Unit 4 Powerpoint
... the job of elected politicians to set goals for regulators, to deal with externalities, to mediate among different interests, to attend to the demands of social justice, to provide the public goods, and to organize resources for the greater good.” John Kenneth Galbraith The Economist Magazine Januar ...
... the job of elected politicians to set goals for regulators, to deal with externalities, to mediate among different interests, to attend to the demands of social justice, to provide the public goods, and to organize resources for the greater good.” John Kenneth Galbraith The Economist Magazine Januar ...
Neo-Colonialism, Modernisation and Dependency. Ch. II in
... international relations of production which had permitted a vast accumulation of wealth and progress in the west. It is the very success of this pattern of global accumulation that brought forth its own contradictions, so pressures for change and adaptation must be achievd to give continuity to the ...
... international relations of production which had permitted a vast accumulation of wealth and progress in the west. It is the very success of this pattern of global accumulation that brought forth its own contradictions, so pressures for change and adaptation must be achievd to give continuity to the ...
Economics Unpacking
... Terms: business cycle, inflation, unemployment policy, fiscal policy, monetary policy, Great Depression, change reaction of policies, interdependency of economics, standard of living, GDP Causes of unemployment, inflation, Impact of Federal Reserve, Government securities Measurement: ...
... Terms: business cycle, inflation, unemployment policy, fiscal policy, monetary policy, Great Depression, change reaction of policies, interdependency of economics, standard of living, GDP Causes of unemployment, inflation, Impact of Federal Reserve, Government securities Measurement: ...
Economic Systems of Government - Marine Corps Junior ROTC blog
... profit. He argued that in time, the workers would join together, like slaves overthrowing their masters, in a revolution that would replace capitalism with a form of socialism he called communism. Marx believed in a communist utopia, a perfect society, where everyone would be expected to co-operate ...
... profit. He argued that in time, the workers would join together, like slaves overthrowing their masters, in a revolution that would replace capitalism with a form of socialism he called communism. Marx believed in a communist utopia, a perfect society, where everyone would be expected to co-operate ...
Week 5 - Monday - Université d`Ottawa
... can be understood as ‘the relationship between the development of new communication technologies, on the one hand, and the contexts and politics of the use of that technology, on the other’ ...
... can be understood as ‘the relationship between the development of new communication technologies, on the one hand, and the contexts and politics of the use of that technology, on the other’ ...
Ch. 4 Economic Geography
... • Secondary economic activities use raw materials to make a product that is new and more valuable. • Tertiary economic activities provide services to people and businesses. • Quaternary economic activities process, manage, and distribute information. ...
... • Secondary economic activities use raw materials to make a product that is new and more valuable. • Tertiary economic activities provide services to people and businesses. • Quaternary economic activities process, manage, and distribute information. ...
DETERMINANTS OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT
... structure of the economy. Economy of the country is generally divided into three basic sectors: Primary (such as agricultural, animal husbandry, forestry etc.) , Secondary (such as Industrial production, constructions and the like) and Tertiary (such as trade, banking and commerce. Financial stabi ...
... structure of the economy. Economy of the country is generally divided into three basic sectors: Primary (such as agricultural, animal husbandry, forestry etc.) , Secondary (such as Industrial production, constructions and the like) and Tertiary (such as trade, banking and commerce. Financial stabi ...
Name - Midway ISD
... 1. The fundamental economic problem is __________________. It affects almost every ______________ that we make. 2. Define SCARCITY : 3. Economics is the study of how people try to satisfy what appears to be seemingly ____________________ and ____________________wants through the _____________ use of ...
... 1. The fundamental economic problem is __________________. It affects almost every ______________ that we make. 2. Define SCARCITY : 3. Economics is the study of how people try to satisfy what appears to be seemingly ____________________ and ____________________wants through the _____________ use of ...
1 Overview of Comparative Economics Chapter I How do we
... Social Market Economies (or some advanced capitalist countries) → do their income redistribution through social safety nets Command Socialist Economies → did not have to redistribute income → their governments controlled the distribution of income by setting wages and forbidding capital or land inco ...
... Social Market Economies (or some advanced capitalist countries) → do their income redistribution through social safety nets Command Socialist Economies → did not have to redistribute income → their governments controlled the distribution of income by setting wages and forbidding capital or land inco ...
Capitalism Cons - Social Studies 30
... to the floor. The master, Mr. Newton, kicked her and caused her to wear away till she died. There was another, Caroline Thompson, who was beaten till she went out of her mind. The overlookers used to cut off the hair of any girl caught talking to a lad. This head shaving was a dreadful punishment. W ...
... to the floor. The master, Mr. Newton, kicked her and caused her to wear away till she died. There was another, Caroline Thompson, who was beaten till she went out of her mind. The overlookers used to cut off the hair of any girl caught talking to a lad. This head shaving was a dreadful punishment. W ...
Summary: The United States Economy
... Governments need to pay for police and fire protection, schools, roads, and military forces. Once these needs are met, money can be spent on other things, such as medical research or environmental protection. For an economy to grow, business owners must produce goods and services. The four factors o ...
... Governments need to pay for police and fire protection, schools, roads, and military forces. Once these needs are met, money can be spent on other things, such as medical research or environmental protection. For an economy to grow, business owners must produce goods and services. The four factors o ...
Economic Systems Notes
... o Economic decisions made by customs o Hunting/farming/gathering o No technology o No global trade o Rural & non-industrialized o Africa, South America & Asia o Sometimes known as 3rd World Countries Command Economies o Government makes all economic decisions (3) o Productive resources are owned b ...
... o Economic decisions made by customs o Hunting/farming/gathering o No technology o No global trade o Rural & non-industrialized o Africa, South America & Asia o Sometimes known as 3rd World Countries Command Economies o Government makes all economic decisions (3) o Productive resources are owned b ...
Slide 1 - mebranding
... He described the market mechanism as an "invisible hand" that leads all individuals, in pursuit of their own selfinterests, to produce the greatest benefit for society as a whole. Smith incorporated some of the Physiocrats' ideas, including laissez-faire, into his own economic theories, but rejected ...
... He described the market mechanism as an "invisible hand" that leads all individuals, in pursuit of their own selfinterests, to produce the greatest benefit for society as a whole. Smith incorporated some of the Physiocrats' ideas, including laissez-faire, into his own economic theories, but rejected ...
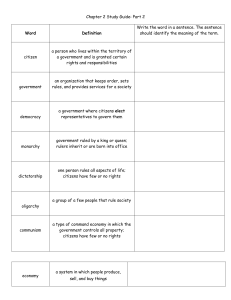
Chapter 2 Study Guide: Part 2 Word Definition Write the word in a
... citizens have few or no rights ...
... citizens have few or no rights ...
3 Questions
... • Place them in their appropriate place on the spectrum • Write a brief explanation of why you placed them where you did. ...
... • Place them in their appropriate place on the spectrum • Write a brief explanation of why you placed them where you did. ...
Module 15 Lesson 1 Remediation Notes Part 2
... By expressing GDP in terms of each person, we can compare one nation’s economic success to another without regard to the size of the two economies. ...
... By expressing GDP in terms of each person, we can compare one nation’s economic success to another without regard to the size of the two economies. ...