extensively in organisms that possess only an innate immune system or simple open circulatory systems in which blood directly bathes the internal tissues. Larval and adult Drosophila are capable of efficiently fighting inf ...
... to be an ancestral function of the immune system (2) but has not been studied extensively in organisms that possess only an innate immune system or simple open circulatory systems in which blood directly bathes the internal tissues. Larval and adult Drosophila are capable of efficiently fighting inf ...
Word - New Haven Science
... substances or mixtures, depending on their chemical and physical properties. Mixtures are made of combinations of elements and/or compounds, and they can be separated by using a variety of physical means. Pure substances can be either elements or compounds, and they cannot be broken down by physical ...
... substances or mixtures, depending on their chemical and physical properties. Mixtures are made of combinations of elements and/or compounds, and they can be separated by using a variety of physical means. Pure substances can be either elements or compounds, and they cannot be broken down by physical ...
Living building blocks
... An adult human body is made up of more than one million million cells. That’s amazing when you consider that a human life begins in the mother’s womb with only two cells: a sperm cell and an egg. All cells are very, very small. The egg cell on the right has been magnified 500 times to allow us to se ...
... An adult human body is made up of more than one million million cells. That’s amazing when you consider that a human life begins in the mother’s womb with only two cells: a sperm cell and an egg. All cells are very, very small. The egg cell on the right has been magnified 500 times to allow us to se ...
32 Cell Division
... particularly harsh, a common soil bacterium called Bacillus subtilis may produce a resilient endospore within the parent vegetative cell that can live for thousands of years. When conditions favor the growth of the species, the endospore germinates, producing a normal bacterium. Other bacteria produ ...
... particularly harsh, a common soil bacterium called Bacillus subtilis may produce a resilient endospore within the parent vegetative cell that can live for thousands of years. When conditions favor the growth of the species, the endospore germinates, producing a normal bacterium. Other bacteria produ ...
File - Dr. Michael Belanich
... • two forms of osseous tissue – spongy bone - spongy in appearance • delicate struts of bone - trabeculae • covered by compact bone • found in heads of long bones and in middle of flat bones such as the ...
... • two forms of osseous tissue – spongy bone - spongy in appearance • delicate struts of bone - trabeculae • covered by compact bone • found in heads of long bones and in middle of flat bones such as the ...
The cell - Libero.it
... In picture1 the students can recognize the shape of different cells and in picture 2 they can see the various sizes of cells and their components. Finally to establish the students’ knowledge there is a chart to fill in with the given definitions. The next step is about what there is inside the cell ...
... In picture1 the students can recognize the shape of different cells and in picture 2 they can see the various sizes of cells and their components. Finally to establish the students’ knowledge there is a chart to fill in with the given definitions. The next step is about what there is inside the cell ...
Summary/Reflection of Dan Freedman`s article, Science Education
... Direct with environment. a. Some animals are small enough to allow gas exchange directly with the outside environment. 1) Many of these animals, such as the Platyhelminthes (flatworms), typically have large surface areas, and every cell either is exposed to the outside environment or is close enough ...
... Direct with environment. a. Some animals are small enough to allow gas exchange directly with the outside environment. 1) Many of these animals, such as the Platyhelminthes (flatworms), typically have large surface areas, and every cell either is exposed to the outside environment or is close enough ...
Unit A: the Science of Biology
... proportions. A molecule is the smallest unit of most compounds. 5. How do van der Waals forces hold molecules together? When the sharing of electrons is unequal, a molecule has regions that are charged. An attraction can occur between oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. 6. How are ionic ...
... proportions. A molecule is the smallest unit of most compounds. 5. How do van der Waals forces hold molecules together? When the sharing of electrons is unequal, a molecule has regions that are charged. An attraction can occur between oppositely charged regions of nearby molecules. 6. How are ionic ...
Cell Differentiation
... Caenorhabditis elegans has become such a well-established laboratory animal that more is known about its biology than that of almost any other organism. Because it is only 1 mm long when mature, C. elegans can be raised in small laboratory dishes. It takes only 12 hours from fertilization of the egg ...
... Caenorhabditis elegans has become such a well-established laboratory animal that more is known about its biology than that of almost any other organism. Because it is only 1 mm long when mature, C. elegans can be raised in small laboratory dishes. It takes only 12 hours from fertilization of the egg ...
Fifth dimension of life and the 4/5 allometric scaling law for human
... Nakaya et al. (1998) have studied the relationship between metabolic rate and body size in colonial organisms. They investigated the relationship between metabolic rate and colony size in the colonial ascidian Botryllus schlosseri. A small colony was put on a glass slide, which was set in a containe ...
... Nakaya et al. (1998) have studied the relationship between metabolic rate and body size in colonial organisms. They investigated the relationship between metabolic rate and colony size in the colonial ascidian Botryllus schlosseri. A small colony was put on a glass slide, which was set in a containe ...
2. Movement In and Out of Cells
... process that occurs by diffusion. What happens when you breathe in? Oxygen in inhaled air diffuses through the lungs and into the bloodstream. The oxygen is then transported throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by respiration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from body tissues into t ...
... process that occurs by diffusion. What happens when you breathe in? Oxygen in inhaled air diffuses through the lungs and into the bloodstream. The oxygen is then transported throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is the waste gas produced by respiration. Carbon dioxide diffuses from body tissues into t ...
MCAS Test Questions - Massachusetts Comprehensive Assessment
... results in paleness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate due to a deficiency in the oxygencarrying component of the blood. When oxygen levels are low in an affected individual, the red blood cells become deformed into a curved, sickle shape. People with sickle cell anemia can expe ...
... results in paleness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and increased heart rate due to a deficiency in the oxygencarrying component of the blood. When oxygen levels are low in an affected individual, the red blood cells become deformed into a curved, sickle shape. People with sickle cell anemia can expe ...
BIOL 463 Final Project 1st draft – Anik
... DNA methylation and histone markers associated with higher incidence for asthma Asthma is a heritable, multifaceted airway inflammatory disease afflicting approximately 8% of the USA population (Yang and Schwartz, 2012). The disease has steadily increased in prevalence and severity in the last coupl ...
... DNA methylation and histone markers associated with higher incidence for asthma Asthma is a heritable, multifaceted airway inflammatory disease afflicting approximately 8% of the USA population (Yang and Schwartz, 2012). The disease has steadily increased in prevalence and severity in the last coupl ...
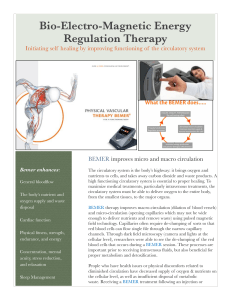
bemer - Anatara Medicine
... availability of oxygen and nutrients is inadequate for healthy cellular metabolism. The BEMER enhances the circulatory system, dilating capillaries and improving blood flow, creating a more difficult environment for cancer cells. BEMER has also been shown to influence the rolling action of white blo ...
... availability of oxygen and nutrients is inadequate for healthy cellular metabolism. The BEMER enhances the circulatory system, dilating capillaries and improving blood flow, creating a more difficult environment for cancer cells. BEMER has also been shown to influence the rolling action of white blo ...
learning outcomes for biology 12 and ib biology 12
... H1. Demonstrate an understanding of the following terms: metabolism, enzyme, active site, substrate, coenzyme, activation energy, denaturation, and cell respiration. p 90-95 H2. Identify the source gland for thyroxin and relate the function of thyroxin to metabolism 351-352 H3. Explain the "lock and ...
... H1. Demonstrate an understanding of the following terms: metabolism, enzyme, active site, substrate, coenzyme, activation energy, denaturation, and cell respiration. p 90-95 H2. Identify the source gland for thyroxin and relate the function of thyroxin to metabolism 351-352 H3. Explain the "lock and ...
Artificial cell

An artificial cell or minimal cell is an engineered particle that mimics one or many functions of a biological cell. The term does not refer to a specific physical entity, but rather to the idea that certain functions or structures of biological cells can be replaced or supplemented with a synthetic entity. Often, artificial cells are biological or polymeric membranes which enclose biologically active materials. As such, nanoparticles, liposomes, polymersomes, microcapsules and a number of other particles have qualified as artificial cells. Micro-encapsulation allows for metabolism within the membrane, exchange of small molecules and prevention of passage of large substances across it. The main advantages of encapsulation include improved mimicry in the body, increased solubility of the cargo and decreased immune responses. Notably, artificial cells have been clinically successful in hemoperfusion.In the area of synthetic biology, a ""living"" artificial cell has been defined as a completely synthetically made cell that can capture energy, maintain ion gradients, contain macromolecules as well as store information and have the ability to mutate. Such a cell is not technically feasible yet, but a variation of an artificial cell has been created in which a completely synthetic genome was introduced to genomically emptied host cells. Although not completely artificial because the cytoplasmic components as well as the membrane from the host cell are kept, the engineered cell is under control of a synthetic genome and is able to replicate.