* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unicellular Organisms
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
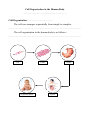
Unicellular and Multicellular Organisms ……………………………………………… Unicellular Organisms ………………………….. A single-celled organisms is also known as a unicellular organisms. ……………………………………………………………………………… A single cell can be a complete organisms and performs the necessary functions to keep it alive. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… Example of unicellular organisms are Euglena, Paramecium Amoeba Yeast and Diatom. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… Euglena Paramecium Yeast Amoeba Diatom Multicellular Organisms………………………….. Living things that are made up of more than one cell are celled multicellular Organisms. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… Bodies of large plants and animals consist of millions of different types of cell. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… There are different types of cells in various shapes and sizes in a multicellular organisms. ……………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………….... Examples of multicellular organisms are Hydra, Mucor, Spyrogira, Plants, Animals and Human. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… Hydra Animals Mucor Spyrogira Plants Human Call Organisation in the Human Body ……………………………………………… Call Organisation………………………….. The cells are arranges sequentially from simple to complex. ……………………………………………………………………………… The cell organisation in the human body is as follows : ……………………………………………………………………………… Cell Tissue Organism/Human Organ System Specialised Cells………………………….. There are billions of cells in the human body. ……………………………………………………………………………… Different cells are specialized to perform specific functions. ……………………………………………………………………………… Nerve cells Carry massage from various part of the body to the brain back to the muscle cells. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Bone cells From bones. Support the body. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Red blood cells Carry oxygen around the body. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Muscle cells Enable movement. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Fat cells Store fat. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… From Cells to Tissues………………………….. Cells of the same type with specialised function are group together to from tissues. ……………………………………………………………………………… Every cell in a tissues are able to carry out more work at a faster rate. ……………………………………………………………………………… Nerve tissue Found in the brain and the spinal cord. Carries messages from one part of the body to another. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Muscle tissue Found in the limb (arms and legs) and in the walls of same organ. Contracts and causes body movement. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Connective tissue Includes bone, fat and cartilage. Used to join parts of organism. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Epithelial tissue Found on the surface of the skin, on the outer covering of tubes and lines the spaces inside the body. Protects structure underneath the surface. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… From Tissues to Organs ………………………….. A number of different types of tissues in human body are group together to form an organ. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… An organ is a specialised structure which is responsible in carrying out certain bodily function. ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………… Brain Consists of connective tissue and nerve tissue. Controls the various part of the body. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Heart Consists of muscle tissue and connective tissue. Pumps blood around the body. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… Stomach Consists of epithelial, muscle tissue and connective tissue. Digest (breaks down) food. …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… …………………………… ……………………………