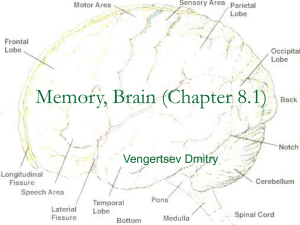
The Nervous System
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Neurons
... controls the right hand and also is the seat of language) left hand: speak! speak! (reason: verbalizing helped by distracting the subjects enough that they didn’t focus too ...
... controls the right hand and also is the seat of language) left hand: speak! speak! (reason: verbalizing helped by distracting the subjects enough that they didn’t focus too ...
Chapter 03 - Jen Wright
... brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do they help us to better understand the mind? GROUP Extra Credit – 2.5 pts: The limbic system ...
... brain? As a classic example, what did the case of Phineas Gage teach us? 16. What is the difference between an EEG, a CT scan, and an fMRI? How do these machines help us to better understand the brain? How do they help us to better understand the mind? GROUP Extra Credit – 2.5 pts: The limbic system ...
Myers` Psychology for AP
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
... 5. Identify the brain areas involved in language, and explain how these areas coordinate to produce speech. aphasia – 6. Discuss the brain’s plasticity following injury or illness. LO #5 plasticity – neurogenesis – Our Divided Brain LO #6 7. Describe split-brain research, and explain how it helps us ...
Your Brain and What It Does
... responses to complex problems, plans steps to an objective, searches memory for relevant experience, adapts strategies to accommodate new data, guides behavior with verbal skills and houses working memory. Its orbitofrontal circuit manages emotional impulses in socially appropriate ways for producti ...
... responses to complex problems, plans steps to an objective, searches memory for relevant experience, adapts strategies to accommodate new data, guides behavior with verbal skills and houses working memory. Its orbitofrontal circuit manages emotional impulses in socially appropriate ways for producti ...
Studying the Brain
... Shows the different levels of activity in the brain when a person is awake, drowsy, or asleep Stimulation Electrodes are used to stimulate the brain & record the activity Used with terminal cancer patients to relieve pain Can be used to treat extreme depression Used to control violent em ...
... Shows the different levels of activity in the brain when a person is awake, drowsy, or asleep Stimulation Electrodes are used to stimulate the brain & record the activity Used with terminal cancer patients to relieve pain Can be used to treat extreme depression Used to control violent em ...
Central Nervous System
... • The spinal cord acts as a central communication conduit between the brain and the rest of the body. • Millions of nerve fibers within the cord carry motor information from the brain to the muscles and other convey sensory information. ...
... • The spinal cord acts as a central communication conduit between the brain and the rest of the body. • Millions of nerve fibers within the cord carry motor information from the brain to the muscles and other convey sensory information. ...
Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do scientists learn about the inner workings of the human brain? Who is Phinneas Gage? How is what happened to him significant for neuroscience? You will need to know the structures and their functions of the brain as discussed in the video ...
... Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do scientists learn about the inner workings of the human brain? Who is Phinneas Gage? How is what happened to him significant for neuroscience? You will need to know the structures and their functions of the brain as discussed in the video ...
Biology 30 – Notes Neurotransmitters and the Brain, September 15
... functions of the synapses and neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine and Cholinesterase Norepinephrine – neurotransmitter released by the sympathetic neurons of the autonomic system to produce an excitatory effect on target muscles. Also a hormone produced by the adrenal medulla along with epinephrine to ...
... functions of the synapses and neurotransmitters. Acetylcholine and Cholinesterase Norepinephrine – neurotransmitter released by the sympathetic neurons of the autonomic system to produce an excitatory effect on target muscles. Also a hormone produced by the adrenal medulla along with epinephrine to ...
05-First 2 years - Biosocial
... • 2X birth weight by 4 months • 3X birth weight by age 1 • 4X birth weight by age 2 ...
... • 2X birth weight by 4 months • 3X birth weight by age 1 • 4X birth weight by age 2 ...
Chapter 8
... What kind of activities ate best to involve children in? Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about the same time as a neighbor child, whose parents did not u ...
... What kind of activities ate best to involve children in? Mabel and Ian wanted their daughter Brianna to learn to read early so they began using flash cards with her when she was two years old. They found that Brianna's skills developed about the same time as a neighbor child, whose parents did not u ...
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
The Brain - Science Leadership Academy
... Dendrites- these parts of the cells make connections with other cells and allow neurons to to talk to tother cells or perceieve the environment. Dendrites are located on both ends of the cell. ...
... Dendrites- these parts of the cells make connections with other cells and allow neurons to to talk to tother cells or perceieve the environment. Dendrites are located on both ends of the cell. ...
Central Nervous System
... • Protective cushion for brain and spinal cord • Blood brain barrier – Brain environment must be constant – Least permeable capillaries in body – Prevents substances from entering brain tissue ...
... • Protective cushion for brain and spinal cord • Blood brain barrier – Brain environment must be constant – Least permeable capillaries in body – Prevents substances from entering brain tissue ...
How Do We Learn?
... Detects active regions of the brain by visualizing where oxygen is being used. ...
... Detects active regions of the brain by visualizing where oxygen is being used. ...
connectome - LjcdsNeuro2011
... dichromate and silver nitrate gave scientists the ability to stain, and highlight, individual brain cells. • 1890s The Spaniard Santiago Rámon y Cajal adopts Golgi's method and proves the brain is a collection of individual but interconnected neurons. • 1929 The EEG, electroencephalogram, is created ...
... dichromate and silver nitrate gave scientists the ability to stain, and highlight, individual brain cells. • 1890s The Spaniard Santiago Rámon y Cajal adopts Golgi's method and proves the brain is a collection of individual but interconnected neurons. • 1929 The EEG, electroencephalogram, is created ...
The Brain and Nervous System
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
... other parts of the brain that influence our motives. This includes release of pleasure hormones, rats that could stimulate their HT electrically would do so 7000 times an hour. ...
Verlamde man bestuurt computer via gedachten
... check e-mail and play computer games using his thoughts. The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they r ...
... check e-mail and play computer games using his thoughts. The device can tap into a hundred neurons at a time, and is the most sophisticated such implant tested in humans so far. Many paralysed people control computers with their eyes or tongue. But muscle function limits these techniques, and they r ...
Nervous System
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...