Economic Systems
... Central bureaucracy: Govt controls all factors of production They allocate all factors based on their analysis of ...
... Central bureaucracy: Govt controls all factors of production They allocate all factors based on their analysis of ...
Economic wants - Teacher Pages
... A country is capable of producing a fixed quantity of goods and services at any one time Total production is divided between capital goods and consumer goods and services Inverse relationship between them ...
... A country is capable of producing a fixed quantity of goods and services at any one time Total production is divided between capital goods and consumer goods and services Inverse relationship between them ...
The Economic Perspective
... • Analyzes the individual components of the economy, such as the choices made by people, firms, and industries. • Markets – make possible the voluntary exchange of resources, goods and services; can take physical, electronic, and other forms. • Market prices – serve as signals that guide the allocat ...
... • Analyzes the individual components of the economy, such as the choices made by people, firms, and industries. • Markets – make possible the voluntary exchange of resources, goods and services; can take physical, electronic, and other forms. • Market prices – serve as signals that guide the allocat ...
Chapter 26.2
... economic questions of what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce determines its economic system. In a pure market economy, also called capitalism, these decisions are made in free markets by the interaction of supply and demand. ...
... economic questions of what to produce, how to produce and for whom to produce determines its economic system. In a pure market economy, also called capitalism, these decisions are made in free markets by the interaction of supply and demand. ...
AP Economics - Hicksville Public Schools
... The concept that society’s goals will be met as individuals seek their own self-interest. Example: Society wants fuel efficient cars… •Profit seeking producers will make more. •Competition between firms results in low prices, high quality, and greater efficiency. •The government doesn’t need to get ...
... The concept that society’s goals will be met as individuals seek their own self-interest. Example: Society wants fuel efficient cars… •Profit seeking producers will make more. •Competition between firms results in low prices, high quality, and greater efficiency. •The government doesn’t need to get ...
mixed economy
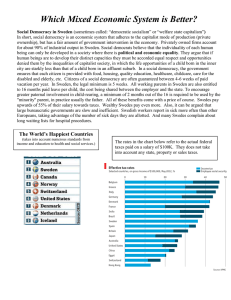
... Which Mixed Economic System is Better? Social Democracy in Sweden (sometimes called: “democratic socialism” or “welfare state capitalism”) In short, social democracy is an economic system that adheres to the capitalist mode of production (private ownership), but has a fair amount of government inter ...
... Which Mixed Economic System is Better? Social Democracy in Sweden (sometimes called: “democratic socialism” or “welfare state capitalism”) In short, social democracy is an economic system that adheres to the capitalist mode of production (private ownership), but has a fair amount of government inter ...
introduction to economics!!!! - Grosse Pointe Public School System
... business practices “hands off” to let the market place determine production, consumption and distribution. Individual freedom and choice ...
... business practices “hands off” to let the market place determine production, consumption and distribution. Individual freedom and choice ...
Economics - Tate County School District
... An economic system in which economic decisions are made by the state or government rather than by the interaction between consumers and businesses. The state can set prices for goods and determine how much is produced, and can focus labor and resources on industries and projects without having to wa ...
... An economic system in which economic decisions are made by the state or government rather than by the interaction between consumers and businesses. The state can set prices for goods and determine how much is produced, and can focus labor and resources on industries and projects without having to wa ...
Introducing Economics SL 1213
... in determining the pattern of production and distribution of goods and services 2) Macroeconomics – the branch of economics that studies economic aggregates (grand totals) the overall level of prices, output and employment in the economy; concerned with the economy as a whole; the overall level of e ...
... in determining the pattern of production and distribution of goods and services 2) Macroeconomics – the branch of economics that studies economic aggregates (grand totals) the overall level of prices, output and employment in the economy; concerned with the economy as a whole; the overall level of e ...
Thinking Like an Economist
... To draw the production possibilities frontier. To calculate the opportunity cost of increasing the ...
... To draw the production possibilities frontier. To calculate the opportunity cost of increasing the ...
4 factors of production
... • Represents all the countries in the world • Arrow at both ends b/c we SELL products to and BUY products from other countries. _________________________________ Define the following: pgs 430-432. (7 minutes) Productivity, specialization, division of labor, human capital and economic interdependence ...
... • Represents all the countries in the world • Arrow at both ends b/c we SELL products to and BUY products from other countries. _________________________________ Define the following: pgs 430-432. (7 minutes) Productivity, specialization, division of labor, human capital and economic interdependence ...
INTRODUCTION TO ECONOMICS!!!!
... • Factors of production (land, labor, capital) are supplied by the household to firms and the firms convert these into finished products for household consumption ...
... • Factors of production (land, labor, capital) are supplied by the household to firms and the firms convert these into finished products for household consumption ...
Chapter 2 Section 2
... • 2. Name the two markets of the circular flow model. • 3. Explain how the circular flow model reflects exchange. ...
... • 2. Name the two markets of the circular flow model. • 3. Explain how the circular flow model reflects exchange. ...
“Answering the Three Economic Questions” Outline
... i. What must contemporary societies distinguish between when deciding what goods and services should be produced? (23) ...
... i. What must contemporary societies distinguish between when deciding what goods and services should be produced? (23) ...
Economic Systems
... deprive him of the power to subjugate the labour of others by means of such appropriation" (99). "In place of the old bourgeois society, with its classes and class antagonisms, we shall have an association, in which the free development of each is the condition for the free development of all" (105) ...
... deprive him of the power to subjugate the labour of others by means of such appropriation" (99). "In place of the old bourgeois society, with its classes and class antagonisms, we shall have an association, in which the free development of each is the condition for the free development of all" (105) ...
Ch - OnCourse
... The money used to buy the tools and equipment needed for production is known as financial capital Actions in one part of country or world that have an economic impact on what happens else where are examples of economic interdependence Microeconomics ...
... The money used to buy the tools and equipment needed for production is known as financial capital Actions in one part of country or world that have an economic impact on what happens else where are examples of economic interdependence Microeconomics ...
Free market economies, Mixed economy and economy
... The needs of the society are often ignored for the betterment of the economy. Workers are not given options on where they can be employed or where they can move The black market explodes in a command economy. Due to the governmental restrictions, good and services that are not offered in the command ...
... The needs of the society are often ignored for the betterment of the economy. Workers are not given options on where they can be employed or where they can move The black market explodes in a command economy. Due to the governmental restrictions, good and services that are not offered in the command ...
Market vs. Command Economy
... • Economies tend to be skeptical of any attempt to change people’s behavior that doesn’t change their incentives. • For example, a plan that calls on manufacturers to reduce pollution voluntarily probably won’t be effective • A plan that gives them a financial incentive to do so is more likely to s ...
... • Economies tend to be skeptical of any attempt to change people’s behavior that doesn’t change their incentives. • For example, a plan that calls on manufacturers to reduce pollution voluntarily probably won’t be effective • A plan that gives them a financial incentive to do so is more likely to s ...
Chapter 19: The American Economy
... • -Represents all of the countries in the world. • -Note that this sector is the only one with a line having an arrow at both ends. • -This is because we buy and sell products from other countries. • -As a result, the two offset each other ending with the foreign sector generally accounting for less ...
... • -Represents all of the countries in the world. • -Note that this sector is the only one with a line having an arrow at both ends. • -This is because we buy and sell products from other countries. • -As a result, the two offset each other ending with the foreign sector generally accounting for less ...
INDUSTRIALIZATION - Norwell Public Schools
... materials, and provides for the workers according to their needs Forms of Socialism Utopian Socialists – Robert Owen- New Lanark, a community in Scotland where the community worked and lived under decent conditions ( Provided by Owen). No Social Classes ...
... materials, and provides for the workers according to their needs Forms of Socialism Utopian Socialists – Robert Owen- New Lanark, a community in Scotland where the community worked and lived under decent conditions ( Provided by Owen). No Social Classes ...