Economics - slhistory
... Variable Costs: expense that change with the number produced. Example: ...
... Variable Costs: expense that change with the number produced. Example: ...
STUDY UNIT 1 CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS ECONOMICS ALL ABOUT 1
... 1.1 Scarcity, choice and opportunity Scarcity (not enough goods/ services to satisfy everyones wants) must not be confused with poverty Wants: human desires for goods and services (biological, spiritual, material, cultural, social) they are unlimited, but the means are scarce Needs: are essent ...
... 1.1 Scarcity, choice and opportunity Scarcity (not enough goods/ services to satisfy everyones wants) must not be confused with poverty Wants: human desires for goods and services (biological, spiritual, material, cultural, social) they are unlimited, but the means are scarce Needs: are essent ...
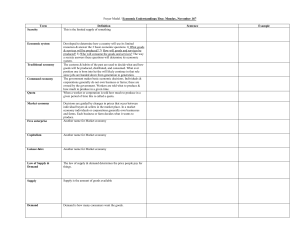
Frayer Model / Economic Understandings
... goods will be produced, distributed, and consumed. What ever position one is born into he/she will likely continue in that role since jobs are handed down from generation to generation. The government makes basic economic decisions. Individuals & corporations generally do not own business or farms; ...
... goods will be produced, distributed, and consumed. What ever position one is born into he/she will likely continue in that role since jobs are handed down from generation to generation. The government makes basic economic decisions. Individuals & corporations generally do not own business or farms; ...
The Circular Flow Model
... Because of economic freedom, capitalism is also called a Make their own Economic Decisions free enterprise system. ...
... Because of economic freedom, capitalism is also called a Make their own Economic Decisions free enterprise system. ...
production - Public Schools of Robeson County
... FERTILE FIELDS, RAINFALL, FOREST, MINERAL DEPOSITS SCHOOLS—BUILT ON/WITH NATURAL RESOUCES ...
... FERTILE FIELDS, RAINFALL, FOREST, MINERAL DEPOSITS SCHOOLS—BUILT ON/WITH NATURAL RESOUCES ...
Unit 3 Vocabulary Words with Answers
... or elements, needed for production to occur. 16. _____Labor Resources____- Workers are needed with the appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience to make goods or provide services. 17. ___Entrepreneurs___- The people who bring natural resources, labor resources, and capital resources together to ...
... or elements, needed for production to occur. 16. _____Labor Resources____- Workers are needed with the appropriate knowledge, skills, and experience to make goods or provide services. 17. ___Entrepreneurs___- The people who bring natural resources, labor resources, and capital resources together to ...
BUS101 A.Lynch Quiz - Ch. 2
... 25. Michael has inherited $500,000 from the sale of a family business. His banker is advising he find multiple banks to deposit his money. Why? a) The Open Market Operations of the Federal Reserve would invest his money in other securities and might lose it without needing to justify the expenditure ...
... 25. Michael has inherited $500,000 from the sale of a family business. His banker is advising he find multiple banks to deposit his money. Why? a) The Open Market Operations of the Federal Reserve would invest his money in other securities and might lose it without needing to justify the expenditure ...
Economic Simulation
... Cartograms are maps in which country size is dependent on a particular variable. They are used as an efficient method to communicate information on relative country data In this project a rectangular cartogram scaled to GDP will be used. ...
... Cartograms are maps in which country size is dependent on a particular variable. They are used as an efficient method to communicate information on relative country data In this project a rectangular cartogram scaled to GDP will be used. ...
Frayer Model / Economic Understandings
... goods will be produced, distributed, and consumed. What ever position one is born into he/she will likely continue in that role since jobs are handed down from generation to generation. The government makes basic economic decisions. Individuals & corporations generally do not own business or farms; ...
... goods will be produced, distributed, and consumed. What ever position one is born into he/she will likely continue in that role since jobs are handed down from generation to generation. The government makes basic economic decisions. Individuals & corporations generally do not own business or farms; ...
The sprawling Chrysler headquarters and plant illustrate the large
... At the other end of the size scale of business, corporate farms are able to make efficient use of capital equipment because they can employ it more intensively; it is not idle as much of the time. In the 1980s at least, the farm production models that seemed to work best were the labor-intensive sma ...
... At the other end of the size scale of business, corporate farms are able to make efficient use of capital equipment because they can employ it more intensively; it is not idle as much of the time. In the 1980s at least, the farm production models that seemed to work best were the labor-intensive sma ...
2. Management as a process of making choice. Human needs
... of human and can being satisfy needs in immediate mean. Production goods – economic goods using to make other goods, we are calling then production elements. Production elements (productive) – they contain material and immaterial resources of resources using in produce process in aim of satisfy huma ...
... of human and can being satisfy needs in immediate mean. Production goods – economic goods using to make other goods, we are calling then production elements. Production elements (productive) – they contain material and immaterial resources of resources using in produce process in aim of satisfy huma ...
Chapter 04
... People who make more money are able to buy more goods and services. Three basic command economy questions – dictators or governments decide what products are needed. Government owns all means of production. Government decides who will get what is produced. Explain why all economies are mixed – eleme ...
... People who make more money are able to buy more goods and services. Three basic command economy questions – dictators or governments decide what products are needed. Government owns all means of production. Government decides who will get what is produced. Explain why all economies are mixed – eleme ...
The American Economy
... •Sell to AND buy from other nations •Value of products bought and sold tends to offset each other • Results in less than 4% of nation’s GDP ...
... •Sell to AND buy from other nations •Value of products bought and sold tends to offset each other • Results in less than 4% of nation’s GDP ...
Economics Notes Chapter One Scarcity – the
... [stocks, bonds, and money] Can’t produce anything directly with these ...
... [stocks, bonds, and money] Can’t produce anything directly with these ...
PPC
... facts, since they are based on a value judgement. They are subjective and can be recognised by words such as “should” or “ought”. Positive – These are statements of fact that be checked against the facts and can be proved correct or incorrect. They are not necessarily true, but can be proved true ...
... facts, since they are based on a value judgement. They are subjective and can be recognised by words such as “should” or “ought”. Positive – These are statements of fact that be checked against the facts and can be proved correct or incorrect. They are not necessarily true, but can be proved true ...
Slide Section 2 Econ Systems
... If consumers want computers and only one company is making them… •Other businesses have the INCENTIVE to start making computers to earn PROFIT. •This leads to more COMPETITION…. •Which means lower prices, better quality, and more product variety. •We produce the goods and services that society wants ...
... If consumers want computers and only one company is making them… •Other businesses have the INCENTIVE to start making computers to earn PROFIT. •This leads to more COMPETITION…. •Which means lower prices, better quality, and more product variety. •We produce the goods and services that society wants ...