Economics PowerPoint
... Wants and needs are met by obtaining goods and services Goods – are tangible, can be seen/touched Services – are intangible, cannot be seen/touched ...
... Wants and needs are met by obtaining goods and services Goods – are tangible, can be seen/touched Services – are intangible, cannot be seen/touched ...
Economic Principles Notes
... a. Producers produce at the lowest cost possible and pay out to workers at the lowest cost possible (Called efficiency or productivity) b. Characterized by division of labor and specialization Production is based on the choices of private businesses and individuals Results: These economies are theor ...
... a. Producers produce at the lowest cost possible and pay out to workers at the lowest cost possible (Called efficiency or productivity) b. Characterized by division of labor and specialization Production is based on the choices of private businesses and individuals Results: These economies are theor ...
Review Questions with answers
... produced in their home country by making foreign made foods more expensive or not available at all 5. What is a trade embargo? when a country refuses to trade with another country 6. What is the GDP of a country? the total value of goods and services produced in a country in a year 7. How can a coun ...
... produced in their home country by making foreign made foods more expensive or not available at all 5. What is a trade embargo? when a country refuses to trade with another country 6. What is the GDP of a country? the total value of goods and services produced in a country in a year 7. How can a coun ...
Blank Jeopardy - Cobb Learning
... The people of this country remain poor, despite being the 6th largest Oil producer ...
... The people of this country remain poor, despite being the 6th largest Oil producer ...
Chapter 25 - Weber State University
... 2. Wartime economic mobilization resulted in a. increased hours for workers. b. dramatic increases in the industrial accident rate. c. some reduction in the quality of output. d. increased production rates. e. all of the above. 3. The draft is analogous to a tax, where the amount of the tax equals t ...
... 2. Wartime economic mobilization resulted in a. increased hours for workers. b. dramatic increases in the industrial accident rate. c. some reduction in the quality of output. d. increased production rates. e. all of the above. 3. The draft is analogous to a tax, where the amount of the tax equals t ...
Post-Fordist - Cloudfront.net
... Post-Fordist – current mode of production with a more flexible set of production practices in which goods are not mass produced. Production is accelerated and dispersed around the globe by multinational companies that shift production, outsourcing it around the world. ...
... Post-Fordist – current mode of production with a more flexible set of production practices in which goods are not mass produced. Production is accelerated and dispersed around the globe by multinational companies that shift production, outsourcing it around the world. ...
Principles of Economics
... 5. Analyze the role of a market economy in establishing and preserving political and personal liberty (e.g., through the works of Adam Smith). 12.2 Students analyze the elements of America's market economy in a global setting. 1. Understand the relationship of the concept of incentives to the law of ...
... 5. Analyze the role of a market economy in establishing and preserving political and personal liberty (e.g., through the works of Adam Smith). 12.2 Students analyze the elements of America's market economy in a global setting. 1. Understand the relationship of the concept of incentives to the law of ...
04- Unit 1 Review Guide
... 1. Absolute advantage: the comparison among producers of a good according to their productivity (NOT their opportunity costs). 2. Allocative efficiency: the apportionment of resources among firms and industries to obtain the production of the products most wanted by society (consumers); the output o ...
... 1. Absolute advantage: the comparison among producers of a good according to their productivity (NOT their opportunity costs). 2. Allocative efficiency: the apportionment of resources among firms and industries to obtain the production of the products most wanted by society (consumers); the output o ...
Presentation
... The social science chiefly concerned with the way individuals and societies choose to use their limited resources, which have alternative uses, to produce goods and services, which satisfy needs and wants, for present and future consumption. ...
... The social science chiefly concerned with the way individuals and societies choose to use their limited resources, which have alternative uses, to produce goods and services, which satisfy needs and wants, for present and future consumption. ...
Financial Operations - International Business (Our Global Economy).
... deliver goods, services, and ideas quickly Agricultural dependency – an economy that is involved in agriculture does not have manufacturing base for high quality products ...
... deliver goods, services, and ideas quickly Agricultural dependency – an economy that is involved in agriculture does not have manufacturing base for high quality products ...
Section 2 — Organizing the American Economy for War As the war
... complied. This program succeeded in reducing the overconsumption of scarce goods and ensured that everyone would have fairly equal access to those goods. Americans also aided the war effort in other ways. They formed car pools or rode bicycles to work. They recycled metals, paper, rubber, and other ...
... complied. This program succeeded in reducing the overconsumption of scarce goods and ensured that everyone would have fairly equal access to those goods. Americans also aided the war effort in other ways. They formed car pools or rode bicycles to work. They recycled metals, paper, rubber, and other ...
Command and Market Economies and the 5 Social
... • Total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country (doesn’t use population) • Example: Bread- only the final price of a loaf of bread is used, because the price of its ingredients (milk, flour, etc.) is already factored into that final price ...
... • Total market value of all final goods and services produced by a country (doesn’t use population) • Example: Bread- only the final price of a loaf of bread is used, because the price of its ingredients (milk, flour, etc.) is already factored into that final price ...
History of Economics
... • The Austrians saw markets and competition as a method for discovering information • In the Austrian view, prices were an information signal in the market. • They thought the competition led to desirable decentralized social planning. • They also proposed that the business cycle was created based u ...
... • The Austrians saw markets and competition as a method for discovering information • In the Austrian view, prices were an information signal in the market. • They thought the competition led to desirable decentralized social planning. • They also proposed that the business cycle was created based u ...
Econ 372 - Marietta College
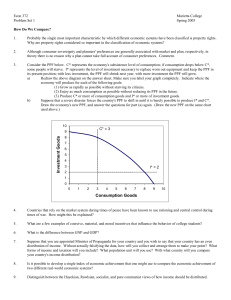
... Suppose that you are appointed Minister of Propaganda for your country and you wish to say that your country has an even distribution of income. Without actually falsifying the data, how will you collect and arrange them to make your point? What forms of income and taxation will you include? What po ...
... Suppose that you are appointed Minister of Propaganda for your country and you wish to say that your country has an even distribution of income. Without actually falsifying the data, how will you collect and arrange them to make your point? What forms of income and taxation will you include? What po ...
how to produce
... A large part of China’s GDP comes from a highly developed, industrial systems much like many other developed countries. Many Chinese people today have small businesses of their own even though the Chinese government still has final authority. ...
... A large part of China’s GDP comes from a highly developed, industrial systems much like many other developed countries. Many Chinese people today have small businesses of their own even though the Chinese government still has final authority. ...
Why government intervention in economy is necessary
... This is to ensure that there is "fair play" of the economy is important. This is among all the players or agents in the because where competition exists economy i.e. consumers and the pro we get a wide variety of goods and ...
... This is to ensure that there is "fair play" of the economy is important. This is among all the players or agents in the because where competition exists economy i.e. consumers and the pro we get a wide variety of goods and ...
Economics
... 3. ___ How the factors of production are used in this type of economy are based on customs and traditions 4. ___ Author of The Wealth of Nations. 5. ___ Type of economy where the government controls the major industries in the country; and provides many services for the people, but this comes with v ...
... 3. ___ How the factors of production are used in this type of economy are based on customs and traditions 4. ___ Author of The Wealth of Nations. 5. ___ Type of economy where the government controls the major industries in the country; and provides many services for the people, but this comes with v ...