Nugget
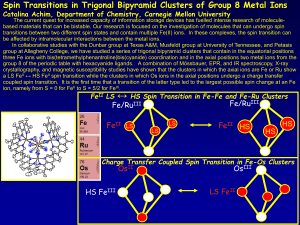
... The current quest for increased capacity of information storage devices has fuelled intense research of moleculebased materials that can be bistable. Our research is focused on the investigation of molecules that can undergo spin transitions between two different spin states and contain multiple Fe( ...
... The current quest for increased capacity of information storage devices has fuelled intense research of moleculebased materials that can be bistable. Our research is focused on the investigation of molecules that can undergo spin transitions between two different spin states and contain multiple Fe( ...
Chapter 11 Coordination Chemistry III: Electronic Spectra
... We observe absorption in band with the energy of each band corresponding to the difference in energy between the initial and final states. We first need to consider electrons in atoms can interact with each other. Electrons tend to occupy separate orbitals ← Πc Electrons in separate orbitals tend to ...
... We observe absorption in band with the energy of each band corresponding to the difference in energy between the initial and final states. We first need to consider electrons in atoms can interact with each other. Electrons tend to occupy separate orbitals ← Πc Electrons in separate orbitals tend to ...
Bormio2016_talk_JFSS
... consisting of n individual quanta. The quanta obey Bose statistics…” Page 330 “… but it might be expected that the zero-point oscillations in the γ direction would be of similar magnitude as those in the β direction. The experimentally observed E2-matrix elements for exciting the β vibrations are co ...
... consisting of n individual quanta. The quanta obey Bose statistics…” Page 330 “… but it might be expected that the zero-point oscillations in the γ direction would be of similar magnitude as those in the β direction. The experimentally observed E2-matrix elements for exciting the β vibrations are co ...
chemistry basics note - bramalea2010-msmanning
... Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms that consist of _____________, ________________and _______________. The _____________ table lists elements in order of increasing atomic number. Molecules are ____________________________________________________. Molecules can contain only on ...
... Matter is composed of tiny particles called atoms that consist of _____________, ________________and _______________. The _____________ table lists elements in order of increasing atomic number. Molecules are ____________________________________________________. Molecules can contain only on ...
An Overview of Computational Chemistry
... When these expressions are used in the time-independent Schrodinger Equation, the dynamics of all electrons and nuclei in a molecule or atom are taken into account. ...
... When these expressions are used in the time-independent Schrodinger Equation, the dynamics of all electrons and nuclei in a molecule or atom are taken into account. ...
Electronic structure (download)
... We can predict the motion of a ball; But not an electron: problems locating small objects ...
... We can predict the motion of a ball; But not an electron: problems locating small objects ...
H - unix.eng.ua.edu
... 2. Sij = dij (orthonormal basis set) 3. Hii = a (negative of the ionization potential of the methyl radical) 4. Hij = b (negative stabilization energy). 90º rotation removes all bonding, thus we can calculate DE: DE = 2Ep - Ep where Ep = a and Ep = 2a + 2b (as shown below) ...
... 2. Sij = dij (orthonormal basis set) 3. Hii = a (negative of the ionization potential of the methyl radical) 4. Hij = b (negative stabilization energy). 90º rotation removes all bonding, thus we can calculate DE: DE = 2Ep - Ep where Ep = a and Ep = 2a + 2b (as shown below) ...
Nuclear quantum effects in molecular dynamics simulations
... condensed matter systems. Interatomic forces are calculated using either force fields or ab initio schemes, such as density functional theory (DFT), while the dynamics of the nuclei is based on classical mechanics. These calculations are thus only valid in the classical limit and so for large temper ...
... condensed matter systems. Interatomic forces are calculated using either force fields or ab initio schemes, such as density functional theory (DFT), while the dynamics of the nuclei is based on classical mechanics. These calculations are thus only valid in the classical limit and so for large temper ...
ATOMIC PHYSICS REVISION NOTES:
... of the perturbing potential. Because kr 1 for r of the order of an atomic radius, this expansion ois truncated at rst order. However, weak transitions arising from higher terms in the expansion are possible (multipole transitions). For these multipole transitions we lose a factor of kr in the tra ...
... of the perturbing potential. Because kr 1 for r of the order of an atomic radius, this expansion ois truncated at rst order. However, weak transitions arising from higher terms in the expansion are possible (multipole transitions). For these multipole transitions we lose a factor of kr in the tra ...
Nuclear Forces and Mesons
... Positions of spectral lines would be different if potential V(r) were different. The spectrum of hydrogen tells us that the force holding the electron to the proton is the Coulomb ...
... Positions of spectral lines would be different if potential V(r) were different. The spectrum of hydrogen tells us that the force holding the electron to the proton is the Coulomb ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy
... chemical shift. Chemical shifts depend upon the electron density around a nucleus and are thus controlled by the structural environment of the nucleus. The NMR chemical shifts provide important clues for determining the molecular structure of a chemical compound. ...
... chemical shift. Chemical shifts depend upon the electron density around a nucleus and are thus controlled by the structural environment of the nucleus. The NMR chemical shifts provide important clues for determining the molecular structure of a chemical compound. ...
Quantum Mechanics in 3
... inside the well is zero and outside the well is infinity. Then the question is how can we obtain wave function and energy of the particle inside the well. We are lucky because the wave function outside the well is ...
... inside the well is zero and outside the well is infinity. Then the question is how can we obtain wave function and energy of the particle inside the well. We are lucky because the wave function outside the well is ...
Franck–Condon principle
The Franck–Condon principle is a rule in spectroscopy and quantum chemistry that explains the intensity of vibronic transitions. Vibronic transitions are the simultaneous changes in electronic and vibrational energy levels of a molecule due to the absorption or emission of a photon of the appropriate energy. The principle states that during an electronic transition, a change from one vibrational energy level to another will be more likely to happen if the two vibrational wave functions overlap more significantly.