Brain-Class Notes
... go through this organ on their way to other parts of the brain for processing Also plays a function in motor control ...
... go through this organ on their way to other parts of the brain for processing Also plays a function in motor control ...
Ch.02
... Severed spinal cord E.g. ◦ Bill - No genital sensations, but has an erection when stimulated. ...
... Severed spinal cord E.g. ◦ Bill - No genital sensations, but has an erection when stimulated. ...
Chapter 2 Summary
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
... The chemical component of neural communication is accomplished through neurotransmitters released at the synapse ...
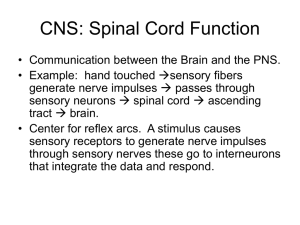
CNS: Spinal Cord Function
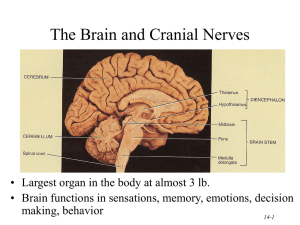
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
... pineal gland. Thalamus receives all sensory input except smell. This area integrates this information and sends it to the appropriate area of the cerebrum. • Cerebellum: Receives sensory input from the eyes, ears, joints, and muscles about the position of body parts. It also receives information fro ...
http://catnet.adventist.ca/files/articles/pdf/oj_ID278.pdf
... Not long ago, I was involved in a course that helped me to understand the amazing intricacies of the human brain. Often referred to as “the last frontier,” the brain still includes mysteries that have yet to be unraveled. But during the past ten years we have begun to understand much more about its ...
... Not long ago, I was involved in a course that helped me to understand the amazing intricacies of the human brain. Often referred to as “the last frontier,” the brain still includes mysteries that have yet to be unraveled. But during the past ten years we have begun to understand much more about its ...
Module 05
... greater amounts of glucose, which can be tracked by the PET scan (PET scan “hot spots”). Myers jokes that the glucose consumed during cognitive activity is like “food for thought.” Such snapshots of the brain’s changing activity are providing new insights . . . into how the brain divides its labor. ...
... greater amounts of glucose, which can be tracked by the PET scan (PET scan “hot spots”). Myers jokes that the glucose consumed during cognitive activity is like “food for thought.” Such snapshots of the brain’s changing activity are providing new insights . . . into how the brain divides its labor. ...
The Teenage Brain
... • Attention • Concentration • Awareness of abilities • Self-control • “do the right thing” ...
... • Attention • Concentration • Awareness of abilities • Self-control • “do the right thing” ...
Document
... Drowsiness is becoming a severe issue in case of traffic accident. Normally, Sleeping can be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , peopl ...
... Drowsiness is becoming a severe issue in case of traffic accident. Normally, Sleeping can be identified from several factors like eyeblink level, yawning ,gripping force on wheel and so on. But all these measuring techniques will check only the physical activities of the human. In some cases , peopl ...
Chapter 4 - (www.forensicconsultation.org).
... show that baby must learn that they have an effect on their environment, and therefore control over their own experience. Important for cognitive and social development • babies need to know that they can make things happen • being responsive to baby ...
... show that baby must learn that they have an effect on their environment, and therefore control over their own experience. Important for cognitive and social development • babies need to know that they can make things happen • being responsive to baby ...
Nervous System
... nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
... nervous system? • What are the 3 major organs in the nervous system? • Which part of the brain controls thought? • Which part of the nervous system control arms and legs? ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
... Neurological Injury • Injury to the nervous system often causes irreversible damage – results in disability, sometimes devastating – occasionally results in very bizarre symptoms ...
Nerves and the brain
... The importance of the brain in the coordination of animal behaviour is highlighted when parts of it are damaged. The paralysis that follows a stroke, or the shaking movements of people with Parkinson’s disease, are signs of damage to the brain. In people with these conditions, muscular contractions ...
... The importance of the brain in the coordination of animal behaviour is highlighted when parts of it are damaged. The paralysis that follows a stroke, or the shaking movements of people with Parkinson’s disease, are signs of damage to the brain. In people with these conditions, muscular contractions ...
Chapter 3 Week 2 Day 4
... on the adjacent neurons grow more branches. 4. Substitution of function is a second way the brain can repair itself. Another area in the brain takes over the functions of the damaged area. 5. Neurogenesis is the process where new neurons are generated. B. Brain Tissue Implants 1. Brain grafts are im ...
... on the adjacent neurons grow more branches. 4. Substitution of function is a second way the brain can repair itself. Another area in the brain takes over the functions of the damaged area. 5. Neurogenesis is the process where new neurons are generated. B. Brain Tissue Implants 1. Brain grafts are im ...
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
... notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
The Nervous System
... • The autonomic nervous system has 2 parts: – Sympathetic : accelerates body activities – Parasympathetic : slows down body activities ...
... • The autonomic nervous system has 2 parts: – Sympathetic : accelerates body activities – Parasympathetic : slows down body activities ...
Why we act when we act: How brain, body, and environment interact
... making is that decisions-to-act are formed in the brain and then transmitted to the body to be carried out; and that the “when” of the action corresponds to a decision about when to act. However, recent evidence shows that the “when” of self-initiated action might be determined in part by ongoing st ...
... making is that decisions-to-act are formed in the brain and then transmitted to the body to be carried out; and that the “when” of the action corresponds to a decision about when to act. However, recent evidence shows that the “when” of self-initiated action might be determined in part by ongoing st ...
SRCD Abstract 01 - University of Illinois Archives
... selection process. Critical or sensitive periods of this sort, where specific experiences must occur at relatively specific times, are more the exception than the rule in overall human brain development. Throughout life, new experiences trigger new brain growth, enhancing and refining existing brain ...
... selection process. Critical or sensitive periods of this sort, where specific experiences must occur at relatively specific times, are more the exception than the rule in overall human brain development. Throughout life, new experiences trigger new brain growth, enhancing and refining existing brain ...
Wilson Language Training 10th Annual Conference Providence
... “Just as the printing press…changed how knowledge works, we have hypothesized that these new digital media will have the same effect. It’s critical that we understand (digital media’s) benefits and its unintended consequences. There are implications for both of those for schools.” --Connie Yowell, M ...
... “Just as the printing press…changed how knowledge works, we have hypothesized that these new digital media will have the same effect. It’s critical that we understand (digital media’s) benefits and its unintended consequences. There are implications for both of those for schools.” --Connie Yowell, M ...
7-9_BrainDev_ValaczkaiR
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
... sensory dorsal root ganglia in the spinal cord. At one end of the neural tube cells divide more rapidly and this part becomes the brain later. Neurons cannot divide freely in contrast to glia cells, therefore proliferation zones are needed along the neural tube where neuroblasts and glioblasts produ ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
Methods to Study the Brain
... PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
Methods to Study the Brain - Grand Haven Area Public Schools
... PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...
... PET (positron emission tomography) scans reveal the activity of different areas of the brain by showing consumption of radioactive glucose (active neurons use more glucose) as the subject performs various mental activities. ...