REACTION DYNAMICS
... Vibrational excitation to v=1 in HCl increases σr much more than the equivalent amount of energy in translational excitation. What qualitative conclusion can you draw about the shape of the potential energy surface? ...
... Vibrational excitation to v=1 in HCl increases σr much more than the equivalent amount of energy in translational excitation. What qualitative conclusion can you draw about the shape of the potential energy surface? ...
Lecture Notes for Chemistry 543, Part III
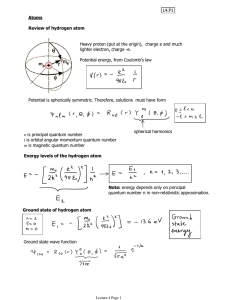
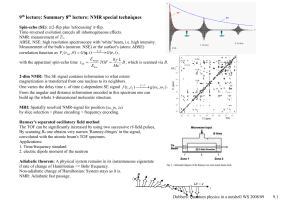
... Reading: Chapters 6 and 7 of Bernath; Levine pp 142-174. As in any branch of spectroscopy, we need to determine (1) the eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian in order to know the frequencies of the possible transitions, (2) the selection rules to determine what transitions actually occur, (3) the transitio ...
... Reading: Chapters 6 and 7 of Bernath; Levine pp 142-174. As in any branch of spectroscopy, we need to determine (1) the eigenvalues of the Hamiltonian in order to know the frequencies of the possible transitions, (2) the selection rules to determine what transitions actually occur, (3) the transitio ...
7.3-Flame Test Lab
... in our visible light spectrum, and therefore we can observe the different colors of the different metals. (The finger prints of metals) Only the metal in the compound is affected by the flame. By placing atoms of a metal into a flame, electrons can be induced to absorb energy and jump to an excited ...
... in our visible light spectrum, and therefore we can observe the different colors of the different metals. (The finger prints of metals) Only the metal in the compound is affected by the flame. By placing atoms of a metal into a flame, electrons can be induced to absorb energy and jump to an excited ...
Optical Properties of Condensed Matters
... luminesce strongly When electrons are promoted into the excited states of the molecule. The luminescence is Stokes shifted to lower energy compared to absorption, and typically occurs in the middle of the visible spectral region. The emission wavelength can be tuned by small alternation to the chemi ...
... luminesce strongly When electrons are promoted into the excited states of the molecule. The luminescence is Stokes shifted to lower energy compared to absorption, and typically occurs in the middle of the visible spectral region. The emission wavelength can be tuned by small alternation to the chemi ...
Excited States, Lasers and Non-Linear Optics
... Powerful Continuous Wave operation can be achieved by discharge (15-50 Amps!) to maximize the pumping power. Several watts CW output or upto 1 kilowatt in microsecond pulses can be generated. Pump to 4P states, 35eV above ground state by multiple collisions. Transitions correspond to 4P-4S, 514.5nm ...
... Powerful Continuous Wave operation can be achieved by discharge (15-50 Amps!) to maximize the pumping power. Several watts CW output or upto 1 kilowatt in microsecond pulses can be generated. Pump to 4P states, 35eV above ground state by multiple collisions. Transitions correspond to 4P-4S, 514.5nm ...
Quantum Readiness
... 25. The orbitals of a molecule hold six electrons. Through spectroscopy and computations the lowest four energy levels of the molecule are determined. The energy levels can be indicated schematically as follows: ...
... 25. The orbitals of a molecule hold six electrons. Through spectroscopy and computations the lowest four energy levels of the molecule are determined. The energy levels can be indicated schematically as follows: ...
Diameters of rotationally and vibrationally excited diatomic molecules
... been studied extensively, and mathematical descriptions of various low-temperature processes based on the model have been developed. Therefore, the finite-size model of atom-molecule and molecule-molecule collisions would also be of great advantage in studies of transport phenomena in high-temperatu ...
... been studied extensively, and mathematical descriptions of various low-temperature processes based on the model have been developed. Therefore, the finite-size model of atom-molecule and molecule-molecule collisions would also be of great advantage in studies of transport phenomena in high-temperatu ...
Gilad Haran - Laboratoire Léon Brillouin
... Fluorescence spectroscopy on the single-molecule level can provide a unique view of the heterogeneous dynamics of folding proteins. We are using a custom-developed set of methodologies, based on intra-molecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), to study folding in real time. In particul ...
... Fluorescence spectroscopy on the single-molecule level can provide a unique view of the heterogeneous dynamics of folding proteins. We are using a custom-developed set of methodologies, based on intra-molecular fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), to study folding in real time. In particul ...
1) Which of the following concepts was discussed in Chapter 1
... 1) Increase the momentum of the particle 2) Decrease the momentum of the particle 3) Decrease the well width 4) Increase the well depth 5) Decrease the well depth ...
... 1) Increase the momentum of the particle 2) Decrease the momentum of the particle 3) Decrease the well width 4) Increase the well depth 5) Decrease the well depth ...
Probing vibrational ladder-excitation in CO2 microwave plasma with a free electron laser to develop a route to efficient solar fuels
... stretch vibrational level of CO 2 . The absorption spectrum thus made resembles the FTIR spectra in Fig 3, that were recorded in-situ under the same conditions, also comparing plasma ‘‘ON’’ and ‘‘OFF’’ using a resolution of 2 cm-1 Comparing the FELIX-absorption for plasma “ON” and “OFF”, we see an a ...
... stretch vibrational level of CO 2 . The absorption spectrum thus made resembles the FTIR spectra in Fig 3, that were recorded in-situ under the same conditions, also comparing plasma ‘‘ON’’ and ‘‘OFF’’ using a resolution of 2 cm-1 Comparing the FELIX-absorption for plasma “ON” and “OFF”, we see an a ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.