Cell Wall - (LTC) de NUTES
... http://www.meningitisuk.org/about-meningitis/bacterial-meningitis.htm ...
... http://www.meningitisuk.org/about-meningitis/bacterial-meningitis.htm ...
CRCT Review PPT
... Use the list below to answer this question. carrying oxygen to the cells carrying carbon dioxide away from the cells carrying food to the cells carrying waste products away from the cells Which system is most responsible for all of the body functions listed above? A. circulatory system B. mu ...
... Use the list below to answer this question. carrying oxygen to the cells carrying carbon dioxide away from the cells carrying food to the cells carrying waste products away from the cells Which system is most responsible for all of the body functions listed above? A. circulatory system B. mu ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 - Organization - mics-bio2
... division of the body into superior and inferior ...
... division of the body into superior and inferior ...
syllabus - Hudson Area Schools
... B2.1 Transformation of Matter and Energy in Cells In multicellular organisms, cells are specialized to carry out specific functions such as transport, reproduction, or energy transformation. B2.1x Cell Differentiation Following fertilization, cell division produces a small cluster of cells that then ...
... B2.1 Transformation of Matter and Energy in Cells In multicellular organisms, cells are specialized to carry out specific functions such as transport, reproduction, or energy transformation. B2.1x Cell Differentiation Following fertilization, cell division produces a small cluster of cells that then ...
File eoct review with answers
... 8. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and give examples. a. Prokaryotes: have no nucleus, are smaller and more simple, and have no membranebound organelles; bacteria only b. Eukaryotes: have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and are larger that prokaryotes: every other cells such as animal ...
... 8. Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and give examples. a. Prokaryotes: have no nucleus, are smaller and more simple, and have no membranebound organelles; bacteria only b. Eukaryotes: have a nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, and are larger that prokaryotes: every other cells such as animal ...
Characteristics Eukaryotic Cells
... 1. A segment of genetic code of DNA from the nucleus is copied onto RNA and passed through the nuclear pores to the rough endoplasmic reticulum 2. Synthesized proteins on the RER are deposited into the lumen and transported to the Golgi apparatus 3. Proteins in the Golgi apparatus are chemically m ...
... 1. A segment of genetic code of DNA from the nucleus is copied onto RNA and passed through the nuclear pores to the rough endoplasmic reticulum 2. Synthesized proteins on the RER are deposited into the lumen and transported to the Golgi apparatus 3. Proteins in the Golgi apparatus are chemically m ...
Cells Worksheet - Qld Science Teachers
... Respiration - using oxygen to release energy from food Sensing - detecting changes around them Growth - increasing in size Nutrition - making or getting food Reproduction - producing young Most living things are made up of microscopic units called cells. Some organisms have only one cell (such as ba ...
... Respiration - using oxygen to release energy from food Sensing - detecting changes around them Growth - increasing in size Nutrition - making or getting food Reproduction - producing young Most living things are made up of microscopic units called cells. Some organisms have only one cell (such as ba ...
./ ` . `.`4 Body Tissues 13. Figure 3-6: A. Simple squamous epLthelium
... 23. 1. Cytoplasm (cytosol). 7. Pores. re ticulum. ...
... 23. 1. Cytoplasm (cytosol). 7. Pores. re ticulum. ...
8.L.5- Energy in Living Organisms - NHCS
... Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some of its energy as thermal energy. All organisms are composed of cells-a group of organelles working together. Most organisms are single cells; other organis ...
... Food provides molecules that serve as fuel and building material for all organisms. Organisms get energy by oxidizing their food, releasing some of its energy as thermal energy. All organisms are composed of cells-a group of organelles working together. Most organisms are single cells; other organis ...
Paper 2 - Soalan-Percubaan-STPM
... 4. Glycoprotein (C) 5. Glycolipid (F) Structure and function: • the biological cell membrane acts as barrier and are selectively permeable • the membrane consists of a fluid bilayer o f phospholipids and various protein molecules act as ion c hannels, CatTier protein or pumps embedded in it • the ph ...
... 4. Glycoprotein (C) 5. Glycolipid (F) Structure and function: • the biological cell membrane acts as barrier and are selectively permeable • the membrane consists of a fluid bilayer o f phospholipids and various protein molecules act as ion c hannels, CatTier protein or pumps embedded in it • the ph ...
ParScore Scantrons for Lecture Tests Introduction to Microbiology Use Your Textbook Wisely
... ! Always lower case ! Usually an adjective, sometimes a proper noun ...
... ! Always lower case ! Usually an adjective, sometimes a proper noun ...
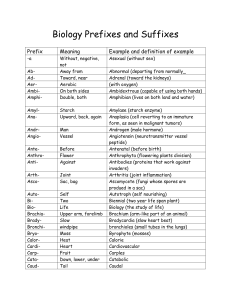
Biology Prefixes and Suffixes
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
... internally to maintain a constant body temperature) Epiphyte (A plant that grows on the surface of another plant for support) Erythrocyte (red blood cell) Eukaryote (Organism whose cells contains a “true” membrane bound nucleus) Exoskeleton (hard outer surface that provides support or protection for ...
Protist and Fungi
... Most unicellular but some are multi-cellular Only found in moist environments (water) Reproduce using Fission (cloning/asexual) and Fussion (conjucation/sexual) ...
... Most unicellular but some are multi-cellular Only found in moist environments (water) Reproduce using Fission (cloning/asexual) and Fussion (conjucation/sexual) ...
National 5 Biology Unit 1 cell Biology – Homework 2
... Please answer all these questions on named, lined refill. ...
... Please answer all these questions on named, lined refill. ...
eoc powerpoint # 2
... • Territoriality: Animal defends territory / Reduces Conflict; uses resources efficiently; controls size of ...
... • Territoriality: Animal defends territory / Reduces Conflict; uses resources efficiently; controls size of ...
Cells Activity - Science
... Respiration - using oxygen to release energy from food Sensing - detecting changes around them Growth - increasing in size Nutrition - making or getting food Reproduction - producing young Most living things are made up of microscopic units called cells. Some organisms have only one cell ( ...
... Respiration - using oxygen to release energy from food Sensing - detecting changes around them Growth - increasing in size Nutrition - making or getting food Reproduction - producing young Most living things are made up of microscopic units called cells. Some organisms have only one cell ( ...
Cell Specialization Powerpoint
... Nerve Cell Job: Send messages throughout the body Shape allows the dendrites to receive message, axon allows message to travel along it, axon endings transmits the message to the next nerve cell. They are lined up end to end in the body in a network (almost like telephone lines) ...
... Nerve Cell Job: Send messages throughout the body Shape allows the dendrites to receive message, axon allows message to travel along it, axon endings transmits the message to the next nerve cell. They are lined up end to end in the body in a network (almost like telephone lines) ...
BIOL 170 Exploring Biology
... 2. Why is it that we humans can break down starch into sugar to be used for energy but cannot break down cellulose into sugar? 3. It is reported that fish and all vertebrates are “nutritionally deficient.” What parts of proteins do we need to take in as part of our diet as we do not have the ability ...
... 2. Why is it that we humans can break down starch into sugar to be used for energy but cannot break down cellulose into sugar? 3. It is reported that fish and all vertebrates are “nutritionally deficient.” What parts of proteins do we need to take in as part of our diet as we do not have the ability ...
Intro: Signal Fusion within the Cell
... • Visualize species that can’t be probed experimentally – Spatiotemporal patterns of post-translational modifications ...
... • Visualize species that can’t be probed experimentally – Spatiotemporal patterns of post-translational modifications ...
biocomp-exam-2009 - National Biology Competition
... In a court case contesting the teaching of evolution in high school, the plaintiff claims that the lack of intermediate evolutionary forms in the fossil record calls into question the scientific validity of evolutionary theory. Which of the following constitutes the strongest rebuttal to the plainti ...
... In a court case contesting the teaching of evolution in high school, the plaintiff claims that the lack of intermediate evolutionary forms in the fossil record calls into question the scientific validity of evolutionary theory. Which of the following constitutes the strongest rebuttal to the plainti ...
Unicellular Organisms
... Unicellular Organisms ………………………….. A single-celled organisms is also known as a unicellular organisms. ...
... Unicellular Organisms ………………………….. A single-celled organisms is also known as a unicellular organisms. ...
Goal 6: Cell Theory Review Guide
... Both are made of cells or are cells and carry all the processes of life. Organisms that are composed of more than one cell are multicellular organisms. The cells that make up an multicellular organism are often specialized to perform specific function to keep the organism alive. Examples of unicellu ...
... Both are made of cells or are cells and carry all the processes of life. Organisms that are composed of more than one cell are multicellular organisms. The cells that make up an multicellular organism are often specialized to perform specific function to keep the organism alive. Examples of unicellu ...
Cellular Form, Function and Genetics
... • All materials inside the cell and outside the nucleus: – cytosol (fluid): • dissolved materials: – nutrients, ions, proteins, and waste products ...
... • All materials inside the cell and outside the nucleus: – cytosol (fluid): • dissolved materials: – nutrients, ions, proteins, and waste products ...
Cell (biology)

The cell (from Latin cella, meaning ""small room"") is the basic structural, functional, and biological unit of all known living organisms. Cells are the smallest unit of life that can replicate independently, and are often called the ""building blocks of life"". The study of cells is called cell biology.Cells consist of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, which contains many biomolecules such as proteins and nucleic acids. Organisms can be classified as unicellular (consisting of a single cell; including bacteria) or multicellular (including plants and animals). While the number of cells in plants and animals varies from species to species, humans contain more than 10 trillion (1013) cells. Most plant and animal cells are visible only under the microscope, with dimensions between 1 and 100 micrometres.The cell was discovered by Robert Hooke in 1665, who named the biological unit for its resemblance to cells inhabited by Christian monks in a monastery. Cell theory, first developed in 1839 by Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure and function in all living organisms, that all cells come from preexisting cells, and that all cells contain the hereditary information necessary for regulating cell functions and for transmitting information to the next generation of cells. Cells emerged on Earth at least 3.5 billion years ago.