* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circular Flow Model
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Socialist calculation debate wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
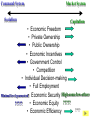
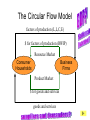
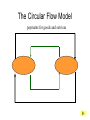
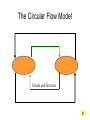
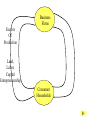
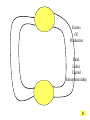
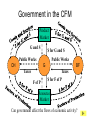
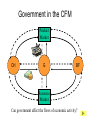
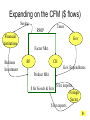
• Economic Freedom • Economic efficiency • Economic security • Economic equity • Full employment • Price stability • Economic Growth • Individual economic choice • Getting the most of what we want from scarce resources. • A cushion against economic risks. • Distributional fairness • Maximizing the use of human resources • Relatively minimal inflation/deflation • Increasing productive potential Is based on? Freedom of Choice Freedom of Enterprise Workers Consumers Producers Savers Investors Etc. Freedom of entrepreneurs to take the risk and have the initiative to start a business. Because of economic freedom, capitalism is also called a Make their own Economic Decisions free enterprise system. = Individual ownership of the factors of production and other possessions. Private ownership is the opposite of: = government ownership of the factors of production and other possessions. To motivate individuals to use their factors of production, they must receive something in return --- a reward --- or income payment. The payment must be sufficient to motivate the property owner. L L C E and abor apital ntrepreneurship R ent W ages I nterest P rofit Economic incentives guide resource allocation --where the resources will go in the economy (to what end will resources be distributed?) Economic Incentives are based on: Individuals: Positive Incentives (Encourage) vs. Negative Incentives (Discourage) Consumers Producers Low prices High prices High prices Low prices Savers High Interest Low Interest Workers High Wages Low Wages Profits Encourage new firms to enter an industry; therefore, more resources go into the industry Losses Discourage new firms from entering an industry; and may cause some businesses to leave. therefore, fewer resources go into the industry – resources actually move to a more profitable industry Definition: Economic Rivalry Assumptions: • Large numbers of buyers and sellers • No barriers to entry or exit from the industry • Knowledge of markets and prices Benefits: • Lower prices • Greater variety • Better quality Coordinates the decisions of buyers and sellers Consumers want low prices! Sellers want high prices! Market Price Based on Supply and Demand in the Marketplace Role of Government: • legal system to protect property • enforce contracts Policy: “let do” -- stay out of the economy and economic decisionmaking Some examples of government involvement in the U.S. economy: • Antitrust laws to maintain competition • Regulation of businesses to protect workers (OSHA) and consumers (FDA, FTC) • Regulation of businesses to protect the environment (EPA) • Minimum wage laws • Social Security and Medicare • Welfare, Medicaid and Unemployment Compensation • Child labor laws • Affirmative action (EEOC) • Monetary and fiscal policies Command System Socialism Market System Capitalism • Economic Freedom • Private Ownership • Public Ownership • Economic Incentives • Government Control • Competition • Individual Decision-making • Full Employment Minimal level guaranteed• Economic Security High-some/low-others ????? • Economic Equity ????? ???? • Economic Efficiency Friday, Feb. 13 • Get a stamp for your characteristics of capitalism paper. • Turn in your characteristics of capitalism paper to the front of the room. An Introduction to economic flows in a pure market economy. The Circular Flow Model • A simplified model of a market economy • It includes an analysis of: Sectors: • Business Firms • Consumer Households Markets: • Where goods and • Where factors of services are production supplied and (land/labor/capital/ demanded entrepreneurship) (bought and sold) are supplied and demanded (bought and sold). –Payments for goods and services (expenditures) –Payments for factors of production (income - RWIP) –Goods and services –Factors of Production The Circular Flow Model factors of production (L,L,C,E) $ for factors of production (RWIP) Resource Market Consumer Households Business Firms Product Market $ for goods and services goods and services GDP and National Income National Income- The total amount of money earned by consumer households. GDP- The total value of all goods and services sold within the nation in a year. The Circular Flow Model factors of production (L,L,C,E) $ for factors of production (RWIP)- national income Resource Market Consumer Households Business Firms Product Market $ for goods and services- GDP goods and services The Circular Flow Model payments for goods and services The Circular Flow Model Goods and Services Business Firms Factors Of Production Land, Labor, Capital Entrepreneurship Consumer Households Factors Of Production Land, Labor, Capital Entrepreneurship What sector excluded from the simplified CF model plays a major role in the U.S. economic system? NEW TERM FOR UNDERSTANDING GOVERNMENT MONEY FLOWS (transfer payments) And other terms: subsidies Tuesday, February 17 Warm-up: Copy this definition down Transfer Payment: • Money that is transferred from one person to another (or group or business). Usually government is doing the redistribution. • Key characteristic --- no good or service or factor of production is exchanged in return (purely financial transaction) Examples of Transfer Payments: • Examples of transfer payments: – Private: Aunt Suzie gives you a check for your birthday. – Public: subsidies to businesses, social security payments, veteran’s benefits, welfare payments, unemployment compensation. – Note: work may have been done in the past for which the recipient is receiving the payment (social security, unemployment compensation, veteran’s benefits); however, no CURRENT PRODUCTION is taking place for receipt of the money NOW. Government in the CFM Product Market G and S $ for G and S Public Works Public Works CH G BF Taxes Taxes F of P $ for F of P Resource Market Can government affect the flows of economic activity? Besides Government, what other sectors interact in the economy? Project: • Draw a CFM with the government and instead of labeling the flow and sectors draw a picture. (See slide below) • Must draw picture for CH, G and BF. Government in the CFM Product Market CH G BF Resource Market Can government affect the flows of economic activity? Expanding on the CFM ($ flows) Saving RWIP Taxes Financial Institutions Gov Factor Mkt. Business Investment BF CH Gov. Expenditures Product Mkt. $ for imports $ for Goods & Serv. Foreign Sector $ for exports Leakages and Injections from Income/Expenditure Flows: • Government – Leakage – Taxes (T) – Injection – Government Expenditures (G) • Financial Institutions – Leakage – Saving (S) (income not spent) – Injection – Business Investment (I) • Foreign Sector – Leakage – Expenditures for Imports (M) – Injection– Expenditures for Exports (X) Aggregate (total) Expenditures = C + I + G + X-M (AE) = GDP = AD